Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 465-477.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.05.005
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Di1( ), NI Jianjiao1, ZHAO Kuaile1, XIANG Jiaqing2, ZHANG Zhen1, ZHANG Junhua1(
), NI Jianjiao1, ZHAO Kuaile1, XIANG Jiaqing2, ZHANG Zhen1, ZHANG Junhua1( )
)
Received:2025-01-08
Revised:2025-03-18
Online:2025-05-30
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
ZHANG Junhua
Share article
CLC Number:
LIU Di, NI Jianjiao, ZHAO Kuaile, XIANG Jiaqing, ZHANG Zhen, ZHANG Junhua. Analysis of clinical features, prognosis and comprehensive therapeutic strategies in 261 patients with limited-stage esophageal small cell carcinoma[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(5): 465-477.
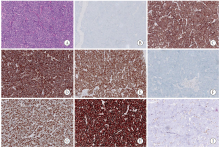
Fig. 1
Histopathological features and immunohistochemical staining of an SCEC specimen (×200) A: SCEC (H-E staining); B: CgA negative (Envision); C: Syn positive (Envision); D: CD56 positive (Envision); E: INSM1 positive (Envision); F: p40 negative (Envision); G: Ki-67 80% (Envision); H: diffusely strong p53 positivity (Envision); I: Rb1 negative (Envision)."
Tab. 1
The clinicopathological characteristics of 261 patients with LS-SCEC [n (%)]"
| Characteristic | Case | Characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Pure SCEC | 222 (85.0) | ||
| Male | 192 (73.6) | Mixed squamous cell/adenocarcinoma | 37 (14.2) | |
| Female | 69 (26.4) | Mixed large cell NEC | 2 (0.8) | |
| Age/year | Surgery | |||
| <75 | 244 (93.5) | Yes | 167 (64.0) | |
| ≥75 | 17 (6.5) | No | 94 (36.0) | |
| Performance status | Curative thoracic radiotherapy | |||
| 0 | 49 (18.8) | Yes | 87 (33.3) | |
| 1 | 212 (81.2) | No | 174 (66.7) | |
| Comorbidity | Chemotherapy | |||
| Yes | 111 (42.5) | Yes | 219 (83.9) | |
| No | 150 (57.5) | No | 42 (16.1) | |
| Family history | T stage (8th) | |||
| No | 198 (75.9) | T1a | 4 (1.5) | |
| Yes | 63 (24.1) | T1b | 56 (21.5) | |
| Length of disease/cm | T2 | 74 (28.4) | ||
| ≤5 | 207 (79.3) | T3 | 96 (36.8) | |
| >5 | 54 (20.7) | T4a | 21 (8.0) | |
| Primary site | T4b | 10 (3.8) | ||
| Cervical | 2 (0.8) | N stage (8th) | ||
| Upper thoracic | 23 (8.8) | N0 | 66 (25.3) | |
| Middle thoracic | 156 (59.8) | N1 | 88 33.7 () | |
| Lower thoracic | 77 (29.5) | N2 | 77 (29.5) | |
| Overlap | 3 (1.1) | N3 | 30 (11.5) | |
| Smoking history | M stage (8th) | |||
| Yes | 143 (54.8) | M0 | 220 (84.3) | |
| No | 118 (45.2) | M1 | 41 (15.7) | |
| Heavy drinking | TNM stage (8th) | |||
| Yes | 97 (37.2) | Ⅰ | 28 (10.7) | |
| No | 164 (62.8) | Ⅱ | 72 (27.6) | |
| Food habit | Ⅲ | 84 (32.2) | ||
| Yes | 63 (24.1) | ⅣA | 36 (13.8) | |
| No | 198 (75.9) | ⅣB | 41 (15.7) | |
| Second tumor | Response rate | |||
| Yes | 23 (8.8) | CR | 152 (58.2) | |
| No | 238 (91.2) | PR | 78 (29.9) | |
| BMI/(kg·m-2) | SD | 31 (11.9) | ||
| <18.5 | 26 (9.9) | PD | 0 (0.0) | |
| 18.5-25 | 191 (73.2) | Chemotherapy regimen | ||
| >25 | 44 (16.9) | Etoposide+platinum | 189 (83.6) | |
| Pathology | Others | 37 (16.4) |
Tab. 3
Analysis of distant metastatic sites at first recurrence in LS-SCEC patients (n)"
| Metastatic site | Case |
|---|---|
| Liver metastasis | 54 |
| Bone metastasis | 25 |
| Brain metastasis | 24 |
| Lung metastasis | 23 |
| Pleural metastasis. | 5 |
| Pancreatic metastasis | 3 |
| Adrenal metastasis | 2 |
| Peritoneal metastasis | 2 |
| Subcutaneous metastasis | 2 |
| Distant lymph node metastasis | |
| Supraclavicular lymph node | 25 |
| Retroperitoneal lymph node | 15 |
| Cervical lymph node | 10 |
| Axillary lymph node | 2 |
Tab. 4
Univariate analysis of the prognostic factors for CSS in LS-SCEC patients"
| Variable | Case n (%) | Median CSS (95% CI)/month | χ2 | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of disease/cm | ||||||
| ≤5 | 207 (79.3) | 28.0 (22.2-33.8) | 5.5 | 0.019 | 0.65 (0.45-0.95) | 0.028 |
| >5 | 54 (20.7) | 18.0 (14.9-21.1) | 1.00 | |||
| Primary site | 14.6 | 0.006 | 0.038 | |||
| Cervical | 2 (0.8) | - | - | - | ||
| Upper thoracic | 23 (8.8) | 26.0 (12.1-40.0) | 1.00 | |||
| Middle thoracic | 156 (59.8) | 25.0 (18.2-31.8) | 1.04 (0.60-1.83) | 0.880 | ||
| Lower thoracic | 77 (29.5) | 24.0 (18.2-29.8) | 1.13 (0.62-2.06) | 0.688 | ||
| Overlap | 3 (11.5) | 6.6 (5.0-8.2) | 6.80 (1.93-23.98) | 0.003 | ||
| Pathology | 9.2 | 0.010 | 0.017 | |||
| Pure SCEC | 222 (85.0) | 23.0 (19.1-26.9) | 0.24 (0.06-0.99) | 0.049 | ||
| Mixed squamous cell/adenocacinoma | 37 (14.2) | 39.0 (12.0-66.0) | 0.15 (0.03-0.64) | 0.011 | ||
| Mixed large cell NEC | 2 (0.8) | 6.2 (-) | 1.00 | |||
| Chemotherapy cycle | ||||||
| <4 | 96 (36.8) | 17.7 (15.1-20.3) | 15.8 | <0.001 | 1.88 (1.37-2.58) | <0.001 |
| ≥4 | 165 (63.2) | 30.1 (23.8-36.4) | 1.00 | |||
| T stage (8th) | 34.0 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| T1a | 4 (1.5) | - | 0.05 (0.01-0.44) | 0.012 | ||
| T1b | 56 (21.5) | 51.0 (6.1-95.9) | 0.14 (0.06-0.32) | <0.001 | ||
| T2 | 74 (28.4) | 27.7 (19.1-36.3) | 0.22 (0.10-0.48) | <0.001 | ||
| T3 | 96 (36.8) | 19.4 (16.5-22.3) | 0.31 (0.15-0.65) | 0.002 | ||
| T4a | 21 (8.0) | 17.2 (11.5-22.9) | 0.38 (0.16-0.91) | 0.029 | ||
| T4b | 10 (3.8) | 12.0 (10.5-13.5) | 1.00 | |||
| N stage (8th) | 38.2 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| N0 | 66 (25.3) | 51.0 (9.9-92.1) | 0.21 (0.12-0.36) | <0.001 | ||
| N1 | 88 (33.7) | 28.6 (20.3-36.9) | 0.35 (0.22-0.56) | <0.001 | ||
| N2 | 77 (29.5) | 20.0 (16.3-23.7) | 0.47 (0.29-0.76) | 0.002 | ||
| N3 | 30 (11.5) | 15.0 (9.6-20.4) | 1.00 | |||
| M stage (8th) | 4.0 | 0.045 | ||||
| M0 | 220 (84.3) | 26.0 (20.6-31.4) | 0.66 (0.43-0.99) | 0.048 | ||
| M1 | 41 (15.7) | 18.0 (13.0-23.0) | 1.00 | |||
| TNM stage (8th) | 21.3 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Ⅰ | 28 (10.7) | - | 0.27 (0.12-0.60) | 0.001 | ||
| Ⅱ | 72 (27.6) | 49.4 (9.5-89.3) | 0.43 (0.26-0.72) | 0.001 | ||
| Ⅲ | 84 (32.2) | 20.7 (17.0-24.4) | 0.81 (0.51-1.28) | 0.366 | ||
| ⅣA | 36 (13.8) | 16.4 (10.9-21.9) | 1.58 (0.94-2.66) | 0.086 | ||
| ⅣB | 41 (15.7) | 18.0 (13.0-23.0) | 1.00 |
Tab. 5
Multivariate analysis of the prognostic factors for CSS and PFS in LS-SCEC patients"
| Variables | CSS | PFS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P value | HR | 95% CI | P value | ||
| Chemotherapy cycle (<4 vs ≥4) | 1.97 | 1.43-2.72 | <0.001 | 1.93 | 1.44-2.58 | <0.001 | |
| TNM stage | <0.001 | 0.001 | |||||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ vs Ⅲ | 0.50 | 0.33-0.74 | 0.001 | 0.57 | 0.40-0.81 | 0.002 | |
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ vs Ⅳ | 0.31 | 0.21-0.46 | <0.001 | 0.43 | 0.30-0.62 | <0.001 | |
| Ⅲ vs Ⅳ | 0.61 | 0.42-0.89 | 0.010 | 0.74 | 0.52-1.04 | 0.083 | |
Tab. 6
Univariate analysis of the prognostic factors for PFS in LS-SCEC patients"
| Variable | Case n (%) | Median CSS (95%CI)/month | χ2 | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathology | 10.9 | 0.004 | 0.011 | |||
| Pure SCEC | 222 (85.0) | 12.0 (10.9-13.1) | 0.17 (0.04-0.70) | 0.014 | ||
| Mixed squamous cell/adenocacinoma | 37 (14.2) | 17.0 (11.8-22.2) | 0.12 (0.03-0.51) | 0.004 | ||
| Mixed large cell NEC | 2 (0.8) | 5.3 (-) | 1.00 | |||
| Chemotherapy cycle | ||||||
| <4 | 96 (36.8) | 9.7 (7.1-12.3) | 20.3 | <0.001 | 1.90 (1.42-2.55) | <0.001 |
| ≥4 | 165 (63.2) | 14.2 (11.7-16.7) | 1.00 | |||
| T stage (8th) | 19.8 | 0.001 | 0.002 | |||
| T1a | 4 (1.5) | 23.0 (-) | 0.14 (0.03-0.65) | 0.012 | ||
| T1b | 56 (21.5) | 17.0 (14.5-19.5) | 0.25 (0.12-0.51) | <0.001 | ||
| T2 | 74 (28.4) | 13.0 (11.1-14.9) | 0.38 (0.19-0.75) | 0.005 | ||
| T3 | 96 (36.8) | 10.2 (8.9-11.5) | 0.43 (0.22-0.83) | 0.012 | ||
| T4a | 21 (8.0) | 8.4 (7.4-9.4) | 0.52 (0.24-1.15) | 0.106 | ||
| T4b | 10 (3.8) | 7.0 (5.1-8.9) | 1.00 | |||
| N stage (8th) | 28.0 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| N0 | 66 (25.3) | 16.7 (13.1-20.3) | 0.31 (0.19-0.50) | <0.001 | ||
| N1 | 88 (33.7) | 13.8 (10.7-16.9) | 0.37 (0.24-0.59) | <0.001 | ||
| N2 | 77 (29.5) | 11.0 (9.4-12.6) | 0.52 (0.34-0.82) | 0.005 | ||
| N3 | 30 (11.5) | 6.4 (3.3-9.5) | 1.00 | |||
| TNM stage (8th) | 25.7 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Ⅰ | 28 (10.7) | 18.0 (16.5-19.5) | 0.46 (0.25-0.86) | 0.014 | ||
| Ⅱ | 72 (27.6) | 16.0 (12.2-19.8) | 0.56 (0.35-0.89) | 0.015 | ||
| Ⅲ | 84 (32.2) | 11.8 (10.7-12.9) | 0.91 (0.59-1.41) | 0.684 | ||
| ⅣA | 36 (13.8) | 8.0 (4.8-11.2) | 1.46 (0.89-2.41) | 0.137 | ||
| ⅣB | 41 (15.7) | 8.5 (6.7-10.3) | 1.00 |
Tab. 7
Comparison of clinical characteristics between patients receiving chemoradiotherapy and surgery+chemotherapy before and after PSM"
| Characteristic | Before PSM (n=172) | After PSM (n=88) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemoradiotherapy (n=81) | Surgery+chemotherapy (n=91) | P value | Chemoradiotherapy (n=44) | Surgery+chemotherapy (n=44) | P value | ||
| TNM stage | <0.001 | 0.589 | |||||
| Ⅰ | 3 | 16 | 3 | 0 | |||
| Ⅱ | 13 | 37 | 13 | 13 | |||
| Ⅲ | 22 | 31 | 21 | 24 | |||
| ⅣA | 17 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||
| ⅣB | 26 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Tumor length/cm | <0.001 | 1.000 | |||||
| ≤5 | 57 | 84 | 39 | 39 | |||
| >5 | 24 | 7 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Tumor location | 0.014 | 0.582 | |||||
| Cervial | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Upper thoracic | 11 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Middle thoracic | 43 | 55 | 25 | 23 | |||
| Lower thoracic | 23 | 33 | 18 | 21 | |||
| Overlap | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Chemotherapy cycle | 0.002 | 0.395 | |||||
| <4 | 10 | 29 | 6 | 9 | |||
| ≥4 | 71 | 62 | 38 | 35 | |||
| [1] | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| [2] |
ZHU Y, QIU B, LIU H, et al. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: review of 64 cases from a single institution[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2014, 27(2): 152-158.
doi: 10.1111/dote.12069 pmid: 23639106 |
| [3] |
MCKEOWN F. Oat-cell carcinoma of the oesophagus[J]. J Pathol Bacteriol, 1952, 64(4): 889-891.
pmid: 13000600 |
| [4] | YAMASHITA S, ABE H, YAMASHITA H, et al. PD-L1 and HLA-class Ⅰ expression status and their therapeutic implication in oesophageal small-cell carcinoma[J]. Histopathology, 2023, 83(2): 264-275. |
| [5] |
ZHU J, WANG Y, SUN H F, et al. Surgery versus radiotherapy for limited-stage small cell esophageal carcinoma: a multicenter, retrospective, cohort study in China (ChiSCEC)[J]. Int J Surg, 2024, 110(2): 956-964.
doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000912 pmid: 37995095 |
| [6] |
HUNCHAREK M, MUSCAT J. Small cell carcinoma of the esophagus. The Massachusetts General Hospital experience, 1978 to 1993[J]. Chest, 1995, 107(1): 179-181.
doi: 10.1378/chest.107.1.179 pmid: 7813272 |
| [7] | LIU S X, GE X L, GAO Z Z, et al. Clinicopathological analysis of 67 cases of esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma and the effect of postoperative adjuvant therapy on prognosis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, 100(43): e27302. |
| [8] |
HUANG Q, WU H Y, NIE L, et al. Primary high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 42 resection cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2013, 37(4): 467-483.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31826d2639 pmid: 23426118 |
| [9] |
NAKAJIMA Y, ZENDA S, MINASHI K, et al. Non-surgical approach to small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: does this rare disease have the same tumor behavior as SCLC?[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2012, 17(6): 610-615.
doi: 10.1007/s10147-011-0332-1 pmid: 22041926 |
| [10] | AL MANSOOR S, ZISKE C, SCHMIDT-WOLF I G H. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: patient data metaanalysis and review of the literature[J]. Ger Med Sci, 2013, 11: Doc12. |
| [11] | CHEN W W, WANG F, CHEN S B, et al. Detailed analysis of prognostic factors in primary esophageal small cell carcinoma[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2014, 97(6): 1975-1981. |
| [12] |
SITU D R, LIN Y B, LONG H, et al. Surgical treatment for limited-stage primary small cell cancer of the esophagus[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2013, 95(3): 1057-1062.
doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.11.014 pmid: 23333059 |
| [13] | ALFAYEZ M. Primary small cell oesophageal carcinoma: a retrospective study of different treatment modalities[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2020, 11(10): 836-843. |
| [14] | MENG M B, ZAORSKY N G, JIANG C, et al. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are associated with improved outcomes over surgery and chemotherapy in the management of limited-stage small cell esophageal carcinoma[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2013, 106(3): 317-322. |
| [15] |
LV J M, LIANG J, WANG J W, et al. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2008, 3(12): 1460-1465.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31818e1247 pmid: 19057273 |
| [16] |
XU L, YANG Y S, LI B, et al. Multimodality therapy and survival outcomes in resectable primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a multicenter retrospective study[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2025, 32(2): 848-859.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16532-x pmid: 39557721 |
| [17] | VERMA V, SLEIGHTHOLM R L, FANG P, et al. National Cancer Database report of nonmetastatic esophageal small cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(12): 6365-6373. |
| [18] |
RAJA S, RICE T W, RAJESWARAN J, et al. Esophageal small-cell cancer: study of a rare disease[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2013, 26(7): 690-695.
doi: 10.1111/dote.12022 pmid: 23317158 |
| [19] | WANG H H, ZAORSKY N G, MENG M B, et al. Multimodality therapy is recommended for limited-stage combined small cell esophageal carcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2015, 8: 437-444. |
| [20] | YOO J E, HAN K, SHIN D W, et al. Association between changes in alcohol consumption and cancer risk[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(8): e2228544. |
| [21] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会医政医管局. 食管癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2022(10): 1247-1268. |
| Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization for diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer (2022 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2022(10): 1247-1268. | |
| [22] | NISHINO M, JACKMAN D M, HATABU H, et al. New Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) guidelines for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: comparison with original RECIST and impact on assessment of tumor response to targeted therapy[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2010, 195(3): W221-W228. |
| [23] |
WANG H H, CHEN Y B, PI G L, et al. Validation and proposed modification of the 8th edition American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for patients with esophageal neuroendocrine neoplasms: evaluation of a revised lymph node classification[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 19(6): 4122-4132.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11480 pmid: 32382351 |
| [24] | 王肖飞, 张国庆, 吴彬, 等. 食管神经内分泌癌患者原因别死亡竞争风险模型的建立与评价[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 24(3): 231-236. |
| WANG X F, ZHANG G Q, WU B, et al. A competing-risks nomogram for cause-specific mortality in patients with esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2019, 24(3): 231-236. | |
| [25] |
DING J, JI J, ZHU W, et al. A retrospective study of different treatments of limited-stage small-cell esophageal carcinoma and associated prognostic factor analysis[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2013, 26(7): 696-702.
doi: 10.1111/dote.12017 pmid: 23317069 |
| [26] |
GAO R, ZHANG Y, WEN X P, et al. Chemotherapy with cisplatin or carboplatin in combination with etoposide for small-cell esophageal cancer: a systemic analysis of case series[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2014, 27(8): 764-769.
doi: 10.1111/dote.12149 pmid: 24118373 |
| [27] |
ZHANG Y L, REN H Z, WANG L, et al. Clinical impact of tumor-infiltrating inflammatory cells in primary small cell esophageal carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(6): 9718-9734.
doi: 10.3390/ijms15069718 pmid: 24886814 |
| [28] | CHEN W W, WANG F, ZHANG D S, et al. Primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: clinicopathological study of 44 cases[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 222. |
| [29] |
LI J Y, MA J, WANG H, et al. Population-based analysis of small cell carcinoma of the esophagus using the SEER database[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(7): 3529-3538.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1428 pmid: 32802432 |
| [30] | JEENE P M, GEIJSEN E D, MUIJS C T, et al. Small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a nationwide analysis of treatment and outcome at patient level in locoregional disease[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 2019, 42(6): 534-538. |
| [31] | HOU X, WEI J C, WU J X, et al. Multidisciplinary modalities achieve encouraging long-term survival in resectable limited-disease esophageal small cell carcinoma[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(7): e69259. |
| [32] |
WONG A T, SHAO M, RINEER J, et al. Treatment and survival outcomes of small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: an analysis of the National Cancer Data Base[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2017, 30(2): 1-5.
doi: 10.1111/dote.12487 pmid: 27860114 |
| [33] |
JATOI A, MILLER R C. Should we recommend surgery to patients with limited small cell carcinoma of the esophagus?[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2008, 3(12): 1373-1376.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31818dd98f pmid: 19057258 |
| [34] |
KUKAR M, GROMAN A, MALHOTRA U, et al. Small cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a SEER database analysis[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2013, 20(13): 4239-4244.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-013-3167-3 pmid: 23943025 |
| [35] |
SOHDA M, KUWANO H, SAEKI H, et al. Nationwide survey of neuroendocrine carcinoma of the esophagus: a multicenter study conducted among institutions accredited by the Japan Esophageal Society[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56(4): 350-359.
doi: 10.1007/s00535-020-01756-x pmid: 33582864 |
| [36] |
XU L, LI Y, LIU X B, et al. Treatment strategies and prognostic factors of limited-stage primary small cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(12): 1834-1844.
doi: S1556-0864(17)32771-5 pmid: 29024756 |
| [37] | CAI G K, WANG J, ZOU B W, et al. Preoperative chemotherapy for limited-stage small cell carcinoma of the esophagus[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2022, 114(4): 1220-1228. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
