Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2024, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (11): 1020-1027.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.11.004
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Jiaxin( ), WEI Ran, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua(
), WEI Ran, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua( )
)
Received:2024-07-11
Revised:2024-11-07
Online:2024-11-30
Published:2024-12-11
Contact:
YU Baohua
Share article
CLC Number:
LIN Jiaxin, WEI Ran, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua. Clinicopathological analysis of adrenal intravascular large B-cell lymphoma[J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 1020-1027.
Tab. 1
Clinical characteristics of 5 adrenal IVLBCL patients"
| Characteristic | Gender, age/year | Initial clinical presentation | B symptoms | LDH/ (U·L-1) | Hormone | Location | Tumor size/mm | Treatment | Prognosis | OS/month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Male, 82 | None | No | 260 | ACTH increased, ALD and COR were normal | Bilateral | 64 | R-CHOP after needle biopsy | Partial remission | 30 |
| Case 2 | Male, 70 | Recurrent abdominal pain | No | 207 | ACTH, ALD and COR decreased | Bilateral | 67 | Resection only | Dead | 5 |
| Case 3 | Male, 68 | NA | NA | NA | NA | Right | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Case 4 | Male, 50 | Low-grade fever | Yes | 518 | ACTH, ALD and COR were normal | Bilateral | Adrenal masses | Resection+R-CHOP | Complete remission | 87 |
| Case 5 | Male, 54 | Low-grade fever | Yes | NA | NA | Bilateral | Adrenal masses | NA | NA | NA |
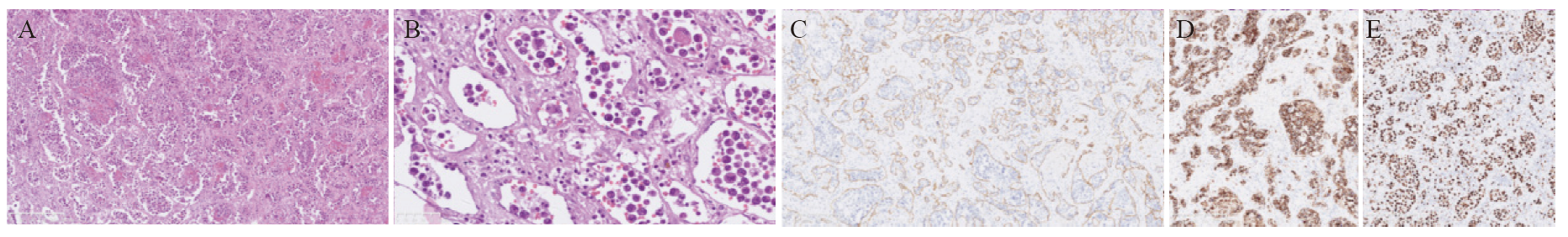
Fig. 1
Morphological and immunohistochemical features of adrenal IVLBCL A: Atypical lymphocytes were infiltrated in sheets or clusters (H-E, ×100); B: Atypical lymphoid cells were mainly large-sized with round or oval nuclei (H-E, ×400); C: CD34 highlighted the atypical cells confined to the vascular lumina (×100); D: The neoplastic cells stained positive for CD20 (×100); E: The Ki-67 proliferation index of neoplastic cells was very high (×100)."
Tab. 2
Immunophenotypes of 5 adrenal IVLBCL patients"
| Case | CD20 | PAX5 | CD3 | CD10 | BCL6 | MUM1 | BCL2 | MYC | CD5 | CD30 | Ki-67 proliferation index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | + | ND | - | - | - | + | 80%+ | 70%+ | weakly+ | ND | 90%+ |
| Case 2 | + | ND | - | - | + | + | 70%+ | 70%+ | - | - | 90%+ |
| Case 3 | + | + | - | - | + | + | ND | ND | ND | - | 90%+ |
| Case 4 | + | + | - | + | - | + | 80%+ | 50%+ | - | ND | 90%+ |
| Case 5 | + | ND | - | - | + | + | 90%+ | 40%-50%+ | - | - | 80%+ |
Tab. 3
Previous literature of adrenal IVLBCL"
| Literature | Gender, age/year | Initial clinical Presentation | LDH | Hormonal levels | Imaging test | Treatment | Prognosis | OS/month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiriakopoulos, et al[ | Male, 52 | Proximal muscle weakness | Normal | Normal | Left adrenal mass (80 mm) | Left adrenalectomy+6 cycles of R-CHOP | Complete remission | 72 |
| Fukushima, et al[ | Female, 66 | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss | Elevated LDH level | All adrenocortical hormones were at low level | Bilateral adrenal masses (left 50 mm, right 30 mm) | Bilateral adrenalectomy+10 cycles of CHOP | Recurrence with brain metastases | 6 |
| Yu, et al[ | Male, 55 | Conus medullaris-cauda equina syndrome | NA | NA | Increased uptake of the right adrenal gland | Two cycles of R-CHOP | Complete remission | 4 |
| Takahashi, et al[ | Female, 75 | Temporary chest pain | Slightly elevated LDH level and anemia | Normal | Left adrenal mass (35 mm) | Left adrenalectomy+8 cycles of R-CHOP | Complete remission | 12 |
| Li, et al[ | Male, 61 | None | Normal | NA | Bilateral adrenal masses (left 14 mm, right 15mm) | Left adrenalectomy | Complete remission | 35 |
| Cui, et al[ | Male, 61 | None (routine physical check-up) | Normal | NA | Bilateral adrenal masses | Left adrenalectomy+4 cycles of R-CHOP | Complete remission | 11 |
| Srivatsa, et al[ | Female, 43 | Flank pain | Normal | Normal | Left adrenal mass (65 mm×58 mm) | Left adrenalectomy+R-CHOP | Complete remission | 9 |
| Venizelos, et al[ | Male, 68 | Nausea, fever, diarrhoea and generalized pigmentation | Elevated LDH level | ACTH increased, ALD decreased | Bilateral adrenal masses (left 20 mm, right 50 mm) | Left adrenalectomy+2 cycles of CHOP | Dead | 7 |
| [1] |
LIU Z Y, ZHANG Y L, ZHU Y C, et al. Prognosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma (IVLBCL): analysis of 182 patients from global case series[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 10531-10540.
doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S267825 pmid: 33122951 |
| [2] | WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Haematolymphoid tumours (5th ed)[M]. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2024. |
| [3] |
HANS C P, WEISENBURGER D D, GREINER T C, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray[J]. Blood, 2004, 103(1): 275-282.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1545 pmid: 14504078 |
| [4] |
WAWIRE J, SAYED S, MOLOO Z, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Kenya: MYC, BCL2, and the cell of origin[J]. J Glob Oncol, 2019, 5: 1-8.
doi: 10.1200/JGO.18.00203 pmid: 31045473 |
| [5] | CAMPUZANO-ZULUAGA G, CIOFFI-LAVINA M, LOSSOS I S, et al. Frequency and extent of CD30 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its relation to clinical and biologic factors: a retrospective study of 167 cases[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2013, 54(11): 2405-2411. |
| [6] | SWERDLOW S H, CAMPO E, HARRIS N L, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumors of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues[M]. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2008. |
| [7] |
MURASE T, YAMAGUCHI M, SUZUKI R, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL): a clinicopathologic study of 96 cases with special reference to the immunophenotypic heterogeneity of CD5[J]. Blood, 2007, 109(2): 478-485.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-021253 pmid: 16985183 |
| [8] | 中华医学会血液学分会淋巴细胞疾病学组, 中国临床肿瘤学会CSCO淋巴瘤专家委员会. 血管内大B细胞淋巴瘤诊治中国专家共识(2023年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2023, 44(3): 177-181. |
| Lymphoid Disease Group, Chinese Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association; Lymphoma Expert Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology CSCO. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and management of intravascular large B cell lymphoma (2023)[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2023, 44(3): 177-181. | |
| [9] | MATSUE K, ABE Y, NARITA K, et al. Diagnosis of intravascular large B cell lymphoma: novel insights into clinicopathological features from 42 patients at a single institution over 20years[J]. Br J Haematol, 2019, 187(3): 328-336. |
| [10] | KIRIAKOPOULOS A, LINOS D. Intravascular B-large cell lymphoma: an unexpected diagnosis of an incidental adrenal mass[J]. J Surg Case Rep, 2019, 2019(2): rjz048. |
| [11] | FUKUSHIMA A, OKADA Y, TANIKAWA T, et al. Primary bilateral adrenal intravascular large B-cell lymphoma associated with adrenal failure[J]. Intern Med, 2003, 42(7): 609-614. |
| [12] | YU Y, GOVINDARAJAN R. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma presenting as an isolated cauda equina-conus medullaris syndrome-a case report[J]. J Spinal Cord Med, 2020, 43(4): 556-559. |
| [13] | TAKAHASHI Y, IIDA K, HINO Y, et al. Silent intravascular lymphoma initially manifesting as a unilateral adrenal incidentaloma[J]. Case Rep Med, 2012, 2012: 849285. |
| [14] |
LI W, LIN W, MA C, et al. A case of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in the left adrenal and another tumor in the right adrenal detected by (18)F-FDG PET/CT[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2016, 19(1): 57-59.
doi: 10.1967/s002449910342 pmid: 26929945 |
| [15] |
CUI J, LIU Q, CHENG Y X, et al. An intravascular large B-cell lymphoma with a t(3;14)(q27;q32) translocation[J]. J Clin Pathol, 2014, 67(3): 279-281.
doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201980 pmid: 24357441 |
| [16] |
SRIVATSA S, SHARMA J, LOGANI S. Intravascular lymphoma: an unusual diagnostic outcome of an incidentally detected adrenal mass[J]. Endocr Pract, 2008, 14(7): 884-888.
doi: 10.4158/EP.14.7.884 pmid: 18996818 |
| [17] |
VENIZELOS I, TAMIOLAKIS D, PETRAKIS G. High grade primary adrenal intravascular large B-cell lymphoma manifesting as Addison disease[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2007, 99(8): 471-474.
pmid: 18020866 |
| [18] |
ASKARIAN F, XU D S. Adrenal enlargement and insufficiency: a common presentation of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Am J Hematol, 2006, 81(6): 411-413.
pmid: 16680734 |
| [19] |
COLAVOLPE C, EBBO M, TROUSSE D, et al. FDG-PET/CT is a pivotal imaging modality to diagnose rare intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: case report and review of literature[J]. Hematol Oncol, 2015, 33(2): 99-109.
doi: 10.1002/hon.2140 pmid: 24850057 |
| [20] | SCHRADER A M R, JANSEN P M, WILLEMZE R, et al. High prevalence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2018, 131(18): 2086-2089. |
| [21] | BOONSAKAN P, IAMSUMANG W, CHANTRATHAMMACHART P, et al. Prognostic value of concurrent expression of C-MYC and BCL2 in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma: a 10-year retrospective study[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 1350820. |
| [22] | YEGAPPAN S, COUPLAND R, ARBER D A, et al. Angiotropic lymphoma: an immunophenotypically and clinically heterogeneous lymphoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2001, 14(11): 1147-1156. |
| [23] | YAMAGUCHI M, SETO M, OKAMOTO M, et al. De novo CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 109 patients[J]. Blood, 2002, 99(3): 815-821. |
| [24] |
GUPTA G K, JAFFE E S, PITTALUGA S. A study of PD-L1 expression in intravascular large B cell lymphoma: correlation with clinical and pathological features[J]. Histopathology, 2019, 75(2): 282-286.
doi: 10.1111/his.13870 pmid: 30938862 |
| [25] | SUEHARA Y, SAKATA-YANAGIMOTO M, HATTORI K, et al. Liquid biopsy for the identification of intravascular large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Haematologica, 2018, 103(6): e241-e244. |
| [26] |
SHIMADA K, YOSHIDA K, SUZUKI Y, et al. Frequent genetic alterations in immune checkpoint-related genes in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2021, 137(11): 1491-1502.
doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007245 pmid: 33512416 |
| [27] |
WILSON W H, YOUNG R M, SCHMITZ R, et al. Targeting B cell receptor signaling with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma[J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21(8): 922-926.
doi: 10.1038/nm.3884 pmid: 26193343 |
| [28] | XIE J L, SHEN X, SHI Q, et al. Clinical significance of MYD88 non-L265P mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Hematol Oncol, 2022, 40(5): 885-893. |
| [29] | JIANG S Y, QIN Y, GUI L, et al. Genomic alterations and MYD88MUT variant mapping in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and response to ibrutinib[J]. Target Oncol, 2020, 15(2): 221-230. |
| [30] |
ZENZ T, KREUZ M, FUGE, et al. TP53 mutation and survival in aggressive B cell lymphoma[J]. Int J Cancer, 2017, 141(7): 1381-1388.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.30838 pmid: 28614910 |
| [31] | JACOBS G, HELLMIG S, HUSE K, et al. Polymorphisms in the 3’-untranslated region of the CDH1 gene are a risk factor for primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Haematologica, 2011, 96(7): 987-995. |
| [32] | CARRERAS J, IKOMA H, KIKUTI Y Y, et al. Mutational, immune microenvironment, and clinicopathological profiles of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma with BCL6 rearrangement[J]. Virchows Arch, 2024, 484(4): 657-676. |
| [33] | DE MIRANDA N F, PENG R J, GEORGIOU K, et al. DNA repair genes are selectively mutated in diffuse large B cell lymphomas[J]. J Exp Med, 2013, 210(9): 1729-1742. |
| [34] | ZHANG Y, JIA C W, WANG W, et al. The interim analysis from a prospective single-center phase 2 study of zanubrutinib plus R-CHOP in treat-Naïve intravascular large B cell lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2021, 138(Supplement 1): 3563. |
| [35] | RAJYAGURU D J, BHASKAR C, BORGERT A J, et al. Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma in the United States (US): a population-based study using Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program and National Cancer Database[J]. Leuk Lymphoma, 2017, 58(9): 1-9. |
| [1] | JIANG Lili, MA Yan, ZHANG Tiantian, HUANG Shan. Clinical analysis of 21 cases of primary Ewing sarcoma of the thoracic wall [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(1): 74-81. |
| [2] | WEI Jing, HE Yaqi, XUE Tian, BAI Qianming, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua. Clinicopathological analysis of DLBCL/HGBL with MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 gene rearrangement [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 809-817. |
| [3] | ING Ping’an, YANG Peigang, TIAN Yuan, LIN Yecheng, LIU Yang, GUO Honghai, ZHANG Zhidong, WANG Dong, LI Yong, ZHAO Qun. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis analysis of gastric cancer patients with elevated serum alpha- fetoprotein [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(11): 887-896. |
| [4] | WEN Duo, LIU Wanlin, CAO Yiming, QU Ning, ZHU Yongxue. The expressions of cortactin and N-WASP in thyroid papillary carcinoma and their significance [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(9): 688-692. |
| [5] | YU Baohua, XUE Tian, ZHANG Yan, et al. MYD88 gene mutation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its clinicopathological relevance [J]. China Oncology, 2018, 28(9): 679-685. |
| [6] | SHENG Dong, WANG Weige, JIANG Xiangnan, et al. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia: a clinicopathological study of 10 cases with detection of MYD88 L265P mutation [J]. China Oncology, 2018, 28(12): 900-905. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
