Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 355-364.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.04.003
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
DENG Qiling1,2( ), SONG Di2(
), SONG Di2( ), XI Kexin2, XIE Xiaoting2, WU Xiaoyan1(
), XI Kexin2, XIE Xiaoting2, WU Xiaoyan1( ), ZHAO Wei2(
), ZHAO Wei2( )
)
Received:2025-01-21
Revised:2025-03-28
Online:2025-04-30
Published:2025-05-16
Contact:
ZHAO Wei; WU Xiaoyan
Supported by:Share article
DENG Qiling, SONG Di, XI Kexin, XIE Xiaoting, WU Xiaoyan, ZHAO Wei. Research on high-throughput detection of plasma cell-free DNA for targeted therapy-related genes screening and prognosis prediction in non-small cell lung cancer patients[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(4): 355-364.
Tab. 1
Somatic variant classification explained"
| Somatic variant classification | Level of evidence | Explained |
|---|---|---|
| Class Ⅰ variants (strong clinical significance) | A | FDA/NMPA approved for use as a biomarker that is responsive or resistant to cancer treatment in patients |
| A | Professional guidelines (NCCN) identify biomarkers that are responsive to or resistant to cancer treatment in patients | |
| A | professional guideline (NCCN) clarifies biomarkers that have diagnostic or prognostic significance for the patient's tumor | |
| B | Expert consensus studies identify biomarkers that are responsive to or resistant to cancer treatment in patients | |
| B | Expert consensus studies identify biomarkers that have diagnostic or prognostic significance for the patient's tumor | |
| C | FDA/NMPA approved biomarkers for other tumor treatments that are responsive or resistant | |
| Class Ⅱ variant (potential clinical significance) | C | Professional guidelines (NCCN) recommend biomarkers that are responsive to or resistant to other oncology treatments |
| C | Has been used as a biomarker for clinical trial screening and enrolment criteria | |
| C | The results of several small studies have shown biomarkers of significance for the diagnosis or prognosis of cancer in patients | |
| D | The results of the study indicate biomarkers of significance for the diagnosis, treatment, or prognosis of other tumors | |
| D | Biomarkers with potential therapeutic significance in preclinical studies | |
| D | There are a few studies and case reports or conclusions that do not reach a consensus to assess the diagnostic or prognostic significance of the disease with other biomarkers Class Ⅲ variants | |
| Category Ⅲ variants (variants of unknown clinical significance) | - | Not detected in population databases, specific subpopulation databases, pan-cancer databases, tumor-specific databases |
| - | There is no conclusive evidence of a cancer type | |
| Class Ⅳ variants (benign polymorphisms and suspected benign variants) | - | No evidence of cancer associated with the population database, specific subpopulation database. |
Tab. 2
Clinicopathological characteristics of enrolled patients"
| Type | Total (n=313) | pTNM (n) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | ||
| Age/year | |||||
| <50 | 54 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 49 |
| 50-69 | 203 | 20 | 16 | 25 | 142 |
| >70 | 56 | 5 | 0 | 12 | 39 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 170 | 13 | 10 | 27 | 120 |
| Female | 143 | 12 | 10 | 11 | 110 |
| Treatment options | |||||
| Radiotherapy | 94 | 7 | 6 | 20 | 51 |
| Chemotherapy | 214 | 12 | 14 | 26 | 162 |
| Targeted therapy | 265 | 18 | 16 | 29 | 202 |
| Immunotherapy | 90 | 6 | 4 | 12 | 68 |
| No treatment | 8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Surgery | 69 | 19 | 10 | 10 | 30 |
| First-line medication | |||||
| Chemotherapy alone | 67 | 4 | 9 | 14 | 40 |
| Pure targeting | 150 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 119 |
| Immunisation alone | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| Concomitant medications | 90 | 4 | 1 | 9 | 76 |
| Number of months of survival>60 | 56 | 12 | 10 | 6 | 28 |
| History of smoking | |||||
| Yes | 92 | 10 | 3 | 15 | 64 |
| No | 221 | 15 | 17 | 23 | 166 |
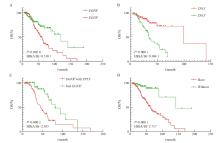
Fig. 5
Effect of hotspot target gene expression on patient survival A: Difference in survival of EGFR gene expression or not; B: Differences in survival of TP53 gene expression and non-expression; C: Differences in survival of EGFR gene expression combined with TP53 gene; D: There was no difference in survival between the expression of gene associated with targeted therapy drugs and those associated with targeted therapy drugs. Targeted therapy-related gene loci only included class Ⅰ and class Ⅱ targeted therapy-related gene loci."
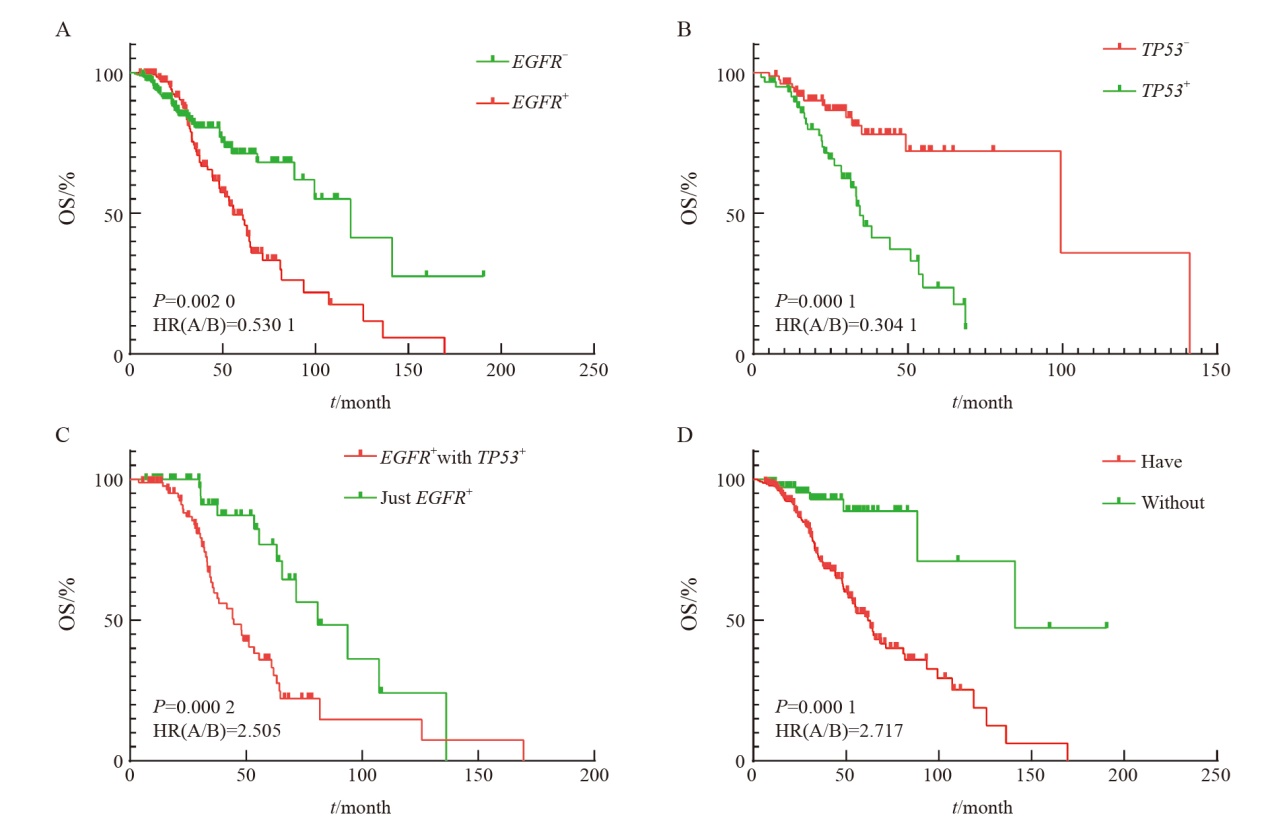
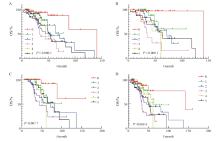
Fig. 7
Survival analysis of different mutations at targeted therapy-related gene loci under different influencing factors A: Differences in the survival of different mutations in stages Ⅲ-Ⅳ; B: Differences in survival of different mutations in patients without smoking history; C: First-line treatment is the difference in survival of patients with different mutations on targeted therapy alone; D: There was no difference in the survival of different mutations without relevant surgical history. Targeted therapy-related gene loci only included class Ⅰ and class Ⅱ targeted therapy-related gene loci."
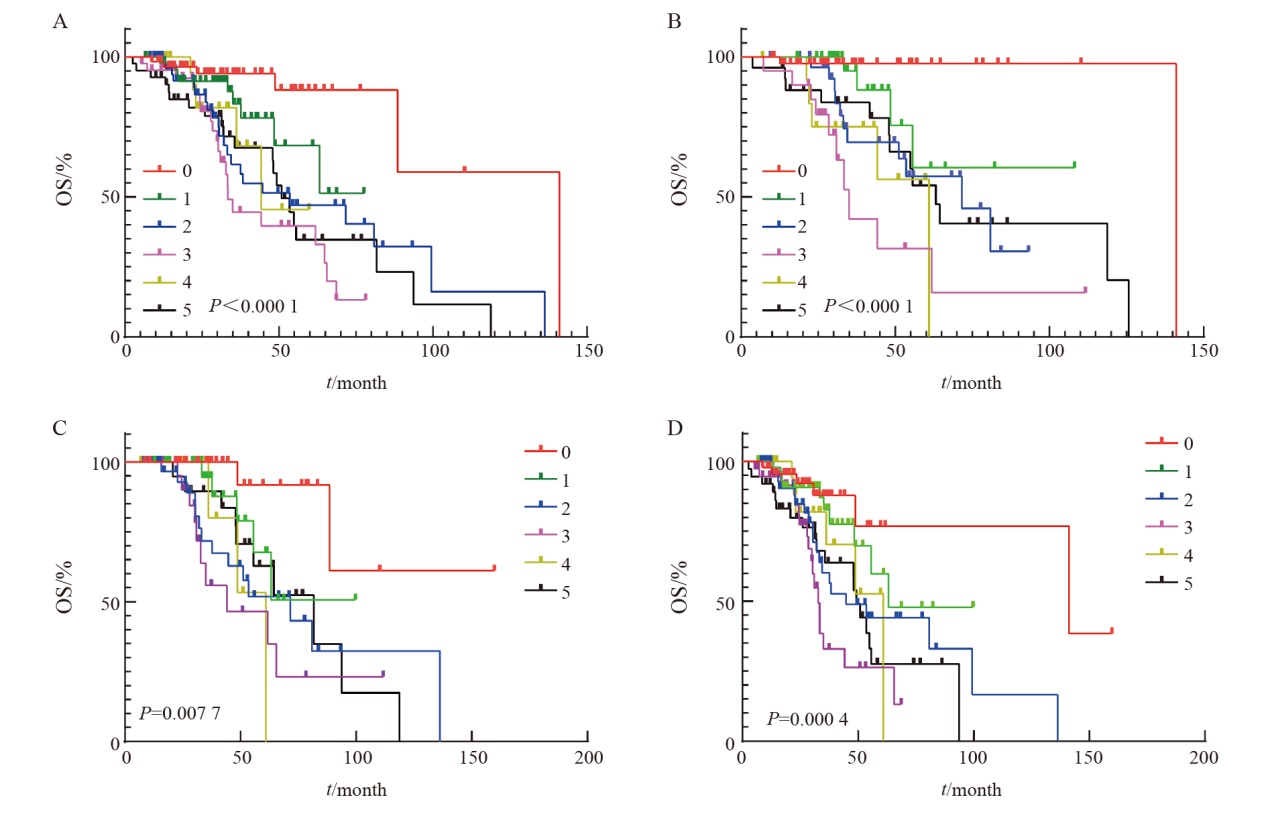
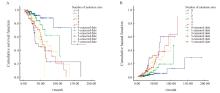
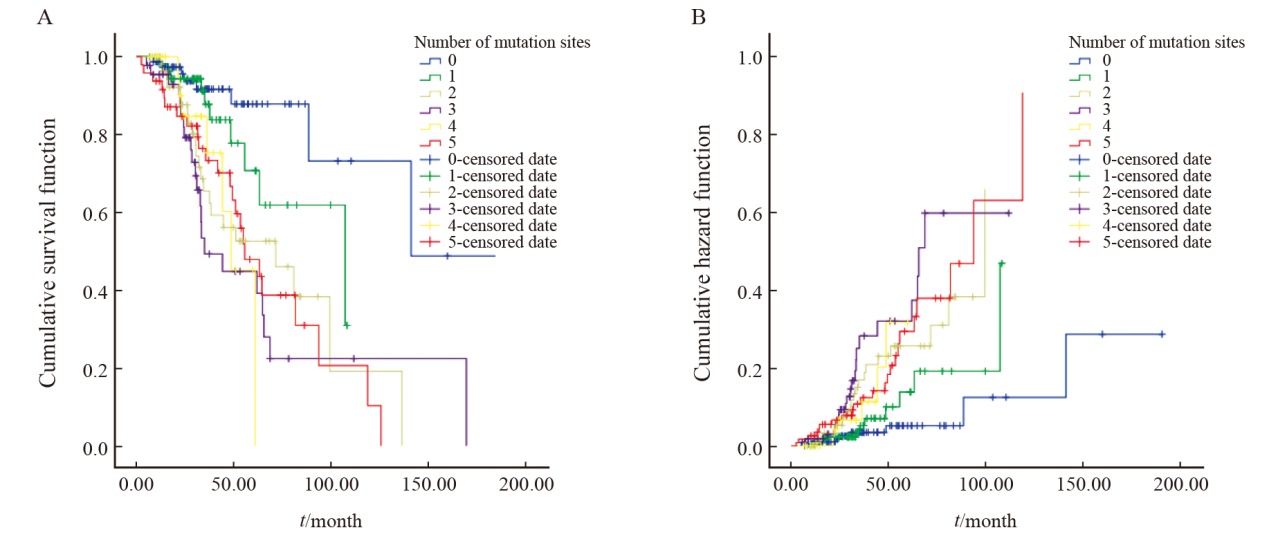
Fig. 8
Cox regression multivariate survival analysis A: Survival analysis of the number of positive sites of different targeted therapy drugs; B: Risk estimation model diagram of the number of positive sites of different targeted therapy drugs. Targeted therapy-related gene loci only include class Ⅰ and class Ⅱ targeted therapy-related gene loci."
Tab. 3
COX regression multivariate survival analysis information table"
| Item | P value | HR(A/B) | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| The number of loci is 0 | 0.001 | - | - |
| The number of loci is 1 | 0.142 | 2.016 | 1.984-5.062 |
| The number of loci is 2 | 0.002 | 3.848 | 1.645-8.824 |
| The number of loci is 3 | 0 | 5.006 | 2.334-12.440 |
| The number of loci is 4 | 0.005 | 4.530 | 1.445-11.734 |
| The number of loci is 5 | 0 | 4.629 | 2.047-10.606 |
| History of surgery | 0.001 | 1.752 | 1.244-2.467 |
| Clinical staging | 0.002 | 0.509 | 0.336-0.773 |
| [1] | NIKITA SANDEEP WAGLE MBBS M, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. |
| [2] | FILHO A M, LAVERSANNE M, FERLAY J, et al. The GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: data sources, methods, and a snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide[J]. Int J Cancer, 2025, 156(7): 1336-1346. |
| [3] | 张景暄, 付庭吕, 李宁, 等. 《肺癌的全球负担: 当前状态和未来趋势》要点解读[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2024, 31(1): 17-23. |
| ZHANG J X, FU T L, LI N, et al. Interpretation of the global burden of lung cancer: current status and future trends[J]. Chin J Clin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2024, 31(1): 17-23. | |
| [4] | RAHADIANI N, STEPHANIE M, MANATAR A F, et al. The diagnostic utility of cfDNA and ctDNA in liquid biopsies for gastrointestinal cancers over the last decade[J]. Oncol Res Treat, 2025, 48(3): 125-141. |
| [5] |
SON J W, LEE J, JEON J H, et al. Validation of IASLC 9th edition TNM classification for lung cancer: focus on N descriptor[J]. BMC Cancer, 2024, 24(1): 1460.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13139-z pmid: 39604857 |
| [6] | 应超, 蔡燕宁, 郝淑文, 等. 三种游离核酸提取试剂盒对血浆cfDNA提取性能的比较[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2023, 39(12): 1556-1563. |
| YING C, CAI Y N, HAO S W, et al. Performance comparison of three cell-free nucleic acid extraction kits for plasma cfDNA extraction[J]. J Pract Med, 2023, 39(12): 1556-1563. | |
| [7] | 李营歌, 董熠, 余舒阳, 等. 《2023 CSCO非小细胞肺癌诊疗指南》罕见靶点诊疗更新[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2023, 50(12): 1232-1236. |
| LI Y G, DONG Y, YU S Y, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic strategy updates of rare oncogenic mutations in Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (2023 edition)[J]. Cancer Res Prev Treat, 2023, 50(12): 1232-1236. | |
| [8] | CHANG Y S, TU S J, CHEN Y C, et al. Mutation profile of non-small cell lung cancer revealed by next generation sequencing[J]. Respir Res, 2021, 22(1): 3. |
| [9] |
林艺聪, 王悦, 薛倩倩, 等. EGFR T790M突变非小细胞肺癌患者的临床病理学、免疫微环境特征及对预后预测的意义[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2024, 34(4): 368-379.
doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.04.004 |
| LIN Y C, WANG Y, XUE Q Q, et al. Clinical pathological characteristics and immune microenvironment significance of EGFR T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients and its prognostic implications[J]. China Oncol, 2024, 34(4): 368-379. | |
| [10] | SINGH V, KATIYAR A, MALIK P, et al. Identification of molecular biomarkers associated with non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) using whole-exome sequencing[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2024, 41(3/4): CBM-220211. |
| [11] | AKIRA S, SHINGO M, HIBIKI U, et al. A large-scale prospective concordance study of plasma- and tissue-based next-generation targeted sequencing for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (LC-SCRUM-liquid)[J]. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res, 2022, 29(8): 1506-1514. |
| [12] | LEE S B, KIM J W, KIM H G, et al. Longitudinal comparative analysis of circulating tumor DNA and matched tumor tissue DNA in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer receiving palliative first-line systemic anti-cancer therapy[J]. Cancer Res Treat, 2024, 56(4): 1171-1182. |
| [13] |
BAE J H, LIU R L, ROBERTS E, et al. Single duplex DNA sequencing with CODEC detects mutations with high sensitivity[J]. Nat Genet, 2023, 55(5): 871-879.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-023-01376-0 pmid: 37106072 |
| [14] | WANG Z J, CHENG Y, AN T T, et al. Detection of EGFR mutations in plasma circulating tumor DNA as a selection criterion for first-line gefitinib treatment in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma (BENEFIT): a phase 2, single-arm, multicentre clinical trial[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2018, 6(9): 681-690. |
| [15] |
WU X N, ZHAO J, YANG L, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals age-dependent genetic underpinnings in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2022, 13(5): 1565-1572.
doi: 10.7150/jca.65370 pmid: 35371328 |
| [16] |
PINHEIRO P S, CALLAHAN K E, MEDINA H N, et al. Lung cancer in never smokers: distinct population-based patterns by age, sex, and race/ethnicity[J]. Lung Cancer, 2022, 174: 50-56.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.10.009 pmid: 36334356 |
| [17] | MALHOTRA J, MUDDASANI R, FRICKE J, et al. Clinical utility of a circulating tumor cell-based cerebrospinal fluid assay in the diagnosis and molecular analysis of leptomeningeal disease in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. JCO Precis Oncol, 2024, 8: e2400373. |
| [18] | GEORGE J, MAAS L, ABEDPOUR N, et al. Evolutionary trajectories of small cell lung cancer under therapy[J]. Nature, 2024, 627(8005): 880-889. |
| [19] | AKIN D, KAHRAMAN ÇETI N N, ERDOĞDU İ H, et al. Clinicopathological significance of mutation profile detected by next generation sequencing in different metastatic organs of non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2024, 260: 155463. |
| [20] | MIYAUCHI E, MORITA S, NAKAMURA A, et al. Updated analysis of NEJ009: gefitinib-alone versus gefitinib plus chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(31): 3587-3592. |
| [1] | YING Leilei, LI Kening, CHEN Chao, WANG Ying, HUANG Haozhe, WANG Biao, LI Wentao, HE Xinhong. Impact of tumor diameter on post-radiofrequency ablation survival and local progression risk in patients with colorectal cancer lung metastasis [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(5): 449-456. |
| [2] | LIN Yicong, WANG Yue, XUE Qianqian, ZHENG Qiang, JIN Yan, HUANG Ziling, LI Yuan. Clinical pathological characteristics and immune microenvironment significance of EGFR T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients and its prognostic implications [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(4): 368-379. |
| [3] | ZHANG Lingling, WANG Xiangyi, WEI Xing, LIN Li, TANG Chuanhao, LIANG Jun. A study on prevention and treatment of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting in non-small cell lung cancer patients with low-frequency electrical stimulator for antiemesis [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 776-781. |
| [4] | SU Chunxia, ZHOU Caicun. Important clinical research progress in lung cancer in 2022 [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 218-227. |
| [5] | HE Liyuan, WANG Yudong. Research progress of ALK kinase domain drug resistance mutation and its future countermeasures [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(8): 736-746. |
| [6] | HONG Yaping, HUANG Yunjian, HUANG Zhangzhou, CHEN Shengjia, ZHONG Qiaofeng, ZENG Hongfu, ZHUANG Wu. Efficacy and prognostic predictors of first-generation EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(7): 624-634. |
| [7] | SU Chunxia, ZHOU Caicun. Current status and future directions of immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(6): 478-486. |
| [8] | YU Silai, NI Jianjiao, ZHU Zhengfei. Treatment of unresectable locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the era of immunotherapy: status and prospects [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(6): 487-498. |
| [9] | FU Yuanyuan, HOU Runping, FU Xiaolong. Research progress in predicting the risk of lymphatic or hematologic metastasis based on chest CT in early non-small cell lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(4): 343-350. |
| [10] | ZHOU Changshuai, YANG Yuechao, CUI Huanhuan, CHEN Lei, CHEN Xin, HAO Bin, TONG Tong, CAO Yiqun. Prognostic factor analysis of surgical treatment for cerebellar metastases in 36 patients [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(4): 357-362. |
| [11] | WANG Zezhou , ZHANG Yang , MO Miao , YUAN Jing , ZHOU Changming , SHEN Jie , FENG Xiaoshuang , WU Haoxuan , LI Hang , YE Ting , HU Hong , CHEN Haiquan , ZHENG Ying . Distribution of metastatic sites and survival analysis of patients with non-metastatic lung cancer at initial diagnosis based on hospital registration [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(9): 775-782. |
| [12] | ZHU Yihui, LI Ting, HU Xichun. Clinical research progress and prospect of trastuzumab deruxtecan [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(8): 754-761. |
| [13] | LI Haizhou , ZHANG Yanwei , XU Yingjie , YANG Men , ZHANG Lei , HAN Jingjun . miR-933 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer cell lines by regulation of KLF6 gene [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 581-588. |
| [14] | YANG Jia , LIU Shuyuan , WANG Yingying , LI Yingfu , MA Qianli , LI Yu , WANG Yongrong , LI Chuanyin , TAN Fang . The association of polymorphisms in TNF-α gene with non-small cell lung cancer in Han population of Yunnan Province [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 616-628. |
| [15] | YI Weili , ZHAO Wencheng , HUANG Dongning , QIN Li , WU Xintian , ZHOU Fei , WU Fengying . Analysis of immune-related adverse events and its correlation with efficacy of anti-PD-1 monotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(3): 203-211. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
