Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 478-484.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.05.006
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
TONG Gang( ), HUA Yang, PENG Wei, ZHAO Ju, HU Junwen(
), HUA Yang, PENG Wei, ZHAO Ju, HU Junwen( )
)
Received:2024-11-03
Revised:2025-03-26
Online:2025-05-30
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
HU Junwen
Supported by:Share article
CLC Number:
TONG Gang, HUA Yang, PENG Wei, ZHAO Ju, HU Junwen. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of TACE combined with anlotinib and sintilimab in the treatment of patient with CNLC stage ⅡB-ⅢB liver cancer[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(5): 478-484.
Tab. 1
General information of selected patients [n (%)]"
| Category | Proportion |
|---|---|
| Age/year median (range) | 57.33 (41-74) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 31 (79.5) |
| Female | 8 (20.5) |
| Performance status | |
| 0 | 11 (28.2) |
| 1 | 28 (71.8) |
| Hbsag positive | 32 (82.1) |
| Cirrhosis | 29 (74.4) |
| Recurrence after local treatment | 8 (20.5) |
| Portal vein cancer thrombus | 20 (51.3) |
| Extrahepatic metastasis | 21 (53.8) |
| Portal vein cancer thrombus and metastasis | 12 (30.8) |
| Hepatic arteriovenous fistula | 4 (10.3) |
| Low to moderate ascites | 12 (30.8) |
| Alpha fetoprotein | |
| <400 | 25 (64.1) |
| ≥400 | 14 (35.9) |
| Child-pugh classification | |
| A | 18 (46.2) |
| B | |
| 7 points | 15 (38.5) |
| 8 points | 6 (15.3) |
| Size/cm | |
| <5 | |
| <5 (first treatment)* | 4 (10.3) |
| <5 (recurrence) | 4 (10.3) |
| 5-10 | 14 (35.9) |
| 10-15 | 15 (38.4) |
| >15 | 2 (5.1) |
| Tumor staging | |
| Ⅱb | 6 (15.4) |
| Ⅲa | 17 (43.6) |
| Ⅲb | 16 (40.0) |
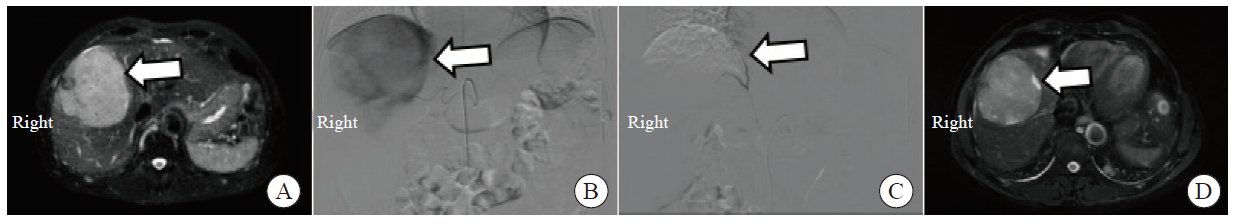
Fig. 4
Comparison of therapeutic effects before and after TACE treatment A: Before treatment, the upper abdominal MRI showed the condition of the tumor lesion (indicated by the arrow); B: Intraoperative hepatic angiography with TACE showed significant tumor staining; C: Postoperative TACE imaging shows disappearance of tumor staining; D: One month after TACE surgery, the upper abdominal MRI showed that most of the tumor lesions were necrotic (indicated by the arrow)."
Tab. 2
Incidence of treatment-related adverse events [n (%)]"
| Item | Adverse event category | Grade 1-2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Grade 5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall adverse reaction rate | 39 (100.0) | 15 (38.5) | 5 (12.8) | 1 (2.6) | ||
| Stage mainly treated with TACE | Total adverse events of TACE | 39 (100.0) | 10 (25.4) | 4 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | |
| pain | 31 (79.5) | 4 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 35 (89.7) | |
| AST rise | 19 (48.7) | 14 (35.9) | 2 (5.1) | 0 (0.0) | 35 (89.7) | |
| ALT rise | 24 (61.5) | 7 (17.9) | 3 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 34 (87.2) | |
| Decreased appetite | 32 (82.1) | 2 (5.1) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 34 (87.2) | |
| Decreased albumin | 24 (61.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 24 (61.5) | |
| Elevated bilirubin | 18 (46.2) | 4 (10.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (56.4) | |
| vomit | 15 (38.5) | 7 (17.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 22 (56.4) | |
| Thrombocytopenia | 13 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 13 (33.3) | |
| Hemoglobin reduction | 10 (25.6) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (28.2) | |
| fever | 7 (17.9) | 0 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (17.9) | |
| Decreased white blood cells | 3 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.7) | |
| The stage mainly treated with anlotinib combined with sintilimab | Total number of targeted combined immune adverse events | 39 (100.0) | 7 (17.9) | 1 (2.6) | 1 (2.6) | |
| Decreased lymphocytes (not differentiated by grade) | 26 (66.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 26 (66.7) | |
| AST rise | 25 (64.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 25 (64.1) | |
| Decreased albumin | 24 (61.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 24 (61.5) | |
| Elevated bilirubin | 16 (41.0) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 17 (43.6) | |
| ALT rise | 15 (38.5) | 2 (5.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 17 (43.6) | |
| Hemoglobin reduction | 15 (38.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 15 (38.5) | |
| Hypothyroidism | 14 (35.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 14 (35.9) | |
| Thrombocytopenia | 12 (30.8) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 13 (33.3) | |
| hypertension | 11 (28.2) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (28.2) | |
| proteinuria | 9 (23.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (23.1) | |
| Decreased appetite | 9 (23.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (23.1) | |
| Upper gastrointestinal bleeding | 4 (10.3) | 3 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) | 8(20.5) | |
| Joint pain, rash | 5 (12.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (12.8) | |
| Decreased white blood cells | 4 (10.3) | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (12.8) | |
| fever | 3 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.7) | |
| Immune pneumonia | 1 (2.6) | 2 (5.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (7.7) | |
| Hyperthyroidism | 1 (2.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.6) |
| [1] | GALLE P R, FINN R S, QIN S K, et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (IMbrave150): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(7): 991-1001. |
| [2] | REN Z G, XU J M, BAI Y X, et al. Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2-3 study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(7): 977-990. |
| [3] | WU J Y, YIN Z Y, BAI Y N, et al. Lenvatinib combined with anti-PD-1 antibodies plus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2021, 8: 1233-1240. |
| [4] | LLOVET J M, RICCI S, MAZZAFERRO V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359(4): 378-390. |
| [5] | EL-KHOUEIRY A B, SANGRO B, YAU T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10088): 2492-2502. |
| [6] | CHENG A L, QIN S K, IKEDA M, et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(4): 862-873. |
| [7] | 郑荣寿, 陈茹, 韩冰峰, 等. 2022年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2024, 46(3): 221-231. |
| ZHENG R S, CHEN R, HAN B F, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2024, 46(3): 221-231. | |
| [8] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会医政司. 原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2024年版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2024, 44(4): 361-386. |
| Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (2024 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2024, 44(4): 361-386. | |
| [9] |
HOY S M. Sintilimab: first global approval[J]. Drugs, 2019, 79(3): 341-346.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1066-z pmid: 30742278 |
| [10] | 古曦, 刘畅, 刘双双, 等. 肝癌患者TACE术治疗前后血清VEGF、bFGF、HIF-1α水平变化及其临床意义[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2019, 26(4): 546-549. |
| GU X, LIU C, LIU S S, et al. Changes of serum VEGF, bFGF and HIF-1α levels in patients with liver cancer before and after TACE and their clinical significances[J]. Labeled Immunoass Clin Med, 2019, 26(4): 546-549. | |
| [11] | 中国医师协会肿瘤医师分会, 中国临床肿瘤学会血管靶向治疗专家委员会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤靶向治疗专业委员会, 等. 盐酸安罗替尼治疗晚期肺癌中国专家共识(2023年版)[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2023, 30(2): 67-78. |
| Chinese Association for Clinical Oncologists, Expert Committee of Vascular Targeted Therapy of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, Cancer Targeted Therapy Professional Committee of China Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on anlotinib hydrochloride for advanced lung cancer (2023 version)[J]. Chin J Clin Oncol Rehabil, 2023, 30(2): 67-78. | |
| [12] |
KASHYAP A S, SCHMITTNAEGEL M, RIGAMONTI N, et al. Optimized antiangiogenic reprogramming of the tumor microenvironment potentiates CD40 immunotherapy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2020, 117(1): 541-551.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1902145116 pmid: 31889004 |
| [13] | HAN X, GUO J, LI L Y, et al. Sintilimab combined with anlotinib and chemotherapy as second-line or later therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a phase Ⅱ clinical trial[J]. Sig Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9: 241. |
| [14] |
SUN X, XU J, XIE L, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitors for patients with previously treated metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2022, 15: 7581-7591.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S379269 pmid: 36196372 |
| [15] | LIU H N, PAN D, YAO Z Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of gemCitabine/nab-paclitaxel combined with anlotinib and PD-1 inhibitors as a first-line treatment for advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 139: 112635. |
| [16] | JIANG J Y, WU B, SUN Y, et al. Anlotinib reversed resistance to PD-1 inhibitors in recurrent and metastatic head and neck cancers: a real-world retrospective study[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2024, 73(10): 199. |
| [17] | 韩春, 叶斯斯, 李娟, 等. 安罗替尼联合PD-1单抗(AK105)治疗13例晚期转移性肝细胞肝癌的疗效及安全性评价[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2020, 41(9): 868-871. |
| HAN C, YE S S, LI J, et al. A preliminary study on effect and safety of anlotinib combined with anti-PD-1 antibody (AK105) in treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Acad J Chin PLA Med Sch, 2020, 41(9): 868-871. | |
| [18] | CHEN X F, LI W, WU X F, et al. Sintilimab plus anlotinib as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(15_suppl): e16146. |
| [19] | HAN C, YE S S, HU C H, et al. Clinical activity and safety of penpulimab (anti-PD-1) with anlotinib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: an open-label, multicenter, phase Ⅰb/Ⅱ trial (AK105-203)[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 684867. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
