Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (11): 1032-1040.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.11.009
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAI Haihui1,2( ), LIU Yuanqi1,2, ZHANG Congzheng1,2, GUAN Liping1,2, HAN Tao1(
), LIU Yuanqi1,2, ZHANG Congzheng1,2, GUAN Liping1,2, HAN Tao1( )
)
Received:2023-08-09
Revised:2023-10-17
Online:2023-11-30
Published:2023-12-14
Share article
CLC Number:
ZHAI Haihui, LIU Yuanqi, ZHANG Congzheng, GUAN Liping, HAN Tao. The latest research progress on P53 and tumor metabolism[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(11): 1032-1040.
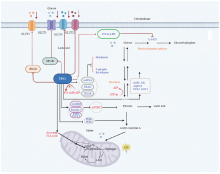
Fig. 1
P53 regulates the glucose metabolism The P53 regulates the transcription of RRAD to inhibit GLUT1 translocation to the plasma membrane or limit the activation of PON2 and NF-κB to downregulate GLUT1 and GLUT3, respectively; P53 can also directly inhibit GLUT 4 and GLUT12 expression to reduce glucose transmembrane transport. Moreover, P53 inhibits glycolysis and thus cancer cell growth through various ways. TIGAR: TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; G6PC: Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic; GK: Glycerokinase; AQP3/9: Aquaporin 3/9; PCK2: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 2; PDK: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase; AMPKβ: AMP-activated protein kinase β; Sestrin1/2: Antioxidant genes 1/2; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten; TSC1/2: Tuberous sclerosis complex 1/2; IDH1: Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; TCG cycle: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; α-KG: α-Ketoglutarate; G-6-PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; P53/G-6-PD: Combination of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and P53."
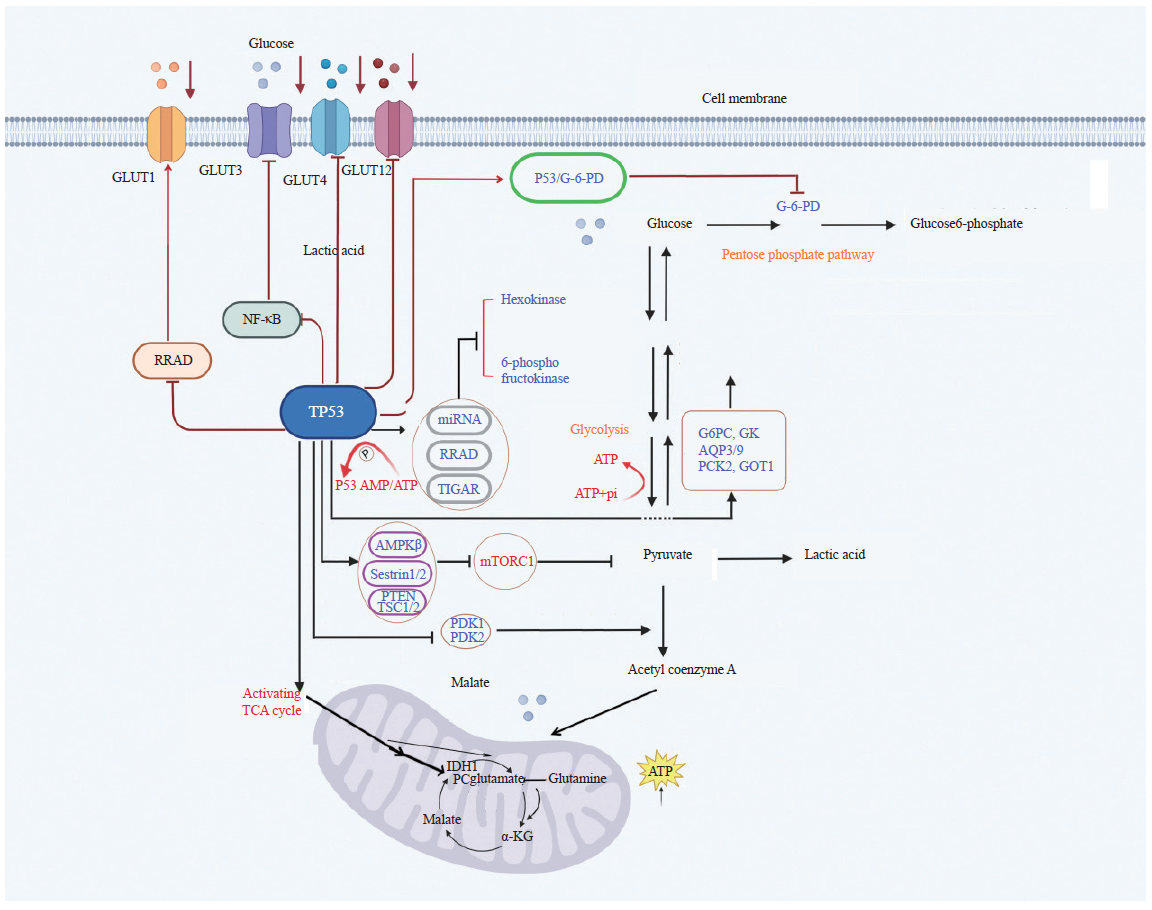
Fig. 2
P53 regulates lipid synthesis and metabolism in tumor cells A: P53 regulates lipid synthesis; B: P53 regulates lipid metabolism. P53 suppresses adipose differentiation and adipogenesis in tumor cells. P53 promotes FAO by activating MLYCD and PANK 1. P53 promotes FAO by activating MLYCD and PANK 1. P53 suppresses sphingosine kinases 1 to regulate S1P metabolism. Lipin 1: Homo sapiens lipin 1."

| [1] |
LACROIX M, RISCAL R, ARENA G, et al. Metabolic functions of the tumor suppressor p53: implications in normal physiology, metabolic disorders, and cancer[J]. Mol Metab, 2020, 33: 2-22.
doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.10.002 |
| [2] |
MAO Y, JIANG P. The crisscross between p53 and metabolism in cancer[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2023, 55(6): 914-922.
doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023109 |
| [3] |
FU X, WU S, LI B, et al. Functions of p53 in pluripotent stem cells[J]. Protein Cell, 2020, 11(1): 71-78.
doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-00665-x |
| [4] |
ZAFAR A, KHAN M J, NAEEM A. MDM2- an indispensable player in tumorigenesis[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2023, 50(8): 6871-6883.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08512-3 pmid: 37314603 |
| [5] |
HOU Y C, ZHANG X T, YAO H, et al. METTL14 modulates glycolysis to inhibit colorectal tumorigenesis in p53-wild-type cells[J]. EMBO Rep, 2023, 24(4): e56325.
doi: 10.15252/embr.202256325 |
| [6] |
MARCUCCI F, RUMIO C. On the role of glycolysis in early tumorigenesis-permissive and executioner effects[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(8): 1124.
doi: 10.3390/cells12081124 |
| [7] | SHEN J Z, WANG Q R, MAO Y N, et al. Targeting the p53 signaling pathway in cancers: molecular mechanisms and clinical studies[J]. MedComm (2020), 2023, 4(3): e288. |
| [8] |
WHITT A G, NEELY A M, SARKAR O S, et al. Paraoxonase 2 (PON2) plays a limited role in murine lung tumorigenesis[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 9929.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37146-5 pmid: 37337025 |
| [9] |
KLEINEHR J, SCHÖFBÄNKER M, DANIEL K, et al. Glycolytic interference blocks influenza A virus propagation by impairing viral polymerase-driven synthesis of genomic vRNA[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2023, 19(7): e1010986.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010986 |
| [10] |
MUKHERJEE A G, GOPALAKRISHNAN A V. The mechanistic insights of the antioxidant Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in oncogenesis: a deadly scenario[J]. Med Oncol, 2023, 40(9): 248.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02124-4 pmid: 37480500 |
| [11] |
EWUNKEM A J, DEVE M, HARRISON S H, et al. Diepoxybutane induces the p53-dependent transactivation of the CCL4 gene that mediates apoptosis in exposed human lymphoblasts[J]. J Biochem Mol Toxicol, 2023, 37(5): e23316.
doi: 10.1002/jbt.v37.5 |
| [12] |
HUANG J J, DU J J, LIN W J, et al. Regulation of lactate production through p53/β-enolase axis contributes to statin-associated muscle symptoms[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 45: 251-260.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.003 |
| [13] |
CHETTA P, SRIRAM R, ZADRA G. Lactate as key metabolite in prostate cancer progression: what are the clinical implications?[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(13): 3473.
doi: 10.3390/cancers15133473 |
| [14] |
KAM C S, HO D W, MING V S, et al. PFKFB4 drives the oncogenicity in TP53-mutated hepatocellular carcinoma in a phosphatase-dependent manner[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 15(6): 1325-1350.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.02.004 |
| [15] |
KOUZU H, TATEKOSHI Y, CHANG H C, et al. ZFP36L2 suppresses mTORc1 through a P53-dependent pathway to prevent peripartum cardiomyopathy in mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132(10): e154491.
doi: 10.1172/JCI154491 |
| [16] |
ROBERSON P A, KINCHELOE G N, WELLES J E, et al. Glucose-induced activation of mTORC1 is associated with hexokinase 2 binding to sestrins in HEK293T cells[J]. J Nutr, 2023, 153(4): 988-998.
doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2022.11.021 |
| [17] | CASTELLANOS G, VALBUENA D S, PÉREZ E, et al. Chromosomal instability as enabling feature and central hallmark of breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press), 2023, 15: 189-211. |
| [18] | WANG H L, GUO M, WEI H D, et al. Targeting p53 pathways: mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 92. |
| [19] |
ZHAN H, ZHANG Q, ZHANG C, et al. Targeted activation of HNF4α by AMPK inhibits apoptosis and ameliorates neurological injury caused by cardiac arrest in rats[J]. Neurochem Res, 2023, 48(10): 3129-3145.
doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03957-1 pmid: 37338793 |
| [20] |
XIONG C, LING H, HAO Q, et al. Cuproptosis: P53-regulated metabolic cell death?[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(4): 876-884.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01125-0 |
| [21] | TANG M, XU H, HUANG H Y, et al. Metabolism-based molecular subtyping endows effective ketogenic therapy in p53-mutant colon cancer[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2022, 9(29): e2201992. |
| [22] |
LIU Y Q, GU W. The complexity of p53-mediated metabolic regulation in tumor suppression[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 85: 4-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.03.010 |
| [23] | HAN Y L, LIANG C, YU Y X, et al. Gluconeogenesis alteration and p53-SIRT6-Fox01 signaling adaptive regulation in sheep from different grazing periods[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2022, 2022: 4614665. |
| [24] |
SANFORD J D, FRANKLIN D, GROIS G A, et al. Carnitine o-octanoyltransferase is a p53 target that promotes oxidative metabolism and cell survival following nutrient starvation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2023, 299(7): 104908.
doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104908 |
| [25] |
ZHANG X Y, TAO G R, JIANG J, et al. PCK1 activates oncogenic autophagy via down-regulation serine phosphorylation of UBAP2L and antagonizes colorectal cancer growth[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 68.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02894-x pmid: 37062825 |
| [26] |
REINISCH I, KLYMIUK I, MICHENTHALER H, et al. p 53 regulates a miRNA-fructose transporter axis in brown adipose tissue under fasting[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 913030.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.913030 |
| [27] |
SAFI A, SABERIYAN M, SANAEI M J, et al. The role of noncoding RNAs in metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2023, 28(1): 37.
doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00447-8 pmid: 37161350 |
| [28] |
LIU Y, WANG J D, JIANG M X. Copper-related genes predict prognosis and characteristics of breast cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1145080.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1145080 |
| [29] |
MORRIS J P 4th, YASHINSKIE J J, KOCHE R, et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate links p53 to cell fate during tumour suppression[J]. Nature, 2019, 573(7775): 595-599.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1577-5 |
| [30] |
DA FONSECA JUNIOR A M, ISPADA J, DOS SANTOS E C, et al. Adaptative response to changes in pyruvate metabolism on the epigenetic landscapes and transcriptomics of bovine embryos[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 11504.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38686-6 pmid: 37460590 |
| [31] |
LI X, WU L M, ZOPP M, et al. p53-TP53-induced glycolysis regulator mediated glycolytic suppression attenuates DNA damage and genomic instability in fanconi anemia hematopoietic stem cells[J]. Stem Cells, 2019, 37(7): 937-947.
doi: 10.1002/stem.3015 pmid: 30977208 |
| [32] |
WEI J, WANG S, ZHU H, et al. Hepatic depletion of nucleolar protein mDEF causes excessive mitochondrial copper accumulation associated with p53 and NRF1 activation[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(7): 107220.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107220 |
| [33] |
JAHOOR ALAM M. Insights from the p53 induced TIGAR protein 2 in the glycolytic pathway model[J]. Bioinformation, 2022, 18(3): 310-317.
doi: 10.6026/bioinformation |
| [34] |
LIU Y Q, GU W. p53 in ferroptosis regulation: the new weapon for the old guardian[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2022, 29(5): 895-910.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-00943-y pmid: 35087226 |
| [35] | DOU X Z, GUO H, D’AMICO T, et al. CryoEM structure with ATP synthase enables late-stage diversification of Cruentaren A[J]. Chemistry, 2023, 29(29): e202300262. |
| [36] |
ROHBECK E, NIERSMANN C, KÖHRER K, et al. Positive allosteric GABAA receptor modulation counteracts lipotoxicity-induced gene expression changes in hepatocytes in vitro[J]. Front Physiol, 2023, 14: 1106075.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1106075 |
| [37] |
HAO Q, CHEN J X, LU H, et al. The ARTS of p53-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 14(10): mjac074.
doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjac074 |
| [38] | LI G, WU J, LI L, et al. p53 deficiency induces MTHFD2 transcription to promote cell proliferation and restrain DNA damage[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(28): e2019822118. |
| [39] |
RAINHO M A, SIQUEIRA P B, DE AMORIM Í S S, et al. Mitochondria in colorectal cancer stem cells-a target in drug resistance[J]. Cancer Drug Resist, 2023, 6(2): 273-283.
doi: 10.20517/cdr |
| [40] |
ZHANG K X, YANG X H, ZHENG M Y, et al. Acetylated-PPARγ expression is regulated by different p53 genotypes associated with the adipogenic differentiation of polyploid giant cancer cells with daughter cells[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2023, 20(1): 56-76.
doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0432 |
| [41] | LI W, KOU J J, ZHANG Z X, et al. Cellular redox homeostasis maintained by malic enzyme 2 is essential for MYC-driven T cell lymphomagenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2023, 120(23): e2217869120. |
| [42] |
MOON S H, HUANG C H, HOULIHAN S L, et al. p53 represses the mevalonate pathway to mediate tumor suppression[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(3): 564-580.e19.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.011 |
| [43] |
ZHANG Y H, MOHIBI S, VASILATIS D M, et al. Ferredoxin reductase and p53 are necessary for lipid homeostasis and tumor suppression through the ABCA1-SREBP pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(12): 1718-1726.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02100-0 |
| [44] |
GÓMEZ-SANTOS B, SAENZ DE URTURI D, NUÑEZ-GARCÍA M, et al. Liver osteopontin is required to prevent the progression of age-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Aging Cell, 2020, 19(8): e13183.
doi: 10.1111/acel.v19.8 |
| [45] |
KANG J G, LAGO C U, LEE J E, et al. A mouse homolog of a human TP53 germline mutation reveals a lipolytic activity of p53[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 30(3): 783-792.e5.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.074 |
| [46] |
WANG C Y, WANG C H, MAI R T, et al. Mutant p53-microRNA-200c-ZEB2-axis-induced CPT1C elevation contributes to metabolic reprogramming and tumor progression in basal-like breast cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 940402.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940402 |
| [47] |
XU R, WANG W N, ZHANG W L. Ferroptosis and the bidirectional regulatory factor p53[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 197.
doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01517-8 |
| [48] | KUO H C, LUO L X, MA Y, et al. The p53 transactivation domain 1-dependent response to acute DNA damage in endothelial cells protects against radiation-induced cardiac injury[J]. Radiat Res, 2022, 198(2): 145-153. |
| [49] |
THIBAULT B, RAMOS-DELGADO F, GUILLERMET-GUIBERT J. Targeting class Ⅰ-Ⅱ-Ⅲ PI3Ks in cancer therapy: recent advances in tumor biology and preclinical research[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2023, 15(3): 784.
doi: 10.3390/cancers15030784 |
| [50] | GAO Y Q, JIAO Y T, GONG X Y, et al. Role of transcription factors in apoptotic cells clearance[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1110225. |
| [51] |
JIAO Z, PAN Y, CHEN F. The metabolic landscape of breast cancer and its therapeutic implications[J]. Mol Diagn Ther, 2023, 27(3): 349-369.
doi: 10.1007/s40291-023-00645-2 |
| [52] | CHEN M, CHEN Y. Bioinformatics analysis of common genetic and molecular traits and association of portal hypertension with pulmonary hypertension[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2022, 2022: 9237701. |
| [53] |
RYBICKA M, VERRIER E R, BAUMERT T F, et al. Polymorphisms within DIO2 and GADD45A genes increase the risk of liver disease progression in chronic hepatitis b carriers[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 6124.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32753-8 |
| [54] |
YAO P B, ZHANG Z X, LIU H C, et al. P53 protects against alcoholic fatty liver disease via ALDH2 inhibition[J]. EMBO J, 2023, 42(8): e112304.
doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112304 |
| [55] |
XU L, CHEN Z J, ZHANG Y, et al. P53 maintains gallid alpha herpesvirus 1 replication by direct regulation of nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis through its target genes[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 1044141.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1044141 |
| [56] |
CHEN S M, DUAN Y M, WU Y H, et al. A novel integrated metabolism-immunity gene expression model predicts the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma patients[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 728368.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.728368 |
| [57] |
KEALEY J, DÜSSMANN H, LLORENTE-FOLCH I, et al. Effect of TP53 deficiency and KRAS signaling on the bioenergetics of colon cancer cells in response to different substrates: a single cell study[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 893677.
doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.893677 |
| [58] |
JACOBERGER-FOISSAC C, COUSINEAU I, BARECHE Y, et al. CD73 inhibits cGAS-STING and cooperates with CD39 to promote pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Immunol Res, 2023, 11(1): 56-71.
doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-22-0260 |
| [59] |
RATHER G M, PRAMONO A A, SZEKELY Z, et al. In cancer, all roads lead to NADPH[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 226: 107864.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107864 |
| [60] |
MIKI K, YAGI M, NOGUCHI N, et al. Induction of glioblastoma cell ferroptosis using combined treatment with chloramphenicol and 2-deoxy-D-glucose[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 10497.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37483-5 pmid: 37380755 |
| [61] |
WANG K, LUO L, FU S Y, et al. PHGDH arginine methylation by PRMT1 promotes serine synthesis and represents a therapeutic vulnerability in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 1011.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36708-5 pmid: 36823188 |
| [62] | SHI T Z, YUAN Z H, HE Y Y, et al. Competition between p53 and YY1 determines PHGDH expression and malignancy in bladder cancer[J]. Cell Oncol (Dordr), 2023: 46(5): 1457-1472. |
| [63] |
SONG X M, CHEN Q, WANG J F, et al. Clinical and prognostic implications of an immune-related risk model based on TP53 status in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2022, 26(2): 436-448.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.v26.2 |
| [64] |
ZAVILEYSKIY L, BUNIK V. Regulation of p53 function by formation of non-nuclear heterologous protein complexes[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(2): 327.
doi: 10.3390/biom12020327 |
| [65] |
INDEGLIA A, LEUNG J C, MILLER S A, et al. An African-specific variant of TP53 reveals PADI4 as a regulator of p53-mediated tumor suppression[J]. Cancer Discov, 2023, 13(7): 1696-1719.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-1315 |
| [1] | SUN Yang, WANG Lian, ZHAO Meng, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, WANG Yueyue, SONG Xue, ZUO Lugen, LI Jing, HU Jianguo. The prognostic value of high expression of FKBP1A in gastric cancer and the regulatory effect of targeted PI3K/AKT on glucose metabolism [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 726-739. |
| [2] | ZOU Chunyuan, XU Xiaofeng, LU Renquan, GUO Lin. Detection of p53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GBU4-5 and MAGE A1 protein levels in lung cancer tissues and peripheral blood and their clinical value [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 36-44. |
| [3] | ZHU Xiaojian, LIN Kang, BU Fanqin, LUO Chen, HUANG Chao, ZHU Zhengming. High expression of DJ-1 promotes growth and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via the cyclin D1/p53-MDM2-AKT signaling pathway [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(3): 208-216. |
| [4] | REN Chunxia,XIA Xiaoai,YANG Shudong,LV Bei,TONG Guoqing . Establishment and initial analysis of an immortalized human ovarian surface epithelial cell line carrying a BRCA1 mutation [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(9): 693-699. |
| [5] | DONG Yinan, KONG Fanming, ZHANG Xinwei, et al. iASPP-SV, as an oncogene, participates in breast tumorigenesis and progression [J]. China Oncology, 2016, 26(10): 831-839. |
| [6] | JIANG Qiqi, ZHANG Hongmei, GUO Ai, et al. Effect and mechanism of rmhTNF on gastric cancer cell lines with different Δ133p53 status [J]. China Oncology, 2015, 25(4): 287-293. |
| [7] | LIU Fei, LI Haoran, CHENG Xi, et al. Research on the cytostatic effect of bufalin on cervical carcinoma cells and the related mechanism [J]. China Oncology, 2015, 25(10): 780-784. |
| [8] | GUO Ai, JI Wansheng, JIANG Qiqi et al. The role of Δ133p53 during 5-FU inhibition experiments on the growth of gastric cancer cell line MKN45 [J]. China Oncology, 2015, 25(1): 25-30. |
| [9] | JIA Xiao-qing, HONG Qi, CHENG Jing-yi, LI Jian-wei, WANG Yu-jie, MO Miao, SHAO Zhi-min, SHEN Zhen-zhou, LIU Guang-yu. Overexpression of P53 is prognostic for aromatase inhibitor resistance in early stage postmenopausal patients with ER-positive breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2014, 24(5): 354-360. |
| [10] | WU You-ming,DING Yan-qing,LI Na,WANG Jin-sheng,GUO Zhou-qing,LENG Lei,HUANG Dong. Comparison of telomerase, p53 and Ki-67 expression on colorectal serrated adenoma, traditional adenoma and colorectal cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2013, 23(7): 519-523. |
| [11] | GAO Wen, ZANG Rong-yu, WANG Yan, YANG Li-na, LIU Yang, QI Zi-hao, YIN Sheng, YANG Gong. Immortalization of human fallopian tube epithelial cells [J]. China Oncology, 2013, 23(4): 241-247. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
