Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 431-439.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.05.001
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
GONG Weihua1( ), CHEN Lan2,3, ZHAO Kun2, KE Zhui2, XU Qing2, GUO Xianling2,3(
), CHEN Lan2,3, ZHAO Kun2, KE Zhui2, XU Qing2, GUO Xianling2,3( )
)
Received:2024-10-15
Revised:2024-12-23
Online:2025-05-30
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
GUO Xianling
Supported by:Share article
CLC Number:
GONG Weihua, CHEN Lan, ZHAO Kun, KE Zhui, XU Qing, GUO Xianling. Mechanism of telomerase inhibitor BIBR1532 combined with autophagy inhibitor CQ in suppressing survival of melanoma cells[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(5): 431-439.
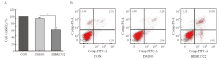
Fig. 2
BIBR1532 significantly promotes the death and apoptosis of malignant melanoma cell A375 A: BIBR1532 treatment significantly promoted the death of malignant melanoma cell A375; B: BIBR1532 significantly promoted the apoptosis of malignant melanoma cell A375. *: P<0.05, assessed by two independent-sample t test."
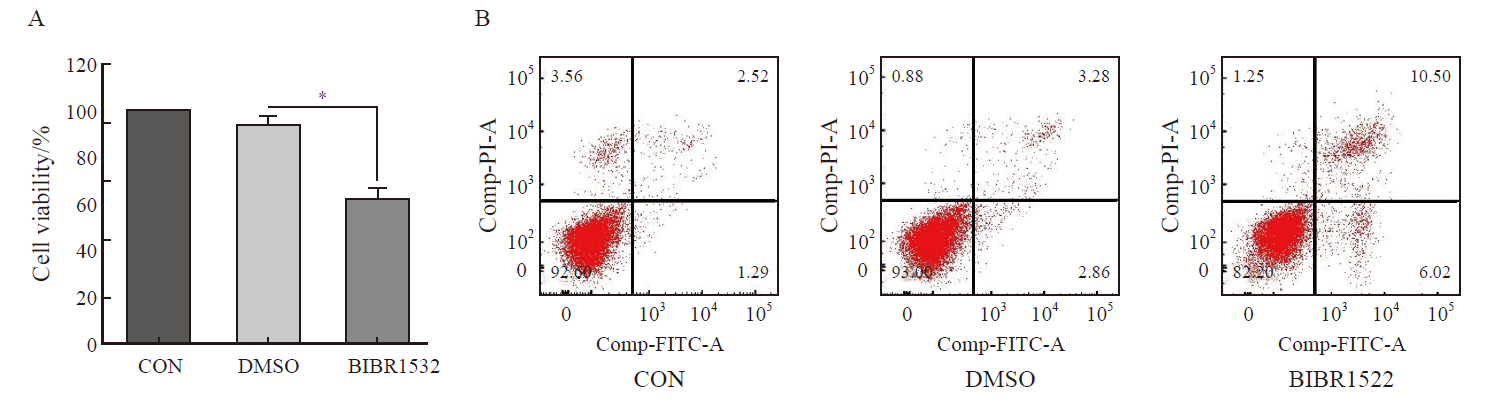
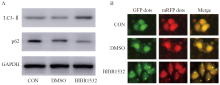
Fig. 3
BIBR1532 promotes the enhancement of autophagy activity of malignant melanoma cell A375 A: BIBR1532 leads to the increase of LC3-Ⅱ protein expression and the decrease of p62 protein expression in malignant melanoma cell A375; B: BIBR1532 promotes the enhancement of autophagy flow labeled by autophagy double-labeled adenovirus in malignant melanoma cell A375; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; mRFP: Monomeric red fluorescent protein."
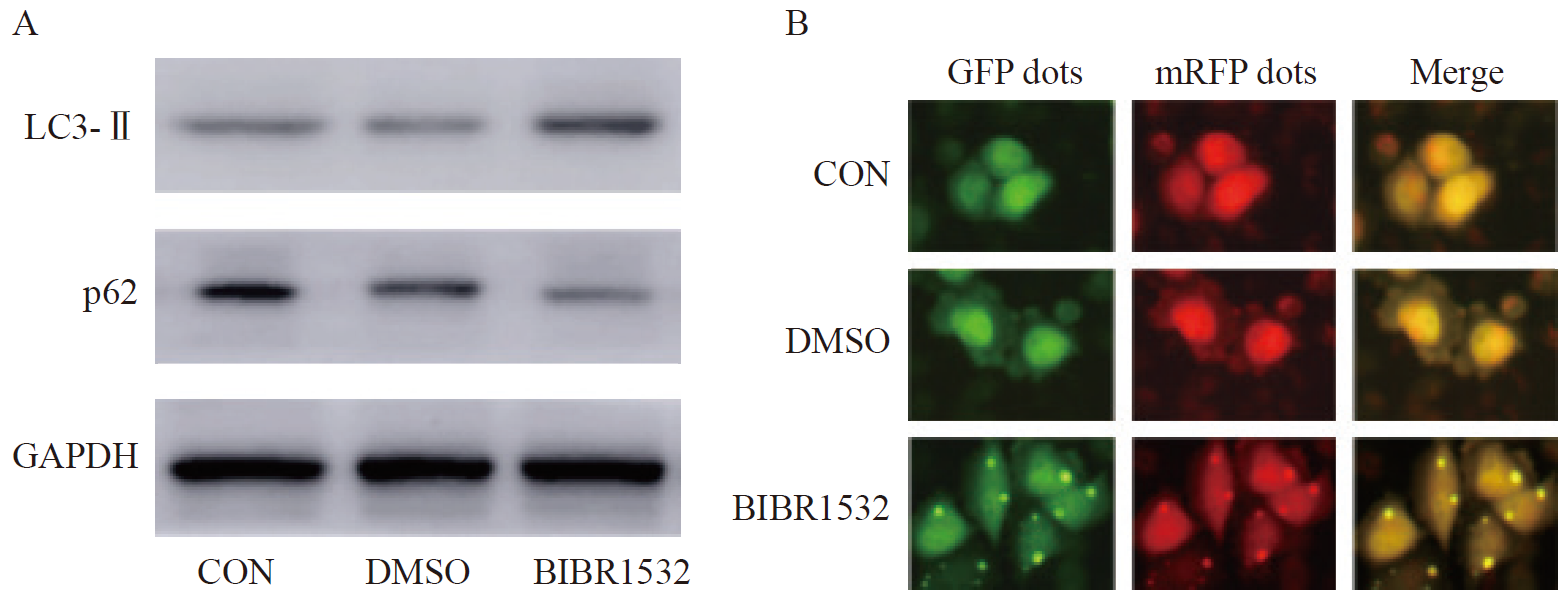
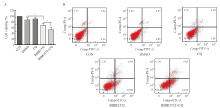
Fig. 4
The combination of BIBR1532 and CQ significantly enhanced the process of death and apoptosis of malignant melanoma cell A375 A: BIBR1532 combined with CQ significantly promoted the death of malignant melanoma cells A375; B: The combination of BIBR1532 and CQ significantly promoted the apoptosis of malignant melanoma cell A375. *: P<0.05, assessed by two independent-sample t test."
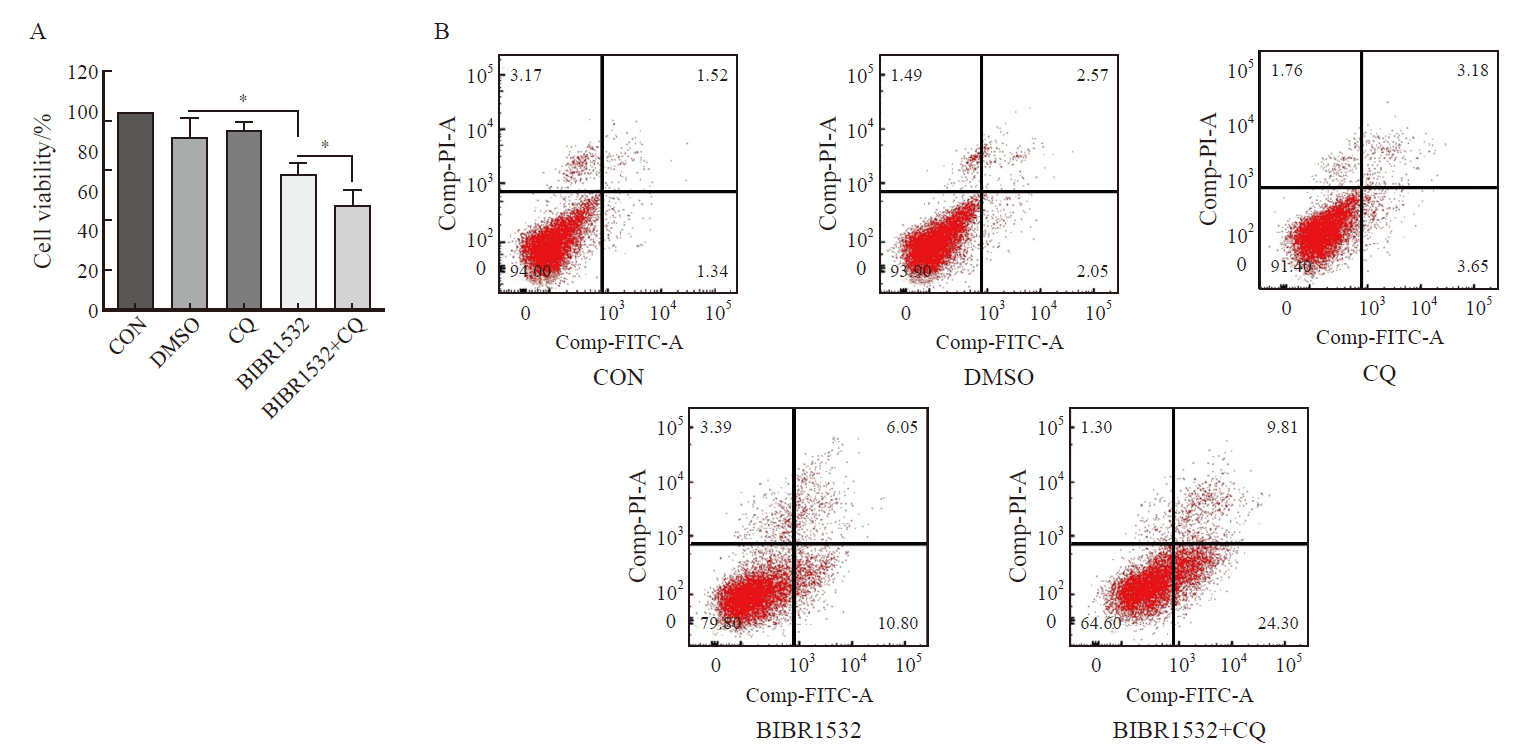
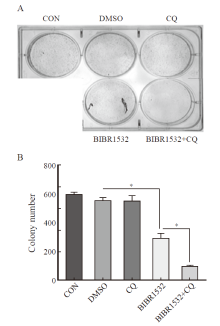
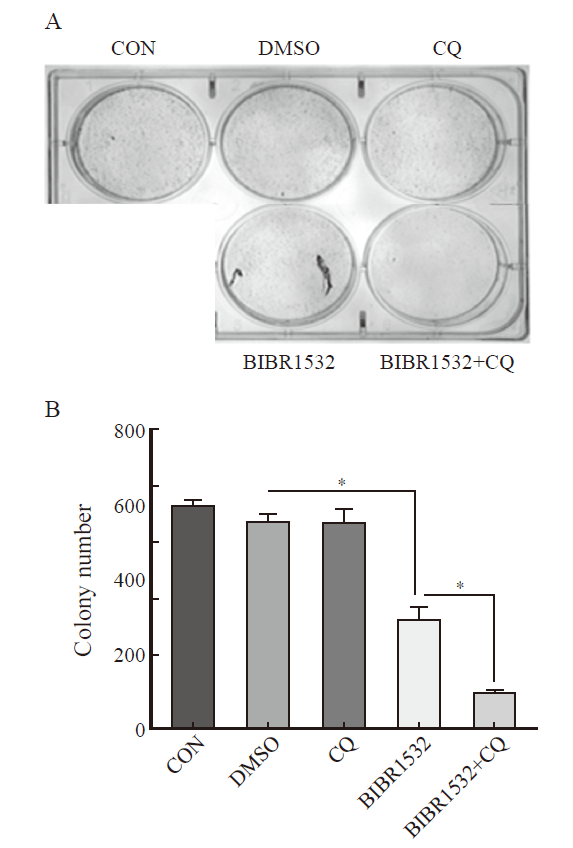
Fig. 7
The combination therapy of BIBR1532 and CQ significantly inhibited the clonal formation of malignant melanoma A375 cells A: The combination therapy of BIBR1532 and CQ significantly inhibited the clonal formation ability of malignant melanoma A375 cells; B: The results of one-way ANOVA on the number of clones formed in each group are provided. *: P<0.05, assessed by One-way ANOVA."
| [1] | AHMED B, QADIR M I, GHAFOOR S. Malignant melanoma: skin cancer-diagnosis, prevention, and treatment[J]. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr, 2020, 30(4): 291-297. |
| [2] | RANDIC T, KOZAR I, MARGUE C, et al. NRAS mutant melanoma: towards better therapies[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2021, 99: 102238. |
| [3] |
YANG F, XIAN R R, LI Y Y, et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase expression elevated by avian leukosis virus integration in B cell lymphomas[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104(48): 18952-18957.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709173104 pmid: 18024587 |
| [4] | SONG Y J, ZHANG S S, GUO X L, et al. Autophagy contributes to the survival of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells in the hypoxic and nutrient-deprived tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013, 339(1): 70-81. |
| [5] | VISHWAKARMA K, DEY R, BHATT H. Telomerase: a prominent oncological target for development of chemotherapeutic agents[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2023, 249: 115121. |
| [6] | JUDASZ E, LISIAK N, KOPCZYŃSKI P, et al. The role of telomerase in breast cancer’s response to therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21): 12844. |
| [7] | LI X H, HE S K, MA B Y. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 12. |
| [8] | DEBNATH J, GAMMOH N, RYAN K M. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24(8): 560-575. |
| [9] |
KENIFIC C M, DEBNATH J. Cellular and metabolic functions for autophagy in cancer cells[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2015, 25(1): 37-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.09.001 pmid: 25278333 |
| [10] | LIU H, HE Z Y, VON RÜTTE T, et al. Down-regulation of autophagy-related protein 5 (ATG5) contributes to the pathogenesis of early-stage cutaneous melanoma[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2013, 5(202): 202ra123. |
| [11] | MIRACCO C, CEVENINI G, FRANCHI A, et al. Beclin 1 and LC3 autophagic gene expression in cutaneous melanocytic lesions[J]. Hum Pathol, 2010, 41(4): 503-512. |
| [12] |
LAZOVA R, KLUMP V, PAWELEK J. Autophagy in cutaneous malignant melanoma[J]. J Cutan Pathol, 2010, 37(2): 256-268.
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2009.01359.x pmid: 19615007 |
| [13] | MAES H, MARTIN S, VERFAILLIE T, et al. Dynamic interplay between autophagic flux and Akt during melanoma progression in vitro[J]. Exp Dermatol, 2014, 23(2): 101-106. |
| [14] |
LAZOVA R, CAMP R L, KLUMP V, et al. Punctate LC3B expression is a common feature of solid tumors and associated with proliferation, metastasis, and poor outcome[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18(2): 370-379.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1282 pmid: 22080440 |
| [15] | MAES H, AGOSTINIS P. Autophagy and mitophagy interplay in melanoma progression[J]. Mitochondrion, 2014, 19 Pt A: 58-68. |
| [16] |
ASHRAFIZADEH M, MOHAMMADINEJAD R, TAVAKOL S, et al. Autophagy, anoikis, ferroptosis, necroptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress: potential applications in melanoma therapy[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(11): 19471-19479.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.28740 pmid: 31032940 |
| [17] | PANGILINAN C, KLIONSKY D J, LIANG C Y. Emerging dimensions of autophagy in melanoma[J]. Autophagy, 2024, 20(8): 1700-1711. |
| [18] | CHUN-ON P, HINCHIE A M, BEALE H C, et al. TPP1 promoter mutations cooperate with TERT promoter mutations to lengthen telomeres in melanoma[J]. Science, 2022, 378(6620): 664-668. |
| [19] |
TANIDA I, UENO T, KOMINAMI E. LC3 and autophagy[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2008, 445: 77-88.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-157-4_4 pmid: 18425443 |
| [20] |
KURUSU R, FUJIMOTO Y, MORISHITA H, et al. Integrated proteomics identifies p62-dependent selective autophagy of the supramolecular vault complex[J]. Dev Cell, 2023, 58(13): 1189-1205.e11.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.04.015 pmid: 37192622 |
| [21] |
BJØRKØY G, LAMARK T, PANKIV S, et al. Monitoring autophagic degradation of p62/SQSTM1[J]. Methods Enzymol, 2009, 452: 181-197.
doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(08)03612-4 pmid: 19200883 |
| [22] | SHEN Z Y, WANG Y H, WANG G Z, et al. Research progress of small-molecule drugs in targeting telomerase in human cancer and aging[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2023, 382: 110631. |
| [23] |
ZVEREVA M I, SHCHERBAKOVA D M, DONTSOVA O A. Telomerase: structure, functions, and activity regulation[J]. Biochemistry (Mosc), 2010, 75(13): 1563-1583.
pmid: 21417995 |
| [24] |
BERNARDES DE JESUS B, BLASCO M A. Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging[J]. Trends Genet, 2013, 29(9): 513-520.
doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.06.007 pmid: 23876621 |
| [25] | BERGER M F, HODIS E, HEFFERNAN T P, et al. Melanoma genome sequencing reveals frequent PREX2 mutations[J]. Nature, 2012, 485(7399): 502-506. |
| [26] | HUANG F W, HODIS E, XU M J, et al. Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6122): 957-959. |
| [27] | CHIBA K, LORBEER F K, HUNTER SHAIN A, et al. Mutations in the promoter of the telomerase gene TERT contribute to tumorigenesis by a two-step mechanism[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6358): 1416-1420. |
| [28] |
GUTERRES A N, VILLANUEVA J. Targeting telomerase for cancer therapy[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(36): 5811-5824.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01405-w pmid: 32733068 |
| [29] | TARAZÓN E, DE UNAMUNO BUSTOS B, MURRIA ESTAL R, et al. miR-138-5p suppresses cell growth and migration in melanoma by targeting telomerase reverse transcriptase[J]. Genes (Basel), 2021, 12(12): 1931. |
| [30] | HRDLIČKOVÁ R, NEHYBA J, BARGMANN W, et al. Multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs regulate telomerase and TCF7, an important transcriptional regulator of the Wnt pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(2): e86990. |
| [31] |
CHO W C S. OncomiRs: the discovery and progress of microRNAs in cancers[J]. Mol Cancer, 2007, 6: 60.
pmid: 17894887 |
| [32] | WANG H, NI J, GUO X H, et al. Effects of folate on telomere length and chromosome stability of human fibroblasts and melanoma cells in vitro: a comparison of folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate[J]. Mutagenesis, 2023, 38(3): 160-168. |
| [33] |
DAMM K, HEMMANN U, GARIN-CHESA P, et al. A highly selective telomerase inhibitor limiting human cancer cell proliferation[J]. EMBO J, 2001, 20(24): 6958-6968.
pmid: 11742973 |
| [34] |
NOWOSAD A, JEANNOT P, CALLOT C, et al. p27 controls Ragulator and mTOR activity in amino acid-deprived cells to regulate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and coordinate cell cycle and cell growth[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2020, 22(9): 1076-1090.
doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0554-4 pmid: 32807902 |
| [1] | XIN Meiyi, LIN Yuhong, ZHAO Kai. Progress in the development of mRNA vaccine and its delivery systems for anti-tumor immunotherapy [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 509-516. |
| [2] | LI Xiaohui, ZHAO Jiaxu, PENG Haibao, ZHANG Ye, ZENG Rui, CHI Yudan. Effects of HMGA2 on migration and proliferation of leptomeningeal metastatic melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(4): 389-399. |
| [3] | TAN Xiaolang, YAO Sha, WANG Guihua, PENG Luogen. Research on uPAR promoting proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting autophagy via MAPK signaling [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 944-956. |
| [4] | YANG Ziyi, LI Panli, GU Bingxin, LIU Cheng, SONG Shaoli, XU Xiaoping. The synthesis of a novel molecular imaging probe 68Ga-DOTA-PDL1P and application in mouse model of melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(4): 354-360. |
| [5] | LENG Jie, QIU Guochun, ZHANG Bo, PU Yan. Mechanism of breast cancer centrosome regulatory protein SEC23B on tumor invasion and metastasis [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(2): 152-161. |
| [6] | ZHAO Bolun, ZHU Guannan. Advances in the treatment of advanced melanoma with NRAS gene mutation [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(10): 936-944. |
| [7] | ZOU Chunyuan, XU Xiaofeng, LU Renquan, GUO Lin. Detection of p53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5 and MAGE A1 protein levels in lung cancer tissues and peripheral blood and their clinical value [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 36-44. |
| [8] | HU Xichun, HU Zhihuang, WANG Biyun, WANG Jialei, TAO Rong, ZHANG Jian, GUO Weijian, CHEN Jie, LUO Zhiguo, LI Ting, HUANG Mingzhu, QIU Lixin, SANG Youzhou. COVID-19 and systemic anti-cancer therapy [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(6): 499-511. |
| [9] | JIANG Jianyun, YING Hongmei. Clinical research progress in the treatment of BRAF V600 mutation-positive advanced melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(5): 445-450. |
| [10] | WANG Zimao, CAO Yuan, WANG Qiying. Construction and validation of the survival prediction model for patients with cutaneous spindle cell melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 234-242. |
| [11] | XU Yu, CHEN Yong, YANG Jilong, ZHU Guannan. Current status and prospect of perioperative treatment of stage Ⅲ melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1133-1146. |
| [12] | LI Ting, XU Yu, JIA Dongdong, LIAO Zhichao, SUN Wei, WU Haixiao, REN Zhiwu, ZHAO Jun, XING Ruwei, TENG Sheng, YANG Yun, CHEN Yong, LI Tao, YANG Jilong. Adjuvant therapy with anti-PD-1 antibody vs targeted therapy for patients with resected stage Ⅲ malignant melanoma: a real-world data analysis from China centers [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1147-1157. |
| [13] | LIN Xinyi, SUN Wei, HU Tu, WANG Chunmeng, YAN Wangjun, LUO Zhiguo, LIU Xin, ZHONG Jingqin, ZOU Zijian, XU Yu, CHEN Yong. Multivariable prognostic analyses of Chinese acral and cutaneous melanoma after surgical treatment for the past five years in a single cancer center [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1158-1167. |
| [14] | ZOU Zijian, SUN Wei, HU Tu, WANG Chunmeng, YAN Wangjun, LUO Zhiguo, LIU Xin, ZHONG Jingqin, LIN Xinyi, XU Yu, CHEN Yong. Clinical value of sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with cutaneous and acral melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1168-1177. |
| [15] | JIA Dongdong, LI Tao. Retrospective analysis of adjuvant therapy with dabrafenib and trametinib for 24 patients with malignant melanoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1178-1183. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
