Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 809-817.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.09.001
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WEI Jing( ), HE Yaqi, XUE Tian, BAI Qianming, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua(
), HE Yaqi, XUE Tian, BAI Qianming, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua( )
)
Received:2023-03-26
Revised:2023-07-03
Online:2023-09-30
Published:2023-10-01
Contact:
YU Baohua.
Share article
CLC Number:
WEI Jing, HE Yaqi, XUE Tian, BAI Qianming, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua. Clinicopathological analysis of DLBCL/HGBL with MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 gene rearrangement[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 809-817.
Tab. 1
Clinical features of 10 cases with THL"
| Case | Biopsy site | Ann Arbor staging | ECOG (score) | Bone marrow invasion | LDH (U/L) | IPI score | B symptom | HBV | Treatment | Follow-up status | OS/month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Right inguinal mass | ⅣA | 1 | + | 362 | Medium and high risk | No | HBsAb+, HBeAb+, HBcAb+, the rest-; HBV-DNA- | DA-EPOCH-R*6 | D | 10 |
| 2 | Small intestine | ⅠA | 2 | - | 220 | Low-risk | No | HBcAb+, the rest-; HBV-DNA- | R-CHOP*8, rituximab monotherapy to maintenance | A | 24.5 |
| 3 | Right testis | ⅣA | 1 | + | 970 | Medium and high risk | No | HBeAb+, the rest-; HBV-DNA- | Supporting treatment after surgical resection | D | 2 |
| 4 | Left testis | ⅠA | 1 | NA | NA | Low/low medium risk | No | Deny the history of hepatitis | Chemotherapy *8 (scheme unknown) | A | 45 |
| 5 | Rectum | ⅠA | 1 | NA | NA | Low/low medium risk | No | Deny the history of hepatitis | Chemotherapy *6 (scheme unknown) | A | 13 |
| 6 | Left tonsil | ⅣB | 1 | + | 312 | Medium and high risk | Yes | All five items are-; HBV-DNA- | DA-EPOCH-R*8, central nervous system prevention | A | 37 |
| 7 | Right jugular foramen area | ⅣB | 3 | + | NA | Medium and high/high risk | Yes | All five items are- | DA-TEDII-R*6, and then go back to the local hospital for radiotherapy | D | 8.5 |
| 8 | Left cervical lymph nodes | ⅡA | 1 | - | 257 | Low-risk | No | All five items are-; HBV-DNA- | DA-EPOCH-R*6, and then received auto-HSCT | A | 20.5 |
| 9 | Retroperitoneal lymph nodes | ⅡA | 1 | - | 149 | Low-risk | No | HBsAb+, HBeAb+, HBcAb+, the rest-; HBV-DNA- | DA-EPOCH-R | A | 55.5 |
| 10 | Gastric body | ⅠA | 1 | - | NA | Low-risk | No | HBsAb+, the rest- | R-CHOP | A | 8.5 |
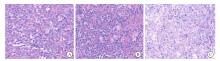
Fig.1
Histological features of THL A: Histological morphology is DLBCL-like (H-E stain, ×400), with vacuolar nuclei and prominent nucleoli; B: This case showed morphological features intermediate both DLBCL and BL (H-E stain, ×400), composing of medium-sized tumor cells with starry-sky appearance; C: This THL case had a blastoid cytomorphology (H-E stain, ×400), the neoplastic cells are monotonous, with inconspicuous nucleoli and overlapping nuclei."
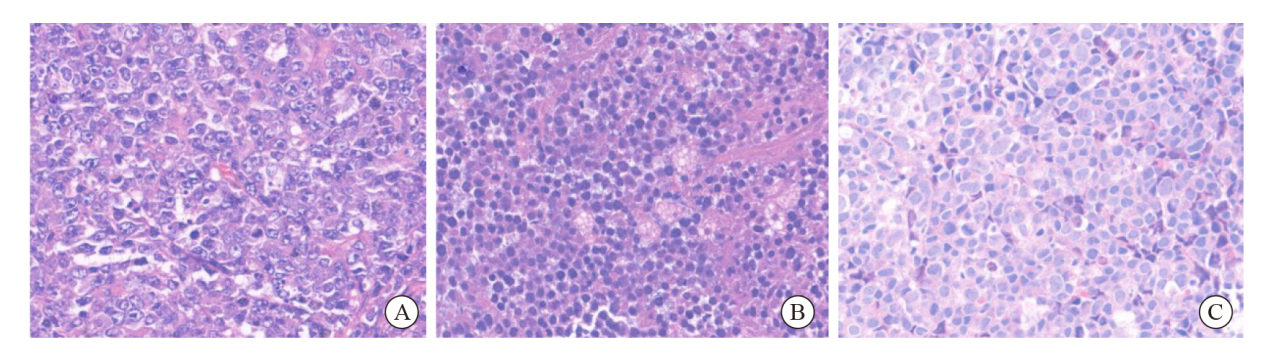
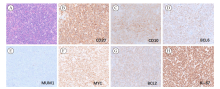
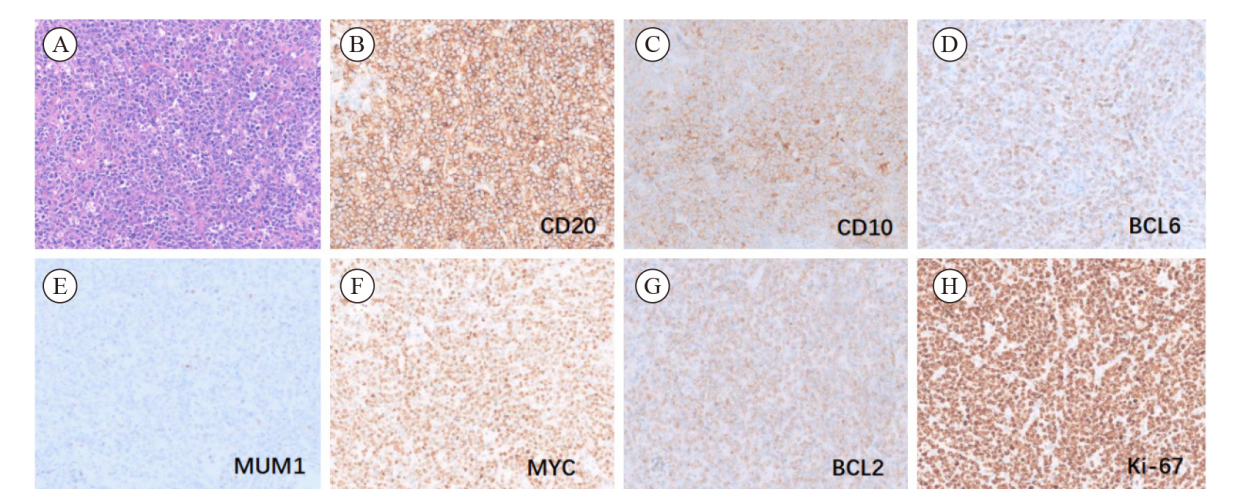
Fig. 2
A representative case of THL occurred in testis (case 4), immunohistochemical staining indicated GCB subtype with MYC/BCL2 double expression A: Histological morphology is DLBCL-like (H-E stain, ×200); B: The tumor cells were strongly positive for CD20 staining (EnVision stain, ×200); C-E: The tumor cells were positive for CD10 and BCL6 and negative for MUM1 (EnVision stain, ×200), indicating a GCB type; F-G: Both MYC and BCL2 were positive, indicating its double expression status (EnVision stain, ×200); H: The Ki-67 proliferation index was as high as 95% (EnVision stain, ×200)."
Tab. 2
Immunohistochemical stain and EBER-in situ hybridization results of 10 cases with THL"
| Case | CD20 | CD10 | BCL6 | MUM1 | BCL2 | MYC | CD5 | CD30 | Ki-67 proliferation index | P53 | EBER | Cyclin D1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | + | - | + (80%) | + (70%) | - | ND | + (80%) | ND | ND | - |
| 2 | + | + | + | - | + (80%) | + (80%) | - | ND | + (80%) | + (40%) | - | - |
| 3 | + | + | + | - | + (95%) | + (95%) | ND | ND | + (95%) | ND | ND | - |
| 4 | + | + | + | - | + (70%) | + (80%) | - | ND | + (95%) | + (8%) | ND | - |
| 5 | + | - | + | + | + (85%) | + (50%) | - | - | + (80%) | + (65%) | - | - |
| 6 | + | + | + | - | + (80%) | + (20%) | - | ND | + (80%) | ND | - | ND |
| 7 | + | - | - | - | + (80%) | ND | - | - | + (80%) | ND | - | - |
| 8 | + | - | + | - | + (90%) | + (75%) | ND | - | + (80%) | ND | - | ND |
| 9 | + | + | - | - | + (80%) | + (50%) | - | ND | + (80%) | ND | ND | - |
| 10 | + | + | + | - | - | + (60%) | ND | - | + (80%) | ND | - | - |
| [1] | SWERDLOW S H, CAMPO E, HARRIS N L, et al. World Health Organization classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues[M]. Lyon: IARC Press, 2017. |
| [2] |
ALAGGIO R, AMADOR C, ANAGNOSTOPOULOS I, et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: lymphoid neoplasms[J]. Leukemia, 2022, 36(7): 1720-1748.
doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01620-2 pmid: 35732829 |
| [3] |
PETRICH A M, GANDHI M, JOVANOVIC B, et al. Impact of induction regimen and stem cell transplantation on outcomes in double-hit lymphoma: a multicenter retrospective analysis[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(15): 2354-2361.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578963 pmid: 25161267 |
| [4] |
SARKOZY C, TRAVERSE-GLEHEN A, COIFFIER B. Double-hit and double-protein-expression lymphomas: aggressive and refractory lymphomas[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(15): e555-e567.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00005-4 pmid: 26545844 |
| [5] |
HOWLETT C, SNEDECOR S J, LANDSBURG D J, et al. Front-line, dose-escalated immunochemotherapy is associated with a significant progression-free survival advantage in patients with double-hit lymphomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Haematol, 2015, 170(4): 504-514.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.2015.170.issue-4 |
| [6] |
OKI Y, NOORANI M, LIN P, et al. Double hit lymphoma: the MD Anderson Cancer Center clinical experience[J]. Br J Haematol, 2014, 166(6): 891-901.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.2014.166.issue-6 |
| [7] | ROSENTHAL A, YOUNES A. High grade B-cell lymphoma with rearrangements of MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6: double hit and triple hit lymphomas and double expressing lymphoma[J]. Blood Rev, 2017, 31(2): 37-42. |
| [8] |
PEMMARAJU N, GILL J, GUPTA S, et al. Triple-hit lymphoma[J]. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent), 2014, 27(2): 125-127.
doi: 10.1080/08998280.2014.11929083 pmid: 24688198 |
| [9] |
BACHER U, HAFERLACH T, ALPERMANN T, et al. Several lymphoma-specific genetic events in parallel can be found in mature B-cell neoplasms[J]. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 2011, 50(1): 43-50.
doi: 10.1002/gcc.v50:1 |
| [10] |
TOMITA N, TOKUNAKA M, NAKAMURA N, et al. Clinicopathological features of lymphoma/leukemia patients carrying both BCL2 and MYC translocations[J]. Haematologica, 2009, 94(7): 935-943.
doi: 10.3324/haematol.2008.005355 |
| [11] |
MOTLLÓ C, GRAU J, JUNCÀ J, et al. Translocation (3;8)(q27;q24) in two cases of triple hit lymphoma[J]. Cancer Genet Cytogenet, 2010, 203(2): 328-332.
doi: 10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2010.08.018 |
| [12] |
ELDESSOUKI T, HANLEY K, HAMADEH F, et al. “Triple hit” lymphomas: a retrospective cytology case series of an uncommon high grade B-cell malignancy with C-MYC, BCL-2 and BCL-6 rearrangements[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2018, 46(9): 807-811.
doi: 10.1002/dc.v46.9 |
| [13] |
WANG W, HU S M, LU X Y, et al. Triple-hit B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 translocations/rearrangements: clinicopathologic features of 11 cases[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2015, 39(8): 1132-1139.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000434 |
| [14] |
HANS C P, WEISENBURGER D D, GREINER T C, et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray[J]. Blood, 2004, 103(1): 275-282.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-05-1545 pmid: 14504078 |
| [15] | 李敏, 张秋露, 赵炜, 等. 伴MYC、BCL2和(或)BCL6重排的高级别B细胞淋巴瘤在弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤中的发生率[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42(2): 124-128. |
| [16] | LI M, ZHANG Q L, ZHAO W, et al. Incidence of high-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 rearrangements in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Chin J Hematol, 2021, 42(2): 124-128. |
| [17] |
HUANG W T, MEDEIROS L J, LIN P, et al. MYC/BCL2/BCL6 triple hit lymphoma: a study of 40 patients with a comparison to MYC/BCL2 and MYC/BCL6 double hit lymphomas[J]. Mod Pathol, 2018, 31(9): 1470-1478.
doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0067-x |
| [18] |
ZHANG J J, WENG Z P, HUANG Y H, et al. High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC, BCL2, and/or BCL6 translocations/rearrangements: clinicopathologic features of 51 cases in a single institution of South China[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2020, 44(12): 1602-1611.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001577 |
| [19] |
TRAN J, VICKERS A, PONCE C P, et al. Triple-hit lymphoma of the cavernous sinus[J]. Can J Ophthalmol, 2019, 54(2): e61-e66.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2018.06.007 |
| [20] |
EFSTATHOPOULOU A, GHIELMINI M, ZUCCA E. MYC/BCL2/BCL6 triple hit lymphoma of the pericardium: a case report and review of the literature[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2020, 146(9): 2435-2438.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03137-6 pmid: 32025812 |
| [21] |
ZHOU X, PAN H X, YANG P, et al. Both chronic HBV infection and naturally acquired HBV immunity confer increased risks of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 477.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5718-x pmid: 31113483 |
| [22] |
ABE S K, INOUE M, SAWADA N, et al. Hepatitis B and C virus infection and risk of lymphoid malignancies: a population-based cohort study (JPHC Study)[J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2015, 39(4): 562-566.
doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2015.06.002 pmid: 26149122 |
| [23] |
ENGELS E A, CHO E R, JEE S H. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South Korea: a cohort study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2010, 11(9): 827-834.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70167-4 pmid: 20688564 |
| [24] |
REN W, YE X, SU H, et al. Genetic landscape of hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Blood, 2018; 131(24): 2670-2681.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-817601 pmid: 29545328 |
| [25] |
DENG L J, SONG Y Q, YOUNG K H, et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: unique clinical features, poor outcome, and hepatitis B surface antigen-driven origin[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(28): 25061-25073.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4677 pmid: 26314957 |
| [26] |
AUKEMA S M, KREUZ M, KOHLER C W, et al. Biological characterization of adult MYC-translocation-positive mature B-cell lymphomas other than molecular Burkitt lymphoma[J]. Haematologica, 2014, 99(4): 726-735.
doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.091827 |
| [27] | SWERDLOW S H. Diagnosis of ‘double hit’ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and B-cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between DLBCL and Burkitt lymphoma: when and how, FISH versus IHC[J]. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 2014, 2014(1): 90-99. |
| [28] |
SCOTT D W, KING R L, STAIGER A M, et al. High-grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma morphology[J]. Blood, 2018, 131(18): 2060-2064.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-820605 |
| [29] |
PEDERSEN M Ø, GANG A O, POULSEN T S, et al. Double-hit BCL2/MYC translocations in a consecutive cohort of patients with large B-cell lymphoma-a single centre’s experience[J]. Eur J Haematol, 2012, 89(1): 63-71.
doi: 10.1111/ejh.2012.89.issue-1 |
| [30] |
ZIEPERT M, LAZZI S, SANTI R, et al. A 70% cut-off for MYC protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies a high-risk group of patients[J]. Haematologica, 2020, 105(11): 2667-2670.
doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.235556 |
| [31] |
CUCCUINI W, BRIERE J, MOUNIER N, et al. MYC+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is not salvaged by classical R-ICE or R-DHAP followed by BEAM plus autologous stem cell transplantation[J]. Blood, 2012, 119(20): 4619-4624.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-406033 |
| [32] |
KÜHNL A, CUNNINGHAM D, COUNSELL N, et al. Outcome of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP: results from the UK NCRI R-CHOP14V21 trial with combined analysis of molecular characteristics with the DSHNHL RICOVER-60 trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(7): 1540-1546.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx128 pmid: 28398499 |
| [33] |
GREEN T M, YOUNG K H, VISCO C, et al. Immunohistochemical double-hit score is a strong predictor of outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(28): 3460-3467.
pmid: 22665537 |
| [34] |
GROSS T G, HALE G A, HE W S, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for refractory or recurrent non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children and adolescents[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2010, 16(2): 223-230.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.09.021 |
| [35] |
KANG J N, ZHANG Y Z, DING S, et al. Modified conditioning regimen with chidamide and high-dose rituximab for triple-hit lymphoma[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(22): 10770-10773.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16999 pmid: 34698437 |
| [36] |
SNUDERL M, KOLMAN O K, CHEN Y B, et al. B-cell lymphomas with concurrent IGH-BCL2 and MYC rearrangements are aggressive neoplasms with clinical and pathologic features distinct from Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2010, 34(3): 327-340.
doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181cd3aeb |
| [37] |
VALERA A, LÓPEZ-GUILLERMO A, CARDESA-SALZMANN T, et al. MYC protein expression and genetic alterations have prognostic impact in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy[J]. Haematologica, 2013, 98(10): 1554-1562.
doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.086173 pmid: 23716551 |
| [38] |
TZANKOV A, XU-MONETTE Z Y, GERHARD M, et al. Rearrangements of MYC gene facilitate risk stratification in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab-CHOP[J]. Mod Pathol, 2014, 27(7): 958-971.
doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2013.214 |
| [39] | ADAMS T, FUCHS D, SHADOAN P K, et al. Unexpected favorable outcome in a patient with high grade B-cell lymphoma with abnormalities of MYC, BCL6 and BCL2 loci[J]. Cancer Genet, 2018, 222-223: 25-31. |
| [1] | LIN Jiaxin, WEI Ran, SHUI Ruohong, LU Hongfen, LI Xiaoqiu, YU Baohua. Clinicopathological analysis of adrenal intravascular large B-cell lymphoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 1020-1027. |
| [2] | JIANG Lili, MA Yan, ZHANG Tiantian, HUANG Shan. Clinical analysis of 21 cases of primary Ewing sarcoma of the thoracic wall [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(1): 74-81. |
| [3] | HE Xiaoshun , JIAO Weijuan , GUO Lingchuan , HUANG Shan , WU Yujin , HUANG Renpeng . A clinicopathological analysis of 6 cases with dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(9): 822-827. |
| [4] | ING Ping’an, YANG Peigang, TIAN Yuan, LIN Yecheng, LIU Yang, GUO Honghai, ZHANG Zhidong, WANG Dong, LI Yong, ZHAO Qun. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis analysis of gastric cancer patients with elevated serum alpha- fetoprotein [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(11): 887-896. |
| [5] | WEN Duo, LIU Wanlin, CAO Yiming, QU Ning, ZHU Yongxue. The expressions of cortactin and N-WASP in thyroid papillary carcinoma and their significance [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(9): 688-692. |
| [6] | YU Baohua, XUE Tian, ZHANG Yan, et al. MYD88 gene mutation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its clinicopathological relevance [J]. China Oncology, 2018, 28(9): 679-685. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
