Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2025, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 440-448.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2025.05.002
• Original article • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Hua( ), ZHOU Guochao(
), ZHOU Guochao( ), CAI Rongmin, SONG Xin, YANG Dinghua
), CAI Rongmin, SONG Xin, YANG Dinghua
Received:2024-12-19
Revised:2025-04-01
Online:2025-05-30
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
ZHOU Guochao
Supported by:Share article
CLC Number:
FU Hua, ZHOU Guochao, CAI Rongmin, SONG Xin, YANG Dinghua. Effect of liposome binding antisense oligonucleotide BP1003 on albumin-bound paclitaxel sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells by inhibiting STAT3[J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(5): 440-448.
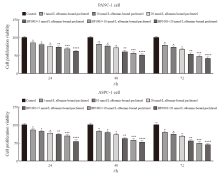
Fig. 5
Effects of BP1003 combined with albumin-bound paclitaxel on proliferation viability rates of PANC-1 and ASPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells (n=5) *: P<0.05, compared with control group; **: P<0.05, compared with 5 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ***: P<0.05, compared with 10 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ****: P<0.05, compared with 20 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel."
Fig. 6
Effects of BP1003 combined with albumin-bound paclitaxel on apoptosis of PANC-1 and ASPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells (n=5) *: P<0.05, compared with control group; **: P<0.05, compared with 5 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ***: P<0.05, compared with 10 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ****: P<0.05, compared with 20 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel."
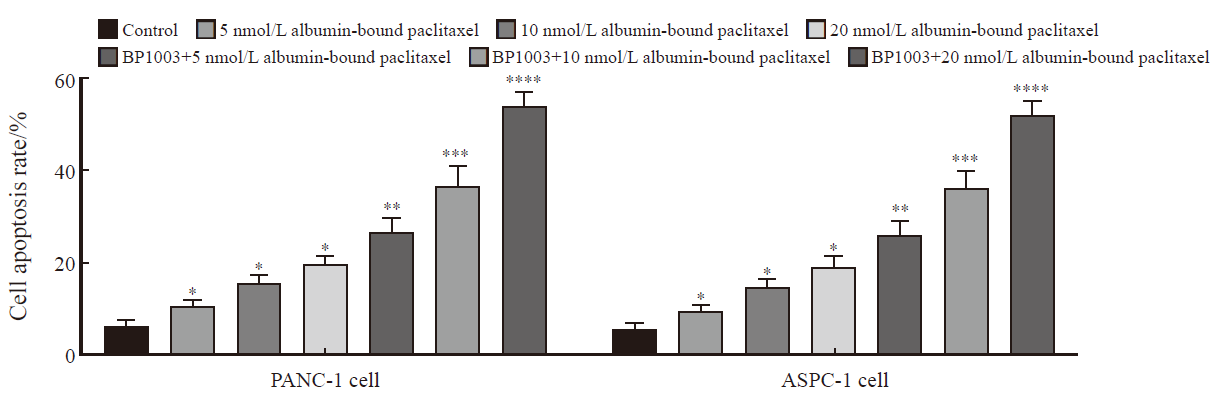
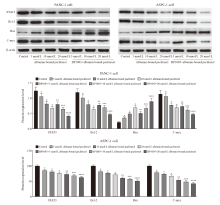
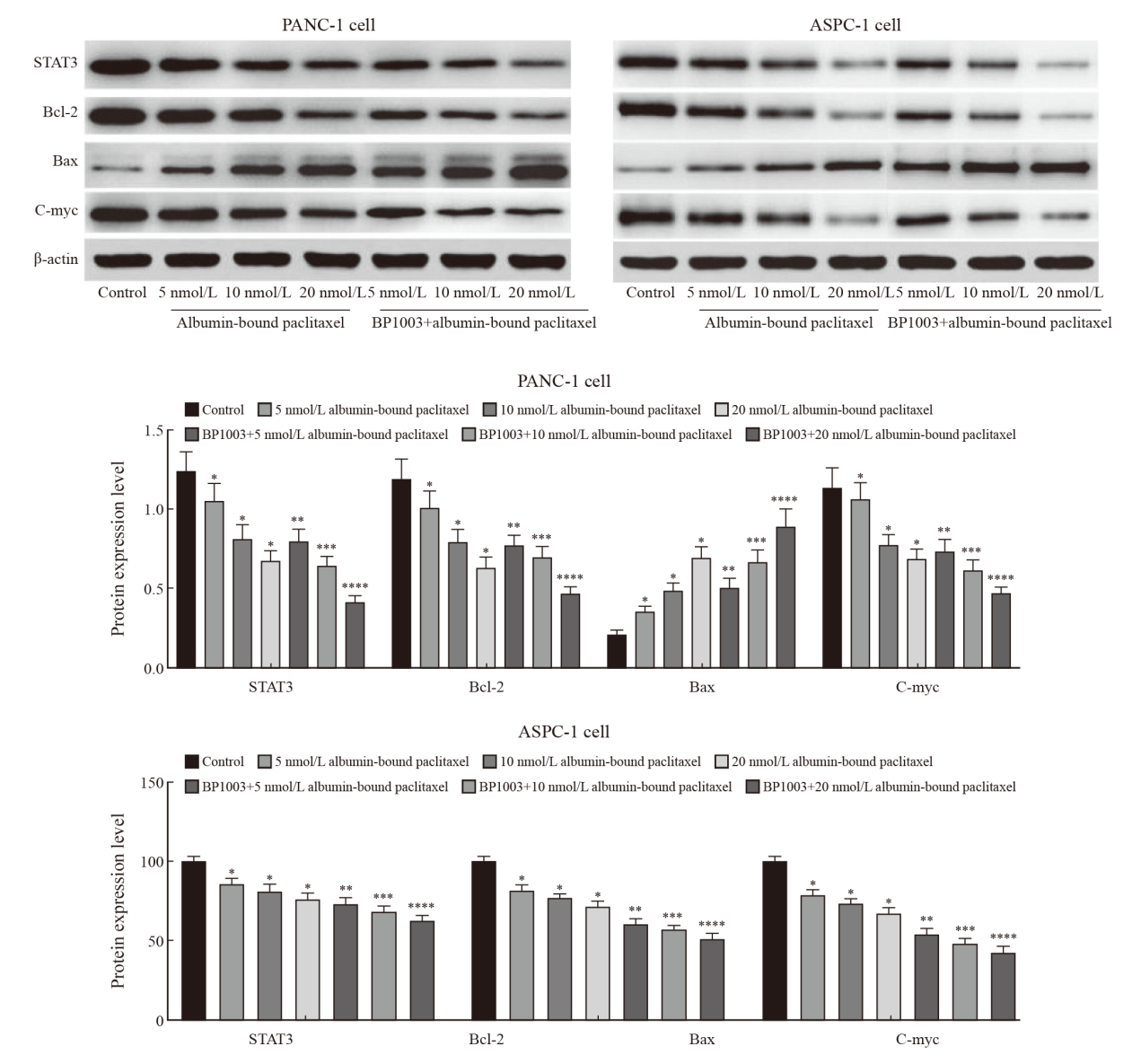
Fig. 7
Effect of BP1003 combined with albumin-bound paclitaxel on the expression of STAT3, Bcl-2, Bax and c-Myc in PANC-1 and ASPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells *: P<0.05, compared with control group; **: P<0.05, compared with 5 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ***: P<0.05, compared with 10 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel; ****: P<0.05, compared with 20 nmol/L albumin-bound paclitaxel."
| [1] |
HUANG J J, LOK V, NGAI C H, et al. Worldwide burden of, risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3): 744-754.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.007 pmid: 33058868 |
| [2] | 刘永鹏, 张晶晶, 任艳, 等. 1990—2019年中国胰腺癌疾病负担变化趋势研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(17): 3079-3085. |
| LIU Y P, ZHANG J J, REN Y, et al. Trends of disease burden of pancreatic cancer in China, 1990: 2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2022, 49(17): 3079-3085. | |
| [3] | BODEKER K L, SMITH B J, BERG D J, et al. A randomized trial of pharmacological ascorbate, gemcitabine, and nab-paclitaxel for metastatic pancreatic cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 77: 103375. |
| [4] | JIN M, LIU H L, XUE J, et al. Nab-paclitaxel plus S-1 versus nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a multicenter, randomized, phase II study[J]. Oncologist, 2024, 29(10): e1406-e1418. |
| [5] | BLASZCZAK W, WHITE B, MONTERISI S, et al. Dynamic IL-6R/STAT3 signaling leads to heterogeneity of metabolic phenotype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(1): 113612. |
| [6] | DING L Y, WANG Q W, MARTINCUKS A, et al. STING agonism overcomes STAT3-mediated immunosuppression and adaptive resistance to PARP inhibition in ovarian cancer[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2023, 11(1): e005627. |
| [7] | ZHU Z Y, XIANG Q, LI S Q, et al. Serine/threonine kinase 16 phosphorylates STAT3 and confers a JAK2-inhibition resistance phenotype in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 225: 116268. |
| [8] | GAGLIARDI M, KEAN R, DAI B B, et al. BP1003 decreases STAT3 expression and its pro-tumorigenic functions in solid tumors and the tumor microenvironment[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(8): 1901. |
| [9] | 李静, 王志芬, 张晓慧, 等. 阿帕替尼与白蛋白结合型紫杉醇在MDA-MB-231乳腺癌细胞系中的协同抗癌作用[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2021, 11(2): 90-98. |
| LI J, WANG Z F, ZHANG X H, et al. Synergistic anticancer effects of apatinib and nab-paclitaxel in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line[J]. Chin J Cell Stem Cell Electron Ed, 2021, 11(2): 90-98. | |
| [10] | AL-HETTY H R A K, ABDULAMEER S J, ALKUBAISY S A, et al. STAT3 signaling in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a candidate therapeutic target[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2023, 245: 154425. |
| [11] |
CHEN H, BIAN A W, YANG L F, et al. Targeting STAT3 by a small molecule suppresses pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(8): 1440-1457.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01626-z pmid: 33420372 |
| [12] | CHEN H, ZHOU W B, BIAN A W, et al. Selectively targeting STAT3 using a small molecule inhibitor is a potential therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 29(4): 815-830. |
| [13] | GUO H C, XIAO Y Y, YUAN Z W, et al. Inhibition of STAT3Y705 phosphorylation by stattic suppresses proliferation and induces mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 116. |
| [14] | HE Y, HAN P Y, CHEN C, et al. circPTPN22 attenuates immune microenvironment of pancreatic cancer via STAT3 acetylation[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2023, 30(4): 559-566. |
| [15] | HE Z W, WANG J, ZHU C H, et al. Exosome-derived FGD5-AS1 promotes tumor-associated macrophage M2 polarization-mediated pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and metastasis[J]. Cancer Lett, 2022, 548: 215751. |
| [16] | LIU H N, PAN D, YAO Z Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel combined with anlotinib and PD-1 inhibitors as a first-line treatment for advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 139: 112635. |
| [17] | GIORDANO G, MILELLA M, LANDRISCINA M, et al. Prognostic analysis and outcomes of metastatic pancreatic cancer patients receiving nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine as second or later-line treatment[J]. Cancer Med, 2024, 13(12): e7345. |
| [18] | AGOSTINI A, GUERRIERO I, PIRO G, et al. Talniflumate abrogates mucin immune suppressive barrier improving efficacy of gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel treatment in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 843. |
| [19] | UDDIN M H, AL-HALLAK M N, KHAN H Y, et al. Molecular analysis of XPO1 inhibitor and gemcitabine-nab-paclitaxel combination in KPC pancreatic cancer mouse model[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2023, 13(12): e1513. |
| [20] | VOISIN T, NICOLE P, GRATIO V, et al. The orexin-A/OX1R system induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells resistant to gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel treatment[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 904327. |
| [21] | OUYANG S M, LI H X, LOU L L, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102317. |
| [22] | SADRKHANLOO M, PASKEH M D A, HASHEMI M, et al. STAT3 signaling in prostate cancer progression and therapy resistance: an oncogenic pathway with diverse functions[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 158: 114168. |
| [23] | SINGH S, GOMEZ H J, THAKKAR S, et al. Overcoming acquired drug resistance to cancer therapies through targeted STAT3 inhibition[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(5): 4722. |
| [24] | HSIEH Y C, DAI Y C, CHENG K T, et al. Blockade of the SRC/STAT3/BCL-2 signaling axis sustains the cytotoxicity in human colorectal cancer cell lines induced by dehydroxyhispolon methyl ether[J]. Biomedicines, 2023, 11(9): 2530. |
| [25] | LIU J S, YEH C A, HUANG I C, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 mediates apoptosis inhibition through reducing mitochondrial ROS and activating Bcl-2 in gemcitabine-resistant lung cancer A549 cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(5): 3896-3905. |
| [26] | XIANG X X, YUAN D, LIU Y, et al. PIM1 overexpression in T-cell lymphomas protects tumor cells from apoptosis and confers doxorubicin resistance by upregulating c-myc expression[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2018, 50(8): 800-806. |
| [27] |
YU S, GONG L S, LI N F, et al. Galangin (GG) combined with cisplatin (DDP) to suppress human lung cancer by inhibition of STAT3-regulated NF-κB and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 97: 213-224.
doi: S0753-3322(17)32622-7 pmid: 29091869 |
| [1] | WANG Ting, QIN Yi, XU Xiaowu, YU Xianjun. New advances in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in 2024 [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 1-11. |
| [2] | Cancer Assessment Society of China Anti-Cancer Association, Cancer Pain Society of Fujian Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on whole-process management of oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 785-805. |
| [3] | CHEN Hong, CAO Zhiyun. Recent progress in the construction and application of patient-derived pancreatic cancer organoid models [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 590-597. |
| [4] | REN Jiaqiang, WU Shuai, SU Tong, LI Jie, HAN Liang, WU Zheng. An exploratory study of INPP4B, a biomarker of gemcitabine chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(12): 1090-1099. |
| [5] | TAN Xiaolang, YAO Sha, WANG Guihua, PENG Luogen. Research on uPAR promoting proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting autophagy via MAPK signaling [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 944-956. |
| [6] | LI Tianjiao, YE Longyun, JIN Kaizhou, WU Weiding, YU Xianjun. Advances in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(1): 1-12. |
| [7] | ZENG Cheng, ZHANG Jian. Leading research progress and prospect of antibody-drug conjugate in pancreatic cancer in 2022 [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 235-240. |
| [8] | FU Qingsheng, JIN Lei, ZHANG Xudong, XU Yingchen, ZHU Chunfu, QIN Xihu, WU Baoqiang. Effect of tRF-Pro-CGG on the biological behavior of mouse pancreatic cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 241-249. |
| [9] | YUE Ming, WANG Liwei, CUI Jiujie. Research progress on the mechanism of organ-specific lung metastasis in pancreatic cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(11): 1026-1031. |
| [10] | JIA Yuming, YE Zeng, DENG Yanli, LI Shengchao, ZHANG Zhilei, WANG Chao, XU Xiaowu, QIN Yi, PENG Li. The research on FBW7 gene enhances antitumor effect of paclitaxel on pancreatic cancer through GSDME-mediated pyroptosis [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(10): 889-897. |
| [11] | WANG Xu, CHENG He, LIU Chen, YU Xianjun. New progress in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in 2022 [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 1-13. |
| [12] | ZHUANG Han, LING Chifang, WANG Jiazhou, HAN Xu, JIANG Rui, HU Weigang. Radiation therapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer with 75 Gy simultaneous integrated boost: a dosimetric feasibility study [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 54-60. |
| [13] | LI Yujie, CHEN Hao. Potential of targeting TROP2 in the treatment of pancreatic cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 268-273. |
| [14] | WU Mengyin, WU Chunxiao, PANG Yi, WANG Chunfang, GU Kai, GONG Yangming, BAO Pingping, SHI Liang, DOU Jianming, XIANG Yongmei, SHI Yan. Incidence and mortality of pancreatic cancer in Shanghai 2016 and epidemic trend analysis from 2002 to 2016 [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(2): 97-105. |
| [15] | LUO Guopei, YU Xianjun. Precision therapy in pancreatic cancer: from streamlet towards mainstream [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(10): 960-970. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
