Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (4): 365-375.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.04.004
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIN Huan1( ), WANG Jie2, YANG Jie1, HUA Yingjie1, QU Huijuan3, JI Honghai3(
), WANG Jie2, YANG Jie1, HUA Yingjie1, QU Huijuan3, JI Honghai3( )
)
Received:2024-10-24
Revised:2025-02-10
Online:2025-04-30
Published:2025-05-16
Contact:
JI Honghai
Share article
QIN Huan, WANG Jie, YANG Jie, HUA Yingjie, QU Huijuan, JI Honghai. Mechanistic study on PLK4 regulation of invasion, proliferation and apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(4): 365-375.
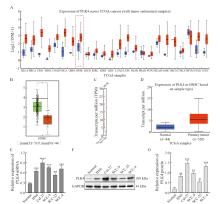
Fig. 1
PLK4 was highly expressed in HNSC and OSCC tissues and cell lines A-D: The expression of PLK4 in OSCC was analyzed in GEPIA2 and UALCAN. The blue color in A and B indicated normal tissue, and the red color indicated tumor tissue; E: The PLK4 mRNA in OSCC and normal cells; F-G: Protein expression of PLK4 in OSCC and normal cells; *: P<0.05, compared with normal; **: P<0.01, compared with normal; ***: P<0.001, compared with normal; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with normal. Normal: Normal oral mucosal epithelial cells."
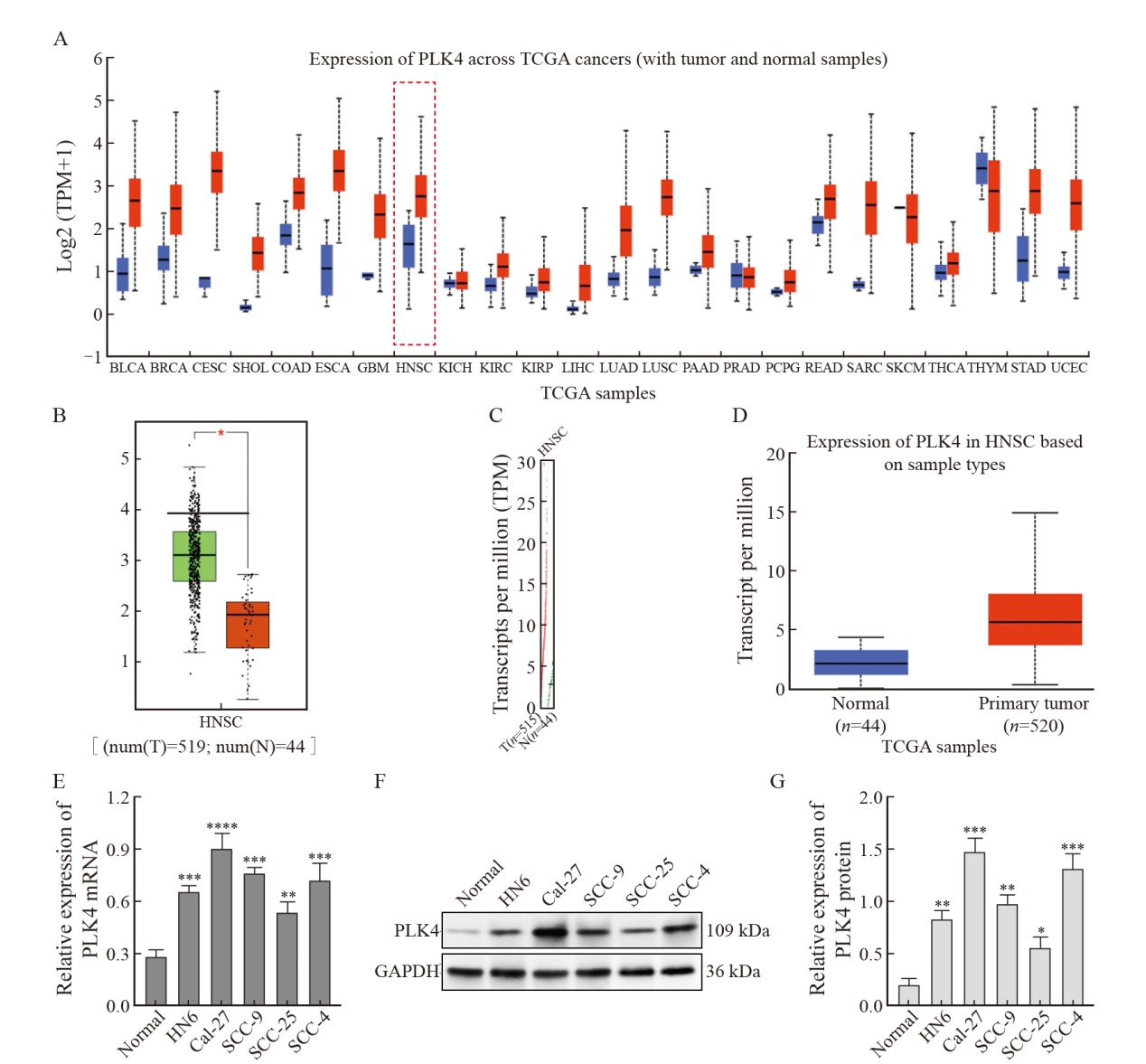
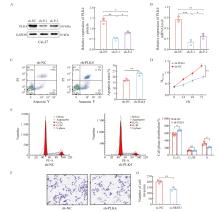
Fig. 2
Knockdown of PLK4 expression inhibited the proliferation and invasion of Cal-27 cells and promoted apoptosis A: Western blot test was used to detect the protein expression of PLK4 in OSCC cells; B: RTFQ-PCR was used to detect the mRNA expression of PLK4 in OSCC cells; C: Effect of PLK4 knockdown on OSCC cell apoptosis; D: Effect of PLK4 knockdown on the proliferation of OSCC cells; E: Effect of PLK4 knockdown on OSCC cell proliferation cycle; F-G: Effect of PLK4 knockdown on OSCC cell invasion. Compared with sh-NC group; *: P <0.05, compared with each other; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other. ns: No significance."
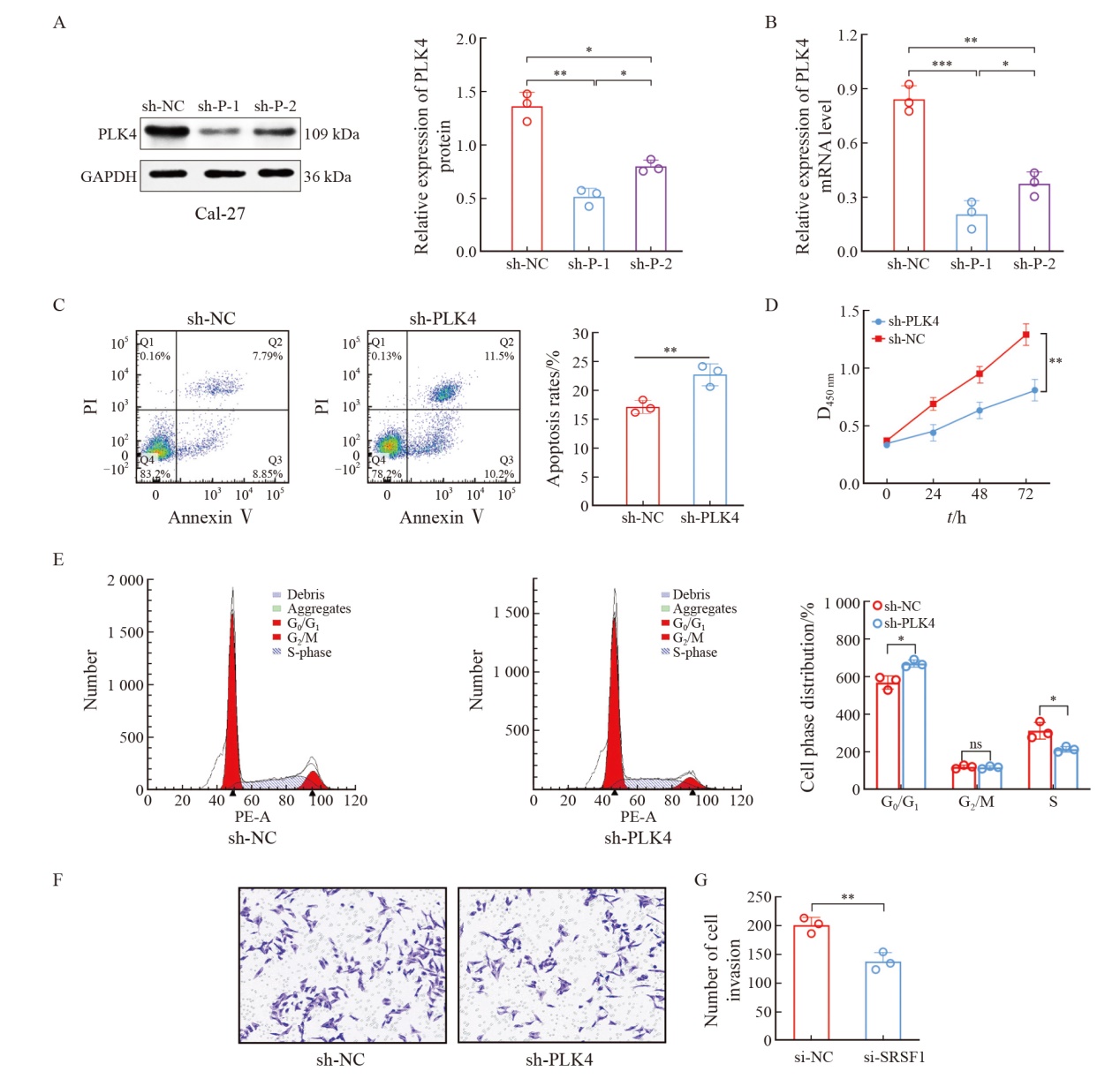
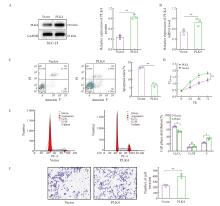
Fig. 3
Overexpression of PLK4 up-regulated the proliferation and invasion of SCC-25 cells and inhibited apoptosis A: Western blot assay was used to detect the protein expression of PLK4 in OSCC cells with overexpression; B: The PLK4 mRNA in OSCC cells with overexpression was analyzed via RTFQ-PCR; C: Effect of PLK4 overexpression on the apoptosis of OSCC cells; D: Effect of PLK4 overexpression on the proliferation of OSCC cells; E: Effect of PLK4 overexpression on the proliferation cycle of OSCC cells; F: Effect of PLK4 overexpression on OSCC cell invasion. *: P<0.05, compared with each other; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with each other."
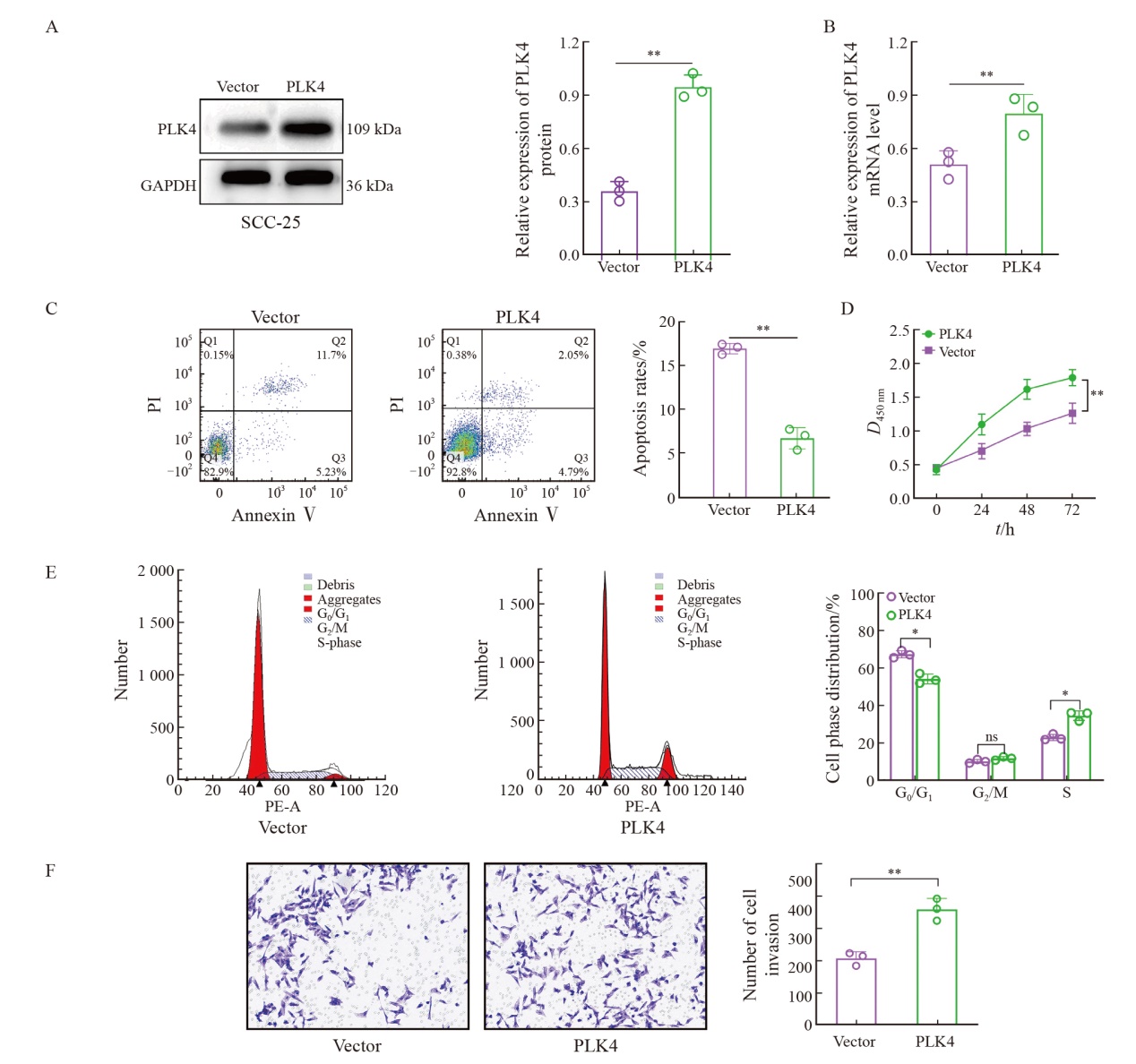
Fig. 4
Inhibitory and promoting effects of knockdown or overexpression of PLK4 on PI3K/AKT pathway and cyclin-related protein expression A-B: The differentially expressed genes in the PLK4 high and PLK4 low differential groups led to the enrichment of PI3K/AKT. C-D: Western blot assay was used to find the expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway proteins. Compared with sh-NC or vector group, *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.000 1."
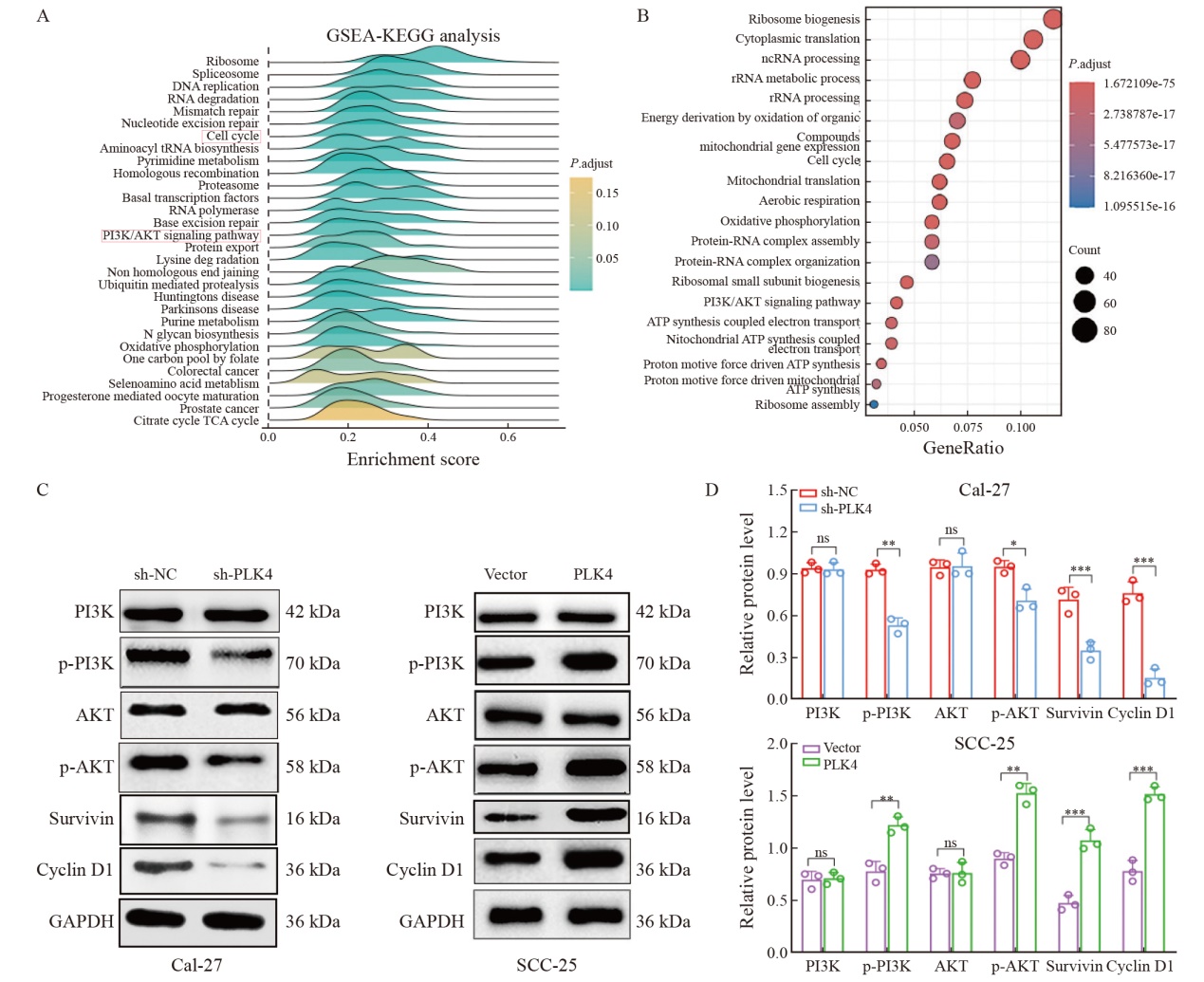
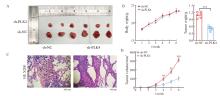
Fig. 5
Knockdown of PLK4 expression inhibited subcutaneous tumor formation in nude mice A: Effect of PLK4 knockdown on subcutaneous tumor formation in nude mice; B: Effects of PLK4 knockdown on body weight, tumor weight and volume of nude mice; C: H-E staining was used to analyze the tumor tissues of sh-NC and sh-PLK4 groups. D: Tumor volume. Compared with sh-NC group, *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; ****: P<0.000 1."
| [1] | 梁壮, 王伟, 郭文博, 等. DPP3在口腔鳞状细胞癌中的表达及生物学作用[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2024, 32(18): 3426-3433. |
| LIANG Z, WANG W, GUO W B, et al. The expression and biological role of DPP3 in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Mod Oncol, 2024, 32(18): 3426-3433. | |
| [2] | SAIKIA P J, PATHAK L, MITRA S, et al. The emerging role of oral microbiota in oral cancer initiation, progression and stemness[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1198269. |
| [3] |
SAIDAK Z, LAILLER C, TESTELIN S, et al. Contribution of genomics to the surgical management and study of oral cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2021, 28(11): 5842-5854.
doi: 10.1245/s10434-021-09904-0 pmid: 33846893 |
| [4] | NIU Q, SUN Q N, BAI R S, et al. Progress of nanomaterials-based photothermal therapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(18): 10428. |
| [5] | LEI Q, YU Q W, YANG N, et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting polo-like kinase 4[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2024, 265: 116115. |
| [6] | CHAN C Y, YUEN V W, CHIU D K, et al. Polo-like kinase 4 inhibitor CFI-400945 suppresses liver cancer through cell cycle perturbation and eliciting antitumor immunity[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(3): 729-744. |
| [7] |
DENG S S, LU X L, ZHANG Z, et al. Identification and assessment of PLK1/2/3/4 in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma: evidence from methylation profile[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(14): 6652-6663.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16668 pmid: 34080290 |
| [8] |
PELLIZZARI S, BHAT V, ATHWAL H, et al. PLK4 as a potential target to enhance radiosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2024, 19(1): 24.
doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02410-z pmid: 38365710 |
| [9] |
ZHAO Y, WANG X. PLK4: a promising target for cancer therapy[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2019, 145(10): 2413-2422.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02994-0 pmid: 31492983 |
| [10] | 宋宁, 李敏敏, 郑文甜, 等. 突触融合蛋白结合蛋白4对口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2023, 39(8): 1390-1398. |
| SONG N, LI M M, ZHENG W T, et al. Effects of syntaxin binding protein 4 on proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2023, 39(8): 1390-1398. | |
| [11] |
CHEN Y F, HAN Z Y, ZHANG L, et al. TIMELESS promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 21.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04791-3 pmid: 38178094 |
| [12] |
GARVEY D R, CHHABRA G, NDIAYE M A, et al. Role of polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) in epithelial cancers and recent progress in its small molecule targeting for cancer management[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2021, 20(4): 632-640.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0741 pmid: 33402398 |
| [13] | KRESSIN M, FIETZ D, BECKER S, et al. Modelling the functions of polo-like kinases in mice and their applications as cancer targets with a special focus on ovarian cancer[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(5): 1176. |
| [14] |
FU F M, CHEN L K, YANG X H, et al. PLK4 is a key molecule in the formation of PGCCs and promotes invasion and migration of progeny cells derived from PGCCs[J]. J Cancer, 2022, 13(9): 2954-2969.
doi: 10.7150/jca.74211 pmid: 35912011 |
| [15] | 张进忠, 李悦淇, 石科, 等. PLK4基因在人食管鳞癌组织中的表达及对癌细胞增殖、侵袭迁移影响的研究[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2021, 31(12): 1185-1193. |
| ZHANG J Z, LI Y Q, SHI K, et al. Expression and clinical significance of PLK4 gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on cell proliferation, invasion and migration[J]. China Oncol, 2021, 31(12): 1185-1193. | |
| [16] | ZHU W, XIE B. PLK4 inhibitor exhibits antitumor effect and synergizes sorafenib via arresting cell cycle and inactivating Wnt/β-catenin pathway in anaplastic thyroid cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2023, 24(1): 2223383. |
| [17] | HE Y, SUN M M, ZHANG G G, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signal transduction for cancer therapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 425. |
| [18] |
XU P, HU K, ZHANG P, et al. Hypoxia-mediated YTHDF2 overexpression promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by activation of the mTOR/AKT axis[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2022, 22(1): 13.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02368-y pmid: 34996459 |
| [19] | MAO X Q, CHENG Y, ZHANG R Z, et al. RNA-seq and ATAC-seq analyses of multilineage differentiating stress enduring cells: comparison with dermal fibroblasts[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2022, 46(9): 1480-1494. |
| [20] | TANG W, JIA P, ZUO L, et al. Suppression of CX3CL1 by miR-497-5p inhibits cell growth and invasion through inactivating the ERK/AKT pathway in NSCLC cells[J]. Cell Cycle, 2022, 21(16): 1697-1709. |
| [21] | TUFAIL M, WAN W D, JIANG C H, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling to overcome drug resistance in cancer[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2024, 396: 111055. |
| [22] |
GLAVIANO A, FOO A S C, LAM H Y, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 138.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01827-6 pmid: 37596643 |
| [23] | YU L, WEI J, LIU P D. Attacking the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 85: 69-94. |
| [24] | HE C P, CHEN Y T, ZHANG X M, et al. Down-regulation of ESRP2 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation via inhibiting cyclinD1[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 28475. |
| [25] | 刘玉娟, 郭明艳. JMJD3与Cyclin D1基因在喉鳞状细胞癌组织中的表达及意义[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2023, 20(8): 1126-1129. |
| LIU Y J, GUO M Y. Expressions and significance of JMJD3 and CyclinD1 in cancer tissues of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Lab Med Clin, 2023, 20(8): 1126-1129. | |
| [26] | SIRAGUSA G, TOMASELLO L, GIORDANO C, et al. Survivin (BIRC5): implications in cancer therapy[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 350: 122788. |
| [1] | ZHENG Wentian, GONG Hui, ZHANG Xinyue, HAO Jiayi, WANG Yajie, JIANG Yingying. Effects of SEC14L1P1 on proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(3): 309-319. |
| [2] | WEN Ziqiang, LAN Junliang, ZHOU Bo, XU Qiwei. PARP1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating expression of POU2F2 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 848-856. |
| [3] | CAO Fei, YU Wenhao, TANG Xiaonan, MA Zidong, CHANG Tingmin, GONG Yabin, LIAO Mingjuan, KANG Xiaohong. Mechanism of LINC01410 promoting proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 753-762. |
| [4] | CHEN Xun, ZHENG Zhenxia, RUAN Xueru. Effects of TMCO1 on proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 571-580. |
| [5] | SUN Rongqi, SONG Ning, ZHENG Wentian, ZHANG Xinyue, LI Minmin, GONG Hui, JIANG Yingying. Effect of long noncoding RNA FLJ30679 on proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 439-450. |
| [6] | XIONG Jiayan, LEI Wei, YOU Bo, ZHANG Zhenxin, XIE Haijing, SHAN Ying, XIA Tian, ZHOU Yong. Study on the mechanism of DDX6 promoting proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by regulating stability of CKMT1A mRNA [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 451-459. |
| [7] | ZHOU Xueqin, LUAN Yanchao, ZHAO Li, RONG Chaochao, YANG Na. Expression of CDC20 in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and its effect on the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 460-472. |
| [8] | GUAN Ruirui, HAO Qian, ZHANG Yaqi, SUN Qinggang, CHEN Yitian, LI Xiumin, ZHOU Xiang, HAN Tao. CDC20 facilitates the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cell by stabilizing NLRP3 expression [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 473-484. |
| [9] | WANG Xiaocong, LI Ming. The value of single-cell sequencing in oral squamous cell carcinoma research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 501-508. |
| [10] | WU Zhibai, XU Guiqin, ZHANG Li, YANG Zhaojuan, LIU Yun, JIAO Kun, CHEN Zehong, XU Chen, ZUO You, ZHENG Ningqian, YE Zhiqian, LIU Yongzhong. Mechanism study of KCMF1 promoting proliferation and NF-κB signaling transduction in colorectal cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 987-997. |
| [11] | XU Ziqi, HU Ruizhi, LI Junjian, WANG Hongxia, SANG Youzhou. Exploring the role of methylation-driven gene IFFO1 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma diagnosis, prognosis and cellular functions [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 998-1010. |
| [12] | JIA Liqing, GE Xiaolu, JIANG Lin, ZHOU Xiaoyan. Effects of lncRNA PKD2-2-3 on cell proliferation, clone formation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 717-725. |
| [13] | WANG Xuemei, CHENG Yu, QI Jiemin. PRMT7 inhibits proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cells by regulating Notch signaling pathway [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 437-444. |
| [14] | ZHANG Pingchuan, DU Mingyu, YAO Chengyun, HE Xia, YIN Li. Mechanism of circular RNA hsa_circ_0012779 expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its influence on cell biological behavior [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 445-451. |
| [15] | XIAO Lanshu, PAN Liudi, LIU Yi, WANG Jie, CHEN Hui. LncRNA DLEU7-AS1 contributes to proliferation and migration of gastric cancer by regulating MSN transcription [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(4): 327-341. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
