Welcome to China Oncology,
|
||
|
Screening recurrent glioblastoma-related genes and analyzing their gene expressions in association with clinicopathological parameters and prognosis
China Oncology
2022, 32 (1):
13-23.
DOI: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.01.002
Background and purpose: Glioma is the most common and malignant primary brain tumor in the central nervous system (CNS). Glioblastoma is highly malignant and aggressive, and the prognosis of patients with recurrent glioblastoma is very poor. This study aimed to screen the genes related to the recurrent glioblastoma, and analyze the relationship between their expressions, clinicopathological parameters and prognosis in glioma. Methods: By mining the relevant datasets of the primary and recurrent cases of glioblastoma in the GEO database, the differentially expressed gene (DEG) in the samples of primary and recurrent glioblastomas were screened and analyzed. All DEGs analyses were carried out in ontology function and pathway enrichment. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed and used for screening Hub gene. Key genes were intersected by PPI network and Venn diagram, and the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) and Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA) database were analyzed for association of key gene expressions and survival status. Key genes were furtherly analyzed to determine the relationship between their expressions and clinicopathological parameters of glioma. Results: There were 40 DEG screened in the dataset GSE62153, including 34 up-regulated genes and 6 down-regulated genes. There were 19 DEG screened in the dataset GSE58399, including 16 up-regulated genes and 3 down-regulated genes. Go functional analyses showed that the DEG of GSE62153 were mainly involved in 11 physiological processes, such as central nervous system development, myelin sheath, actin binding, central nervous system myelination. The DEG of GSE58399 were mainly enriched in the positive regulation of epithelial cell migration. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment showed that the datasets GSE62153 and GSE58399 were both enriched in histidine metabolism. By using the STRING database, the core of PPI network was constructed with 20 protein molecules. A total of 10 hub genes were screened, including MOBP, OPALIN, ERMN, PLP1, MOG, CLDN11, ASPA, TMEM125, KLK6 and NKX6-2 gene. The key genes for recurrent glioblastoma were ERMN, MOG and MOBP gene. Based on analyses using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and CGGA databases, the prognosis of patients with high expressions of ERMN, MOG and MOBP was favorable compared with the low expression group. The expression levels of key genes in glioblastoma were lower compared with the control tissues (P<0.001). There were significant differences in the expressions of ERMN, MOG and MOBP gene among different World Health Organization (WHO) grades (WHO Ⅱ, Ⅲ and Ⅳ) (P<0.001). As the grade of glioblastoma increased, the expressions of ERMN, MOG and MOBP were decreased gradually. The expressions of ERMN, MOG and MOBP gene were correlated with WHO classification, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) status and clinicopathological characteristics (P<0.001). The expression of MOBP gene was correlated with age (P<0.001) and MGMT methylation status (P=0.022). Conclusion: ERMN, MOG and MOBP gene may function as tumor suppressor genes and participate in the recurrence of glioblastoma. The histidine metabolism pathway may be related to the sensitivity of methotrexate treatment. 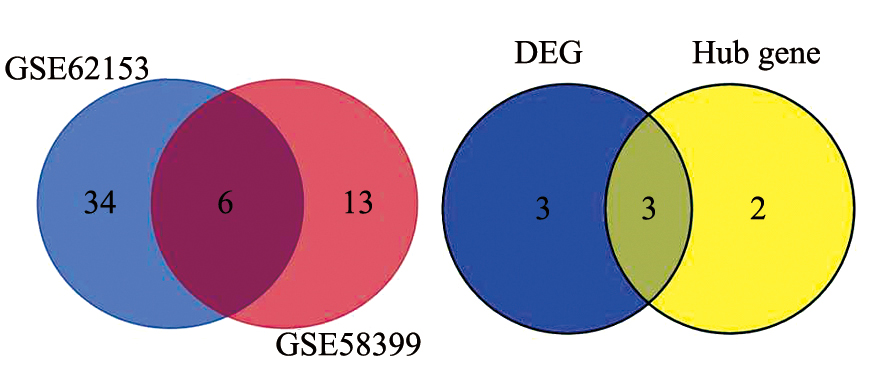
Fig. 4
Venn diagram of DEG and Hub gene
Extracts from the Article
脑胶质瘤是常见的中枢神经系统原发性恶性脑肿瘤之一,约占原发性脑肿瘤的30%,原发恶性脑肿瘤的80%[1]。高级别脑胶质瘤[世界卫生组织(World Health Organization,WHO) Ⅲ~Ⅳ级]恶性程度高、侵袭性强,尤其胶质母细胞瘤患者中位总生存期为12~15个月,容易复发,复发后患者的中位总生存期为3~6个月[2-3]。因此,胶质母细胞瘤复发是临床棘手的问题。突破的关键在于深入探究胶质母细胞瘤的发生、发展机制,寻找复发相关的分子标志物,针对相关靶点进行转化研究。在神经肿瘤领域,基因表达谱数据动态分析(Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis,GEPIA)和中国脑胶质瘤基因组图谱(Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas,CGGA)数据库已经实现数据公开,为胶质瘤相关的标志物研究提供了新的途径[4-5]。本研究通过对GEO、癌症基因组图谱(The Cancer Genome Atlas,TCGA)和CGGA等公共数据库进行挖掘,筛选胶质母细胞瘤复发相关基因,并分析表达、临床病理学参数及临床预后的关系。
PPI网络构建基于GSE62153和GSE58399筛选出来的DEG,通过STRING数据库,获得PPI网络,共有20个蛋白分子构建成为核心相互作用网络,相关基因为MOG、ASPA、ERMN、PTGDS、MOBP、CLDN11、NKX6-2、CNDP1、SH3GL2、OPALIN、KLK6、MYBPC1、SH3GL3、PLP1、TMEM125、AKR1C3、CARNS1、HLA-DPA1、HHATL和SEPP1基因(图2)。而后利用Cytscape软件对构建的PPI网络进行分析和Hub基因挖掘,结果筛选出10个Hub基因,分别为MOBP、OPALIN、ERMN、PLP1、MOG、CLDN11、ASPA、TMEM125、KLK6和NKX6-2基因(图3)。为进一步获得胶质母细胞瘤复发的关键核心基因,通过Venn图工具取出GSE62153和GSE58399芯片的DEG的交集,结果提示共有6个DEG(图4)。最后再选择排名前5的Hub基因与GSE62153和GSE58399筛选出来的DEG取交集,结果提示共有3个基因,分别为ERMN、MOG和MOBP基因。
Other Images/Table from this Article
|