Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 726-739.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.08.002
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Yang1( ), WANG Lian2, ZHAO Meng2, ZHANG Xiaofeng3, GENG Zhijun3, WANG Yueyue3,4, SONG Xue3, ZUO Lugen2,4, LI Jing3,4, HU Jianguo3,4(
), WANG Lian2, ZHAO Meng2, ZHANG Xiaofeng3, GENG Zhijun3, WANG Yueyue3,4, SONG Xue3, ZUO Lugen2,4, LI Jing3,4, HU Jianguo3,4( )
)
Received:2023-03-21
Revised:2023-08-07
Online:2023-08-30
Published:2023-09-01
Contact:
HU Jianguo
Share article
CLC Number:
SUN Yang, WANG Lian, ZHAO Meng, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, WANG Yueyue, SONG Xue, ZUO Lugen, LI Jing, HU Jianguo. The prognostic value of high expression of FKBP1A in gastric cancer and the regulatory effect of targeted PI3K/AKT on glucose metabolism[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 726-739.
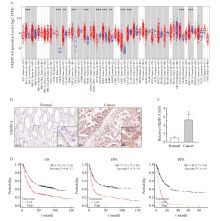
Fig. 1
FKBP1A is highly expressed in gastric cancer and is associated with poor prognosis A: TIMER 2.0 database analysis of FKBP1A expression difference between cancer tissue and normal tissue; B-C: Immunohistochemical staining of FKBP1A in gastric cancer tissue and the adjacent tissue (×100); D: Kaplan-Meier Plotter database analysis of the correlation between FKBP1A and total survival of gastric cancer patients. *: P<0.05, compared with normal tissues."
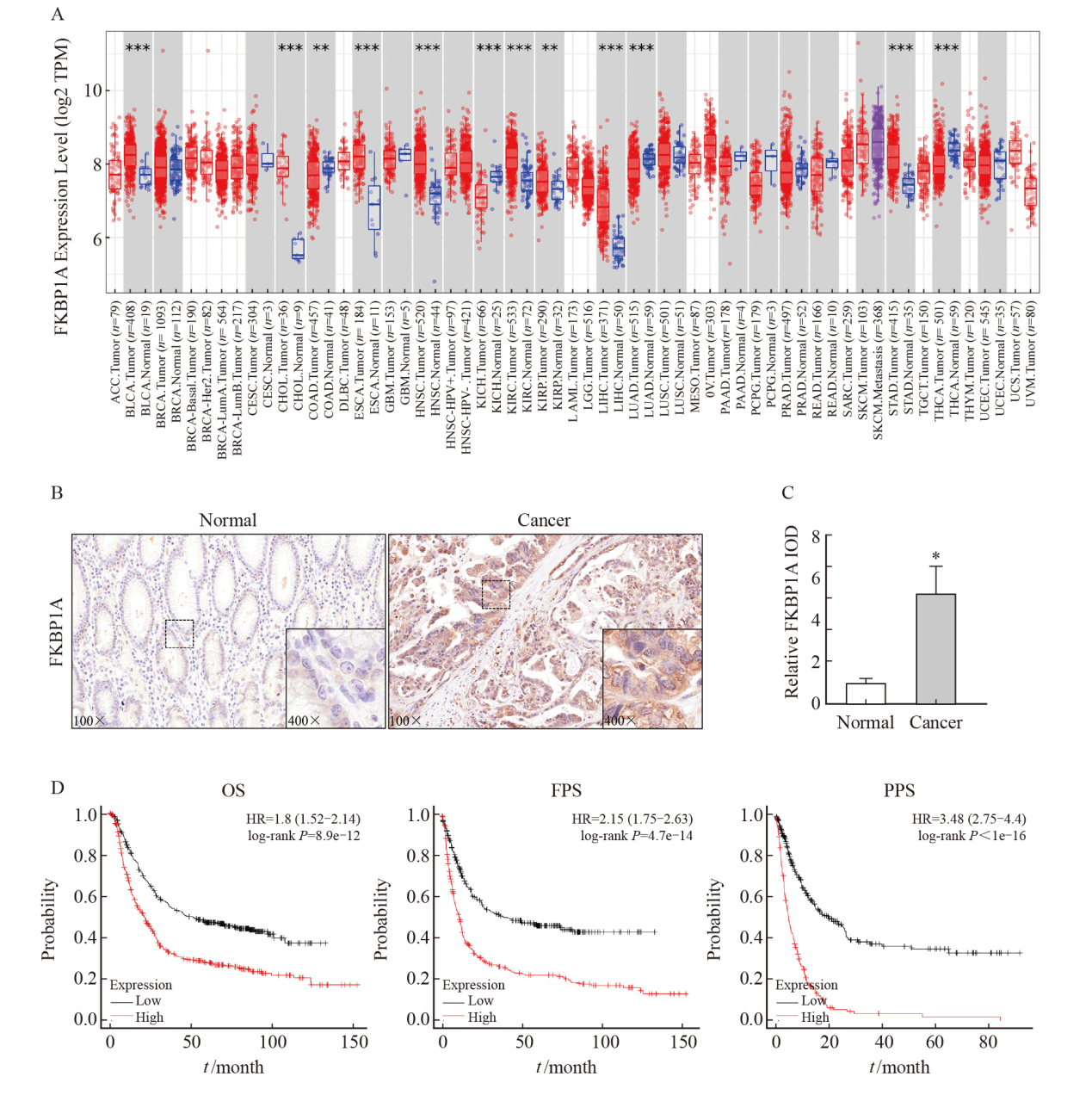
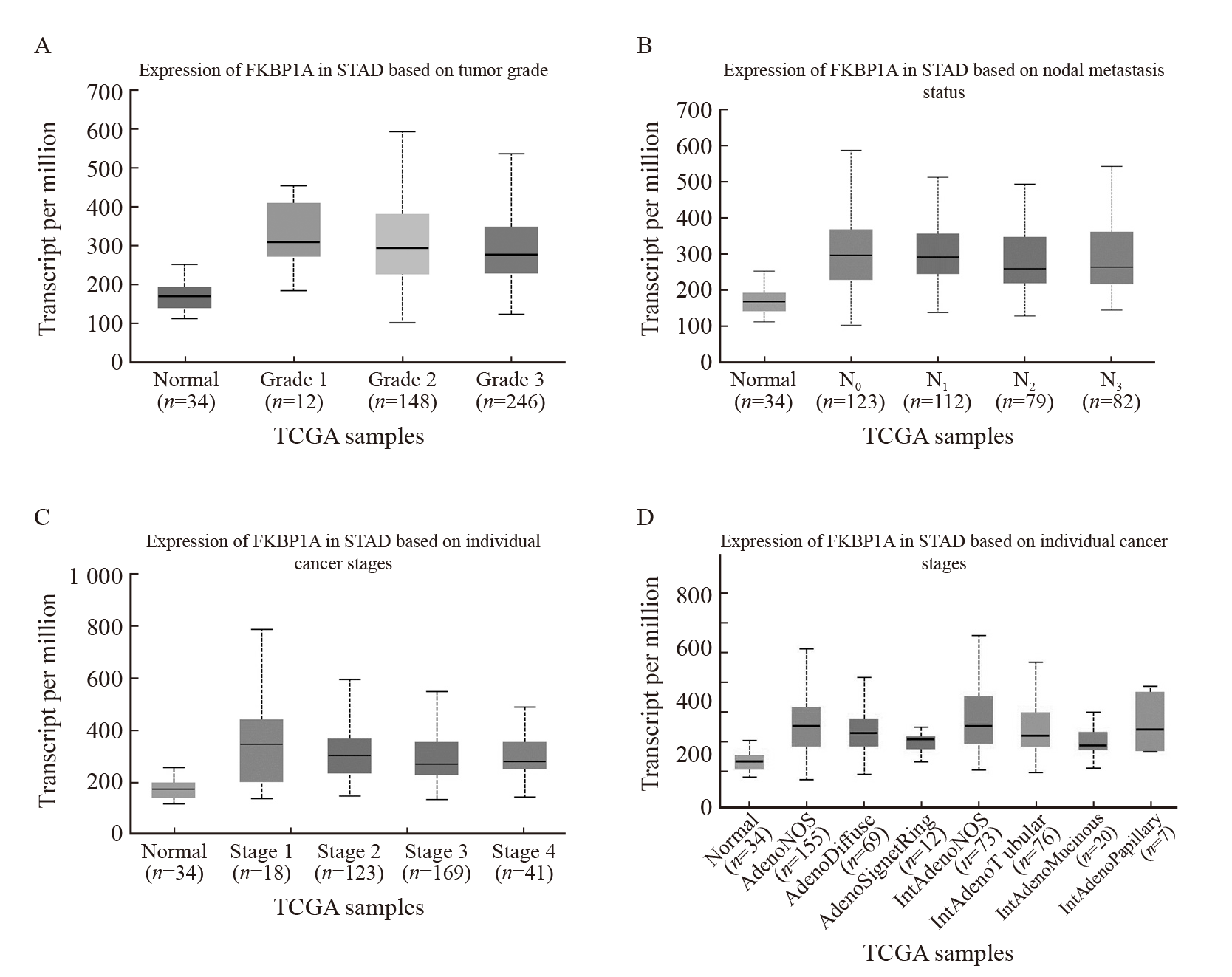
Fig. 2
The relationship between FKBP1A expression and clinicopathologic parameters in gastric cancer A-B: UALCAN database analysis showed that the expression level of FKBP1A was correlated with tumor grade and stage; C-D: Lymph node metastasis and histological type in patients with gastric cancer."
Tab. 1
Relationship between the expression of FKBP1A and clinicopathological parameters of gastric cancer patients"
| Characteristic | Case n | FKBP1A n(%) | χ2 | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low expression (n=54) | High expression (n=53) | ||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 82 | 39 (47.6) | 43 (52.4) | 1.186 | 0.276 |
| Female | 25 | 15 (60.0) | 10 (40.0) | ||
| Age/year | |||||
| <60 | 35 | 17 (48.6) | 18 (51.4) | 0.075 | 0.784 |
| ≥60 | 72 | 37 (51.4) | 35 (48.6) | ||
| CEA/(μg·L-1) | |||||
| <5 | 48 | 31 (64.6) | 17 (35.4) | 6.939 | 0.008 |
| ≥5 | 59 | 23 (39.0) | 36 (61.0) | ||
| CA19-9/(kU·L-1) | |||||
| <37 | 51 | 38 (74.5) | 13 (25.5) | 22.533 | <0.001 |
| ≥37 | 56 | 16 (28.6) | 40 (71.4) | ||
| Tumor size D/cm | |||||
| <5 | 48 | 28 (58.3) | 20 (41.7) | 2.155 | 0.142 |
| ≥5 | 59 | 26 (44.1) | 33 (55.9) | ||
| Histological type | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 80 | 42 (52.5) | 38 (47.5) | 0.524 | 0.469 |
| Other | 27 | 12 (44.4) | 15 (55.6) | ||
| Pathological grading | |||||
| G1-G2 | 54 | 27 (50.0) | 27 (50.0) | 0.010 | 0.922 |
| G3-G4 | 53 | 27 (50.9) | 26 (49.1) | ||
| T stage | |||||
| T1-T2 | 54 | 36 (66.7) | 18 (33.3) | 11.444 | <0.001 |
| T3-T4 | 53 | 18 (34.0) | 35 (66.0) | ||
| N stage | |||||
| N0-N1 | 62 | 41 (66.1) | 21 (33.9) | 14.466 | <0.001 |
| N2-N3 | 45 | 13 (28.9) | 32 (71.1) | ||
Tab. 2
Prognosis factors affecting 5-year OS rate after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer"
| Characteristic | Univariate analysis | Multivariabale analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log-rank χ2 | P value | HR | 95% CI | P value | ||
| Gender (male vs female) | 0.017 | 0.898 | - | - | - | |
| Age (<60 years vs ≥60 years) | 0.468 | 0.494 | - | - | - | |
| FKBP1A expression (high vs low) | 44.469 | <0.001 | 3.342 | 1.617-6.909 | 0.001 | |
| CEA (<5 μg/L vs ≥5 μg/L) | 17.172 | <0.001 | 1.958 | 1.007-3.806 | 0.048 | |
| CA19-9 (<37 kU/L vs ≥37 kU/L) | 25.458 | <0.001 | 2.728 | 1.439-5.170 | 0.002 | |
| Tumor size (<5 cm vs ≥5 cm) | 0.005 | 0.944 | - | - | - | |
| Histological type (STAD vs other) | 1.764 | 0.184 | - | - | - | |
| Pathological grading (G1-G2 vs G3-G4) | 0.466 | 0.495 | - | - | - | |
| T stage (T1-T2 vs T3-T4) | 20.419 | <0.001 | 1.889 | 1.019-3.503 | 0.043 | |
| N stage (N0-N1 vs N2-N3) | 29.513 | <0.001 | 2.119 | 1.116-4.023 | 0.022 | |
Fig. 6
FKBP1A promotes glucose metabolism in gastric cancer cells A-B: Expression of FKBP1A after lentivirus transfection; C-E: Glucose consumption, lactic acid and pyruvate production of MGC803; F-G: Western blot detection of glucose metabolism related protein expression. *: P<0.05, compared with control group."
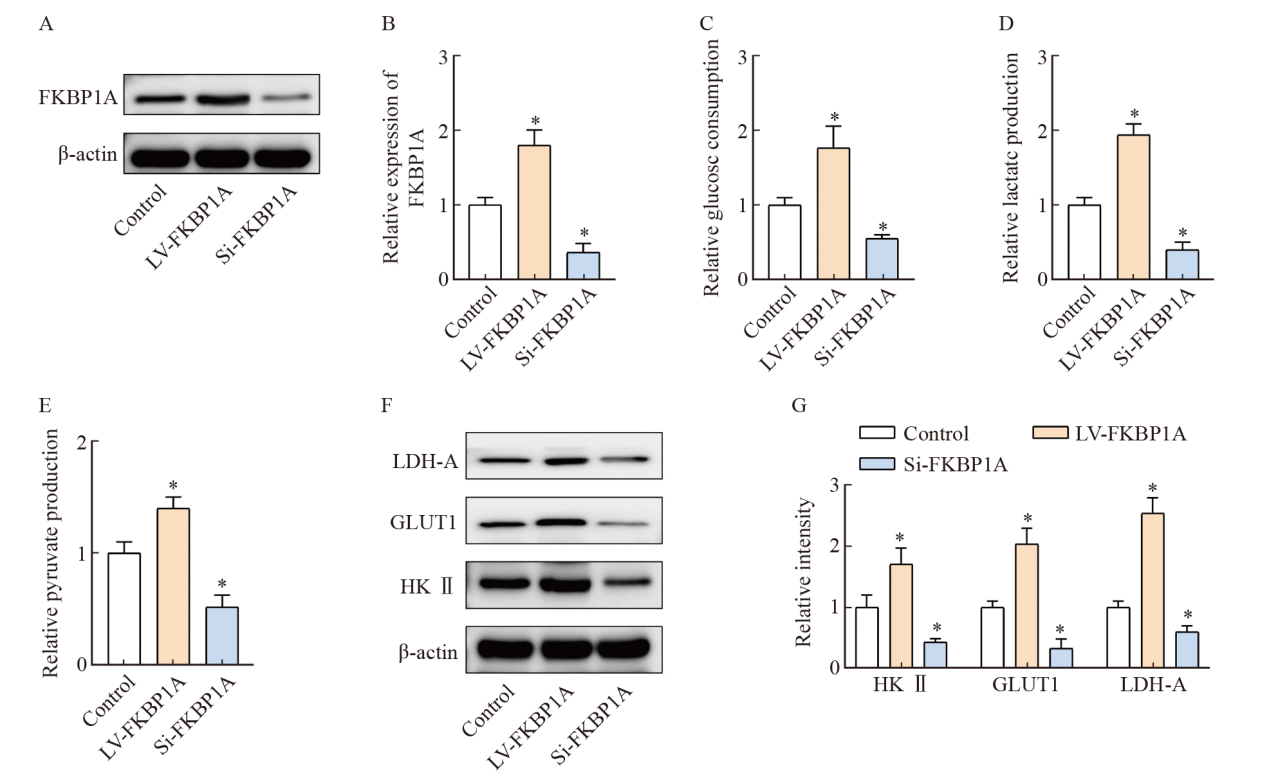
Fig. 7
FKBP1A promotes malignant biological behavior of MGC803 cells A-C: Transwell invasion assay was performed to determine the invasion and migration ability of each group for 48 h; D: Cell viability was assessed using a CCK-8 assay in MGC803 for 48 h; E-F: Detection of tumor volume size in each group. *: P<0.05, compared with control group."
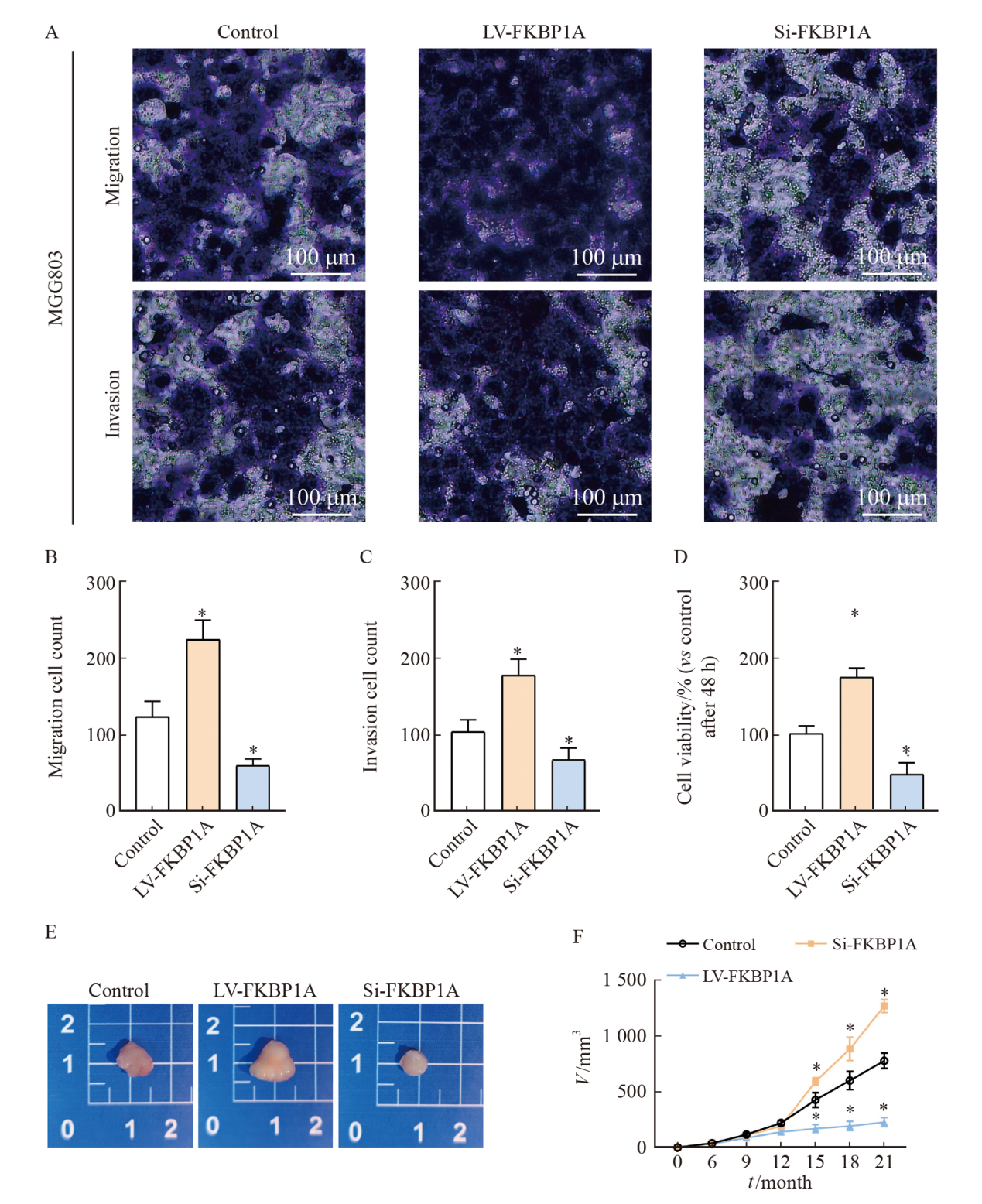
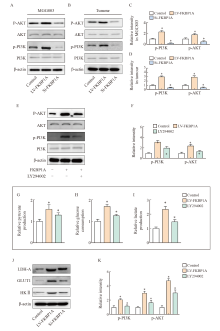
Fig. 8
FKBP1A activated PI3K/AKT signal pathway to promote glucose metabolism A-D: Detection of phosphorylation expression of PI3K and AKT by Western blot in vitro and in vivo; E-F: Western blot detection of the expression levels of AKT and PI3K after intervention with PI3K inhibitors; G-I: Glucose consumption, lactic acid and pyruvate production of MGC803; J-K: Western blot detection of glucose metabolism related protein expression. *: P<0.05, compared with control group."
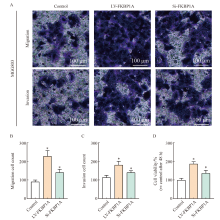
Fig. 9
FKBP1A activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote malignant biological behavior in MGC803 cells A-C: Transwell invasion assay was performed to determine the invasion and migration ability of each group for 48 h; D: Cell viability was assessed using a CCK-8 assay in MGC803 for 48h. *: P<0.05, compared with control group."
| [1] |
RIZZO A, RACCA M, GARROU F, et al. Diagnostic performance of positron emission tomography with fibroblast-activating protein inhibitors in gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(12): 10136.
doi: 10.3390/ijms241210136 |
| [2] |
YU H, ZHAO K, ZENG H, et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase WTAP accelerates the Warburg effect of gastric cancer through regulating HK2 stability[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 133: 111075.
doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111075 |
| [3] |
ZHAO M Y, WEI F, SUN G W, et al. Natural compounds targeting glycolysis as promising therapeutics for gastric cancer: a review[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1004383.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1004383 |
| [4] |
ZHONG X Y, HE X F, WANG Y X, et al. Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: the emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic implications[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15(1): 160.
doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01358-5 |
| [5] | HOU H, LYU Y L, JIANG J, et al. Peripheral blood transcriptome identifies high-risk benign and malignant breast lesions[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(6): e0233713. |
| [6] | LIU Z, ZHANG K, ZHAO Z, et al. Prognosis-related autophagy genes in female lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(1): e28500. |
| [7] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG D, LV J, et al. LncRNA SNHG15 acts as an oncogene in prostate cancer by regulating miR-338-3p/FKBP1A axis[J]. Gene, 2019, 705: 44-50.
doi: S0378-1119(19)30386-5 pmid: 30981837 |
| [8] | WANG G, ZHAO H, DUAN X, et al. CircRNA pappalysin 1 facilitates prostate cancer development through miR-515-5p/FKBP1A axis[J]. Andrologia, 2021, 53(11): e14227. |
| [9] |
FU L S, WANG X Y, YANG Y, et al. Septin11 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility by activating RhoA to regulate cytoskeleton and cell adhesion[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(4): 280.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05726-y pmid: 37080972 |
| [10] |
BIE Q L, SUN C X, GONG A H, et al. Non-tumor tissue derived interleukin-17B activates IL-17RB/AKT/β-catenin pathway to enhance the stemness of gastric cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 25447.
doi: 10.1038/srep25447 pmid: 27146881 |
| [11] |
HOXHAJ G, MANNING B D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(2): 74-88.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0216-7 pmid: 31686003 |
| [12] |
LI Z G, CUI Y, DUAN Q C, et al. The prognostic significance of FKBP1A and its related immune infiltration in liver hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21): 12797.
doi: 10.3390/ijms232112797 |
| [13] |
LENG W, LIU Q, ZHANG S, et al. LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 modulates the sensitivity of paclitaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells to paclitaxel via miR-195-5p/FKBP1A axis[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2020, 21(11): 1072-1080.
doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1829266 pmid: 33138677 |
| [14] |
PATEL D, DABHI A M, DMELLO C, et al. FKBP1A upregulation correlates with poor prognosis and increased metastatic potential of HNSCC[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2022, 46(3): 443-453.
doi: 10.1002/cbin.v46.3 |
| [15] |
DARANG E, PEZESHKIAN Z, MIRHOSEINI S Z, et al. Bioinformatics and pathway enrichment analysis identified hub genes and potential biomarker for gastric cancer prognosis[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1187521.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1187521 |
| [16] |
TANG J, ZHANG C, LIN J, et al. ALOX5-5-HETE promotes gastric cancer growth and alleviates chemotherapy toxicity via MEK/ERK activation[J]. Cancer Med, 2021, 10(15): 5246-5255.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.v10.15 |
| [17] |
XU T P, YU T, XIE M Y, et al. LOC101929709 promotes gastric cancer progression by aiding LIN28B to stabilize c-MYC mRNA[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2023, 26(2): 169-186.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-022-01348-z |
| [18] |
ZHOU Y, GU H J, SHAO B F, et al. Glycolysis-related gene dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase promotes poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through the Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(22): 1240.
doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5272 pmid: 36544660 |
| [19] |
CHENG J, HUANG Y, ZHANG X H, et al. TRIM21 and PHLDA3 negatively regulate the crosstalk between the PI3K/AKT pathway and PPP metabolism[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1880.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15819-3 pmid: 32312982 |
| [20] |
LI Z, JIANG Y, LIU J, et al. Exosomes from PYCR1 knockdown bone marrow mesenchymal stem inhibits aerobic glycolysis and the growth of bladder cancer cells via regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(1): 84.
doi: 10.3892/ijo |
| [21] | WANG Y Y, ZHOU Y Q, XIE J X, et al. MAOA suppresses the growth of gastric cancer by interacting with NDRG1 and regulating the Warburg effect through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2023. Online ahead of print. |
| [22] |
YE W, SHI Z H, ZHOU Y L, et al. Autophagy-related signatures as prognostic indicators for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 654449.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.654449 |
| [23] |
JIN G, LV J, YANG M, et al. Genetic risk, incident gastric cancer, and healthy lifestyle: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies and prospective cohort study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(10): 1378-1386.
doi: S1470-2045(20)30460-5 pmid: 33002439 |
| [1] | WU Wen, ZHANG Ruoxin, WENG Junyong, MA Yanlei, CAI Guoxiang, LI Xinxiang, YANG Yongzhi. Exploring the prognostic value of positive lymph node ratio in stage Ⅲ colorectal cancer patients and establishing a predictive model [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 873-880. |
| [2] | XIAO Feng, XU Tonglin, ZHU Lin, XIAO Jingwen, WU Tianqi, GU Chunyan. Significance of infiltration of M1 tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 726-733. |
| [3] | LIU Shuai, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Xiaoqing, LUAN Wei. An exploratory study on the perioperative treatment of locally advanced gastric cancer with combination of penpulimab, anlotinib and chemotherapy [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 659-668. |
| [4] | ZHANG Ruoxin, YE Zilan, WENG Junyong, LI Xinxiang. Correlation study between advanced age and inferior prognosis in stage Ⅱ colorectal cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 485-492. |
| [5] | WANG Fei, LIU Pei, HU Nan. Effect of bevacizumab assisted PD-1 inhibitor on serum miR-20a-5p and miR-515-3p in the treatment of gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 493-500. |
| [6] | Professional Committee on Gastric Cancer of Shanghai Anticancer Association , Professional Committee on Gastrointestinal Cancer of China Association for Promotion of Health Science and Technology . Chinese expert consensus on clinical practice of locally advanced gastric cancer invading adjacent organs (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 517-526. |
| [7] | XU Yonghu, XU Dazhi. Progress and prospects of gastric cancer treatment in the 21st century [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 239-249. |
| [8] | WANG Xuefei, ZHOU Peng, TANG Zhaoqing. New progress and development trend of surgical treatment for gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 250-258. |
| [9] | XUE Chi, GAO Peng, ZHU Zhi, WANG Zhenning. Application and challenge of immunotherapy in perioperative therapy of gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 259-267. |
| [10] | SHEN Jie, WANG Jiangli, WANG Zezhou, MO Miao, ZHOU Changming, YUAN Jing, XU Dazhi, ZHENG Ying. Survival analysis of 6 737 surgically resected gastric cancer cases in China from a large single institution hospital-based cancer registry database [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 268-277. |
| [11] | LI Jing, ZHENG Lei, GAO Yu. Analysis of effects of trastuzumab assisted modified DOF fortnightly regimen on serum tumor markers and survival rate in patients with cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 286-292. |
| [12] | FENG Huizhi, LIU Jingmei, BU Xiaoqian. A retrospective study of pembrolizumab combined with XELOX regimen in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 1028-1035. |
| [13] | LI Jun, LU Tingwei, FANG Xuqian. Impact of MSI-H/dMMR on clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of patients with BRAF V600E-mutated resectable colorectal cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 1061-1066. |
| [14] | JIN Yizi, LIN Mingxi, ZHANG Jian. Receptor discordance between primary breast cancer and liver metastases [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 834-843. |
| [15] | WU Han, YANG Zhangru, FENG Wen, ZENG Wanqin, GUO Jindong, LI Hongxuan, WANG Changlu, WANG Jiaming, LÜ Changxing, ZHANG Qin, YU Wen, CAI Xuwei, FU Xiaolong. The efficacy and prognosis analysis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for multiple primary early-stage lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 844-856. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
