Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (4): 327-341.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.04.003
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIAO Lanshu1( ), PAN Liudi1, LIU Yi1, WANG Jie2, CHEN Hui1(
), PAN Liudi1, LIU Yi1, WANG Jie2, CHEN Hui1( )
)
Received:2022-12-06
Revised:2023-03-16
Online:2023-04-30
Published:2023-05-15
Contact:
CHEN Hui
Share article
CLC Number:
XIAO Lanshu, PAN Liudi, LIU Yi, WANG Jie, CHEN Hui. LncRNA DLEU7-AS1 contributes to proliferation and migration of gastric cancer by regulating MSN transcription[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(4): 327-341.
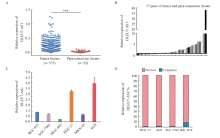
Fig. 1
The expression of DLEU7-AS1 in gastric cancer A: Analysis of DLEU7-AS1 expression in normal and gastric tumor tissues using TCGA database; B: The result of RTFQ-PCR in 37 pairs of gastric cancer tissues and para-cancerous tissues from Xinhua Hospital; C: The relative expression of DLEU7-AS1 in 6 gastric cancer cell lines; D: The distribution of DLEU7-AS1 in cells. ***: P<0.001, compared with control group."
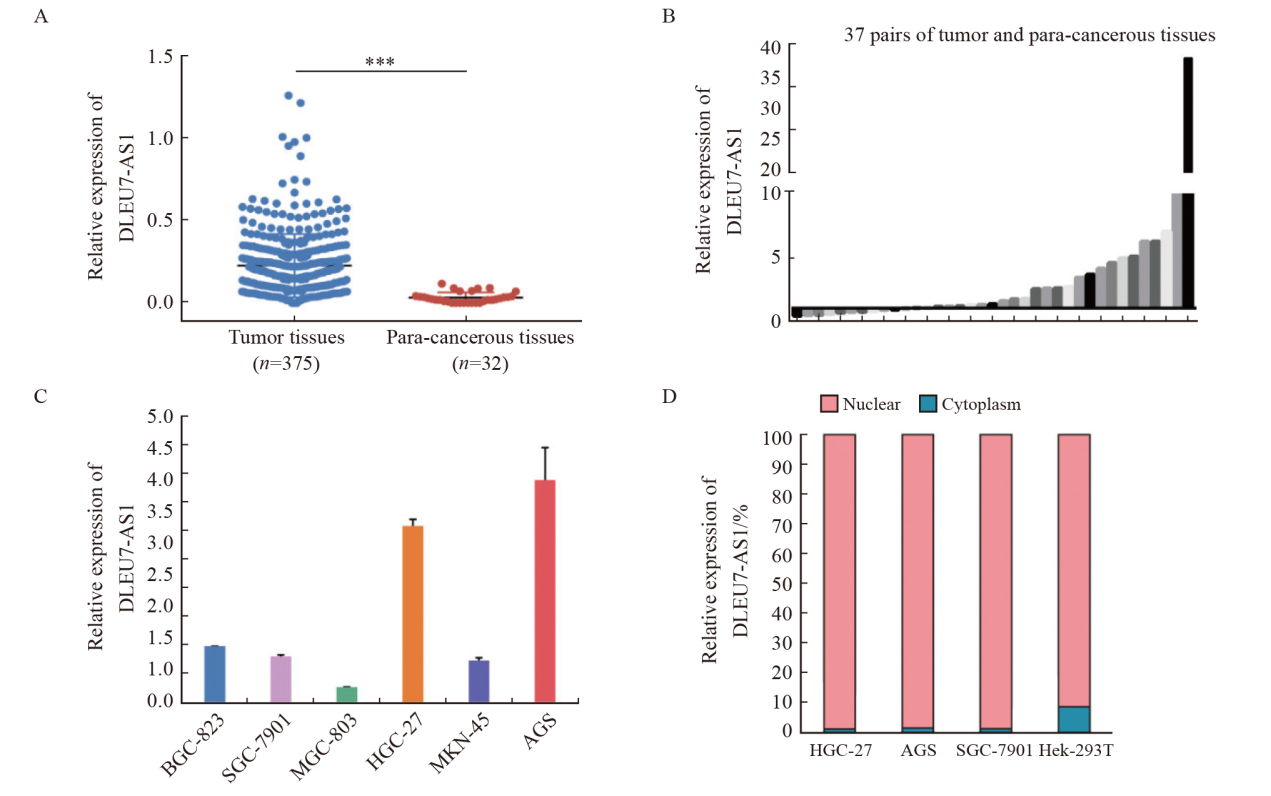
Fig. 3
The correlation between the expression of DLEU7-AS1 and the survival of gastric cancer patients A: The disease-free survival of gastric cancer patients with low and high expression of DLEU7-AS1; B: The post-progression survival of gastric cancer patients with low and high expression of DLEU7-AS1."
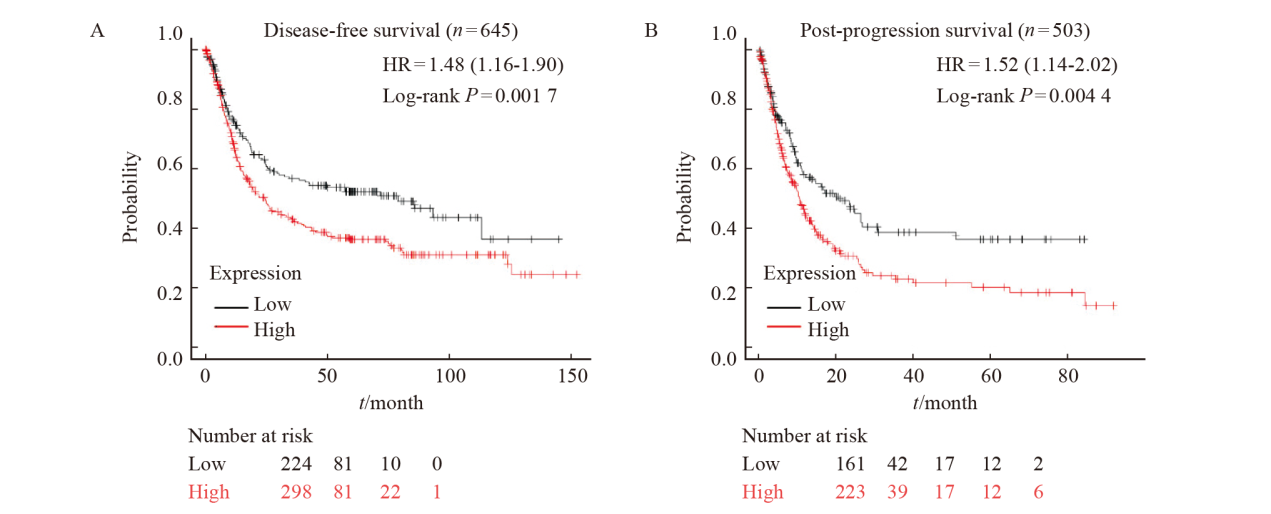
Fig. 4
DLEU7-AS1 silence inhibited proliferation of gastric cancer cells A: The expression of DLEU7-AS1 after transfecting siRNA into HGC-27 and AGS; B: Monitoring gastric cancer cells proliferation by CCK-8 after knockdown DLEU7-AS1. *: P<0.05, compared with si-NC; **: P<0.01, compared with si-NC, Student’s t test."
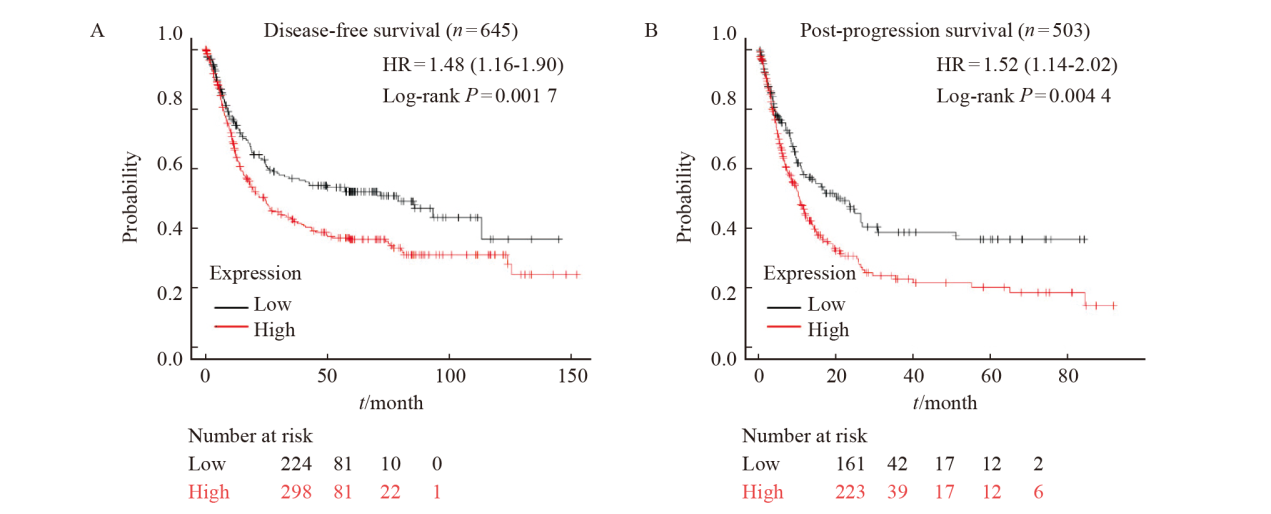
Fig. 5
DLEU7-AS1 promoted proliferation of gastric cancer cells A: The expression of DLEU7-AS1 after transfecting DLEU7-AS1 plasmids into MGC-803 and MKN-45; B: Monitoring gastric cancer cells proliferation by CCK-8 after DLEU7-AS1 overexpression; C: Monitoring gastric cancer cells proliferation by colony formation assay after DLEU7-AS1 overexpression. *: P<0.05, compared with Con260; **: P<0.01, compared with Con260; ***: P<0.001, compared with Con260; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with Con260; Student’s t test."
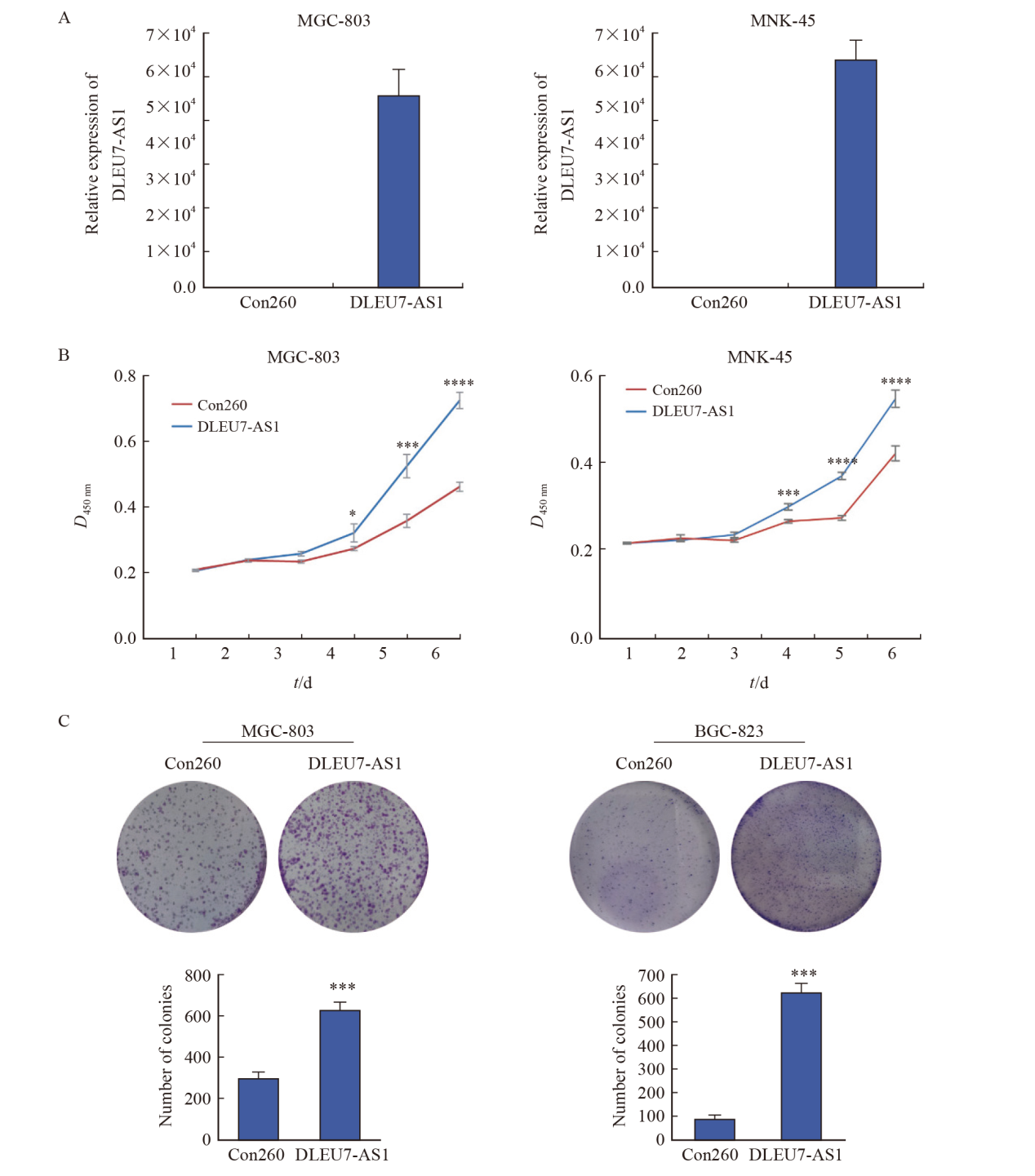
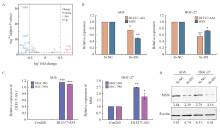
Fig. 10
DLEU7-AS1 regulated MSN expression A: Volcano plot of differential genes by RNA-seq analysis of HGC-27 transfected with si-491 and si-NC; B: RTFQ-PCR analysis of MSN mRNA level after transfection of si-RNA and si-491 in AGS and HGC-27; C: RTFQ-PCR analysis of MSN mRNA level after DLEU7-AS1 overexpression in MGC-803 and SGC-7901; D: Western blot analysis of MSN protein expression level after transfection of si-RNA and si-491 in AGS and HGC-27. *: P<0.05, compared with si-NC/Con260; **: P<0.01, compared with si-NC/Con260; ***: P<0.001, compared with si-NC/Con260."
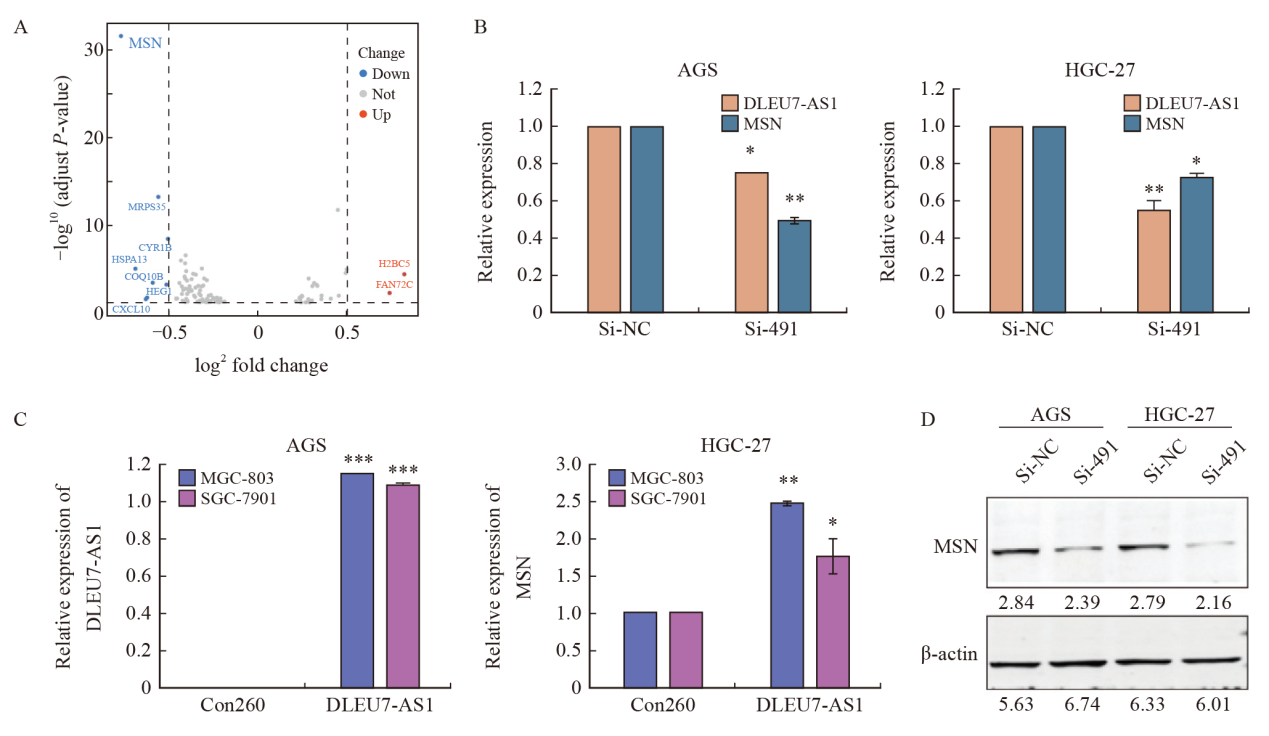
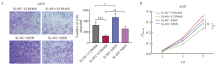
Fig. 11
MSN acted as downstream effector of DLEU7-AS1 A: Transwell chamber assay after knockdown of DLEU7-AS1 and overexpression of MSN; B: CCK-8 cell proliferation toxicity test after knockdown of DLEU7-AS1 and overexpression of MSN. ***: P<0.001, si-NC + CON468 compared with si-491 + CON468; *: P<0.05, si-NC + CON468 compared with si-NC + MSN; **: P<0.01, si-491 + CON468 compared with si-491 + MSN; **: P<0.01, si-491 + CON468 compared with si-491 + MSN; *: P<0.05, si-NC + CON468 compared with si-491+CON468, Student’s t test."
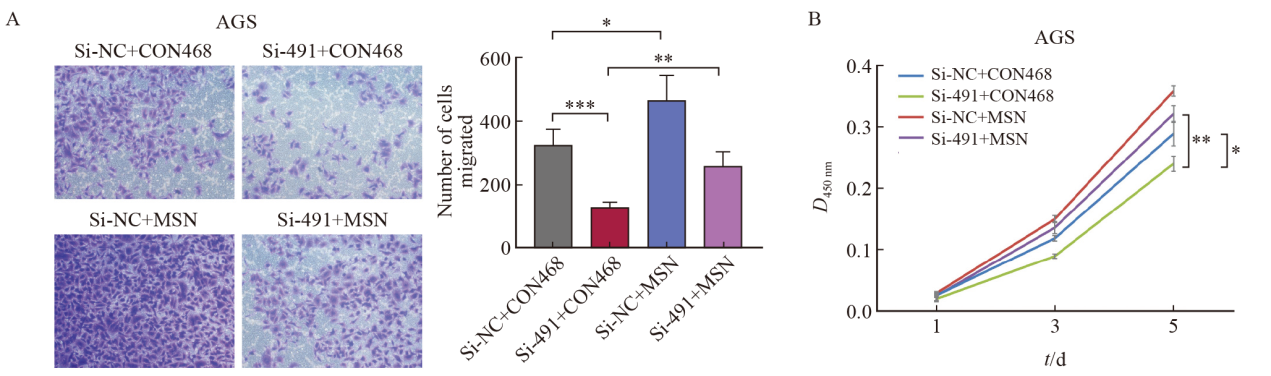
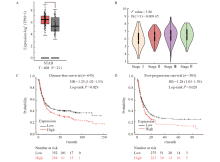
Fig. 12
The expression of MSN in gastric cancer and the correlation between the expression of MSN and the survival of gastric cancer patients A and B: Analysis of MSN expression in normal and gastric tumor tissues using GEPIA2 database; C: The disease-free progressive survival of gastric cancer patients with low and high expression of MSN; D: The post-progression survival of gastric cancer patients with low and high expression of MSN. *: P<0.05, compared with control."
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 |
| [2] |
SMYTH E C, NILSSON M, GRABSCH H I, et al. Gastric cancer[J]. The Lancet, 2020, 396(10251): 635-648.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31288-5 |
| [3] |
QIU H B, CAO S M, XU R H. Cancer incidence, mortality, and burden in China: a time-trend analysis and comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the global epidemiological data released in 2020[J]. Cancer Commun, 2021, 41(10): 1037-1048.
doi: 10.1002/cac2.v41.10 |
| [4] |
CHEN W Q, ZHENG R S, BAADE P D, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66(2): 115-132.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21338 |
| [5] | XIA C F, DONG X S, LI H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(5): 584-590. |
| [6] |
HERMAN A B, TSITSIPATIS D, GOROSPE M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation[J]. Mol Cell, 2022, 82(12): 2252-2266.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.027 pmid: 35714586 |
| [7] |
HUARTE M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer[J]. Nat Med, 2015, 21(11): 1253-1261.
doi: 10.1038/nm.3981 pmid: 26540387 |
| [8] | TAN Y T, LIN J F, LI T, et al. LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(2): 109-120. |
| [9] |
JUSIC A, THOMAS P B, WETTINGER S B, et al. Noncoding RNAs in age-related cardiovascular diseases[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2022, 77: 101610.
doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101610 |
| [10] |
SUN P, HAMBLIN M H, YIN K J. Non-coding RNAs in the regulation of blood-brain barrier functions in central nervous system disorders[J]. Fluids Barriers CNS, 2022, 19(1): 27.
doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00317-z pmid: 35346266 |
| [11] | LIU X B, HAN C, SUN C Z. Long non-coding RNA DLEU7-AS1 promotes the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(1): 110-117. |
| [12] |
WANG X J, CHEN L, XU R, et al. DLEU7-AS1 promotes renal cell cancer by silencing the miR-26a-5p/coronin-3 axis[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2022, 15(8): 1542-1552.
doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac061 |
| [13] | WANG C Z, MA B B, XU Z J, et al. Reduced expression of lncRNA DLEU7-AS1 is a novel favorable prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Biosci Rep, 2022, 42(5): BSR20212078. |
| [14] |
ENCODE PROJECT CONSORTIUM. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome[J]. Nature, 2012, 489(7414): 57-74.
doi: 10.1038/nature11247 |
| [15] |
HUANG W X, LI H, YU Q S, et al. LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 100.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02319-z |
| [16] |
LI K, WANG Z Q. lncRNA NEAT1: key player in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2023, 86: 101878.
doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101878 |
| [17] | NOJIMA T, PROUDFOOT N J. Mechanisms of lncRNA biogenesis as revealed by nascent transcriptomics[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2022, 23(6): 389-406. |
| [18] |
LIU J, LIU Z X, WU Q N, et al. Long noncoding RNA AGPG regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 1507.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15112-3 pmid: 32198345 |
| [19] |
JI X S, LIU Z H, GAO J J, et al. N6-Methyladenosine-modified lncRNA LINREP promotes glioblastoma progression by recruiting the PTBP1/HuR complex[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(1): 54-68.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01045-5 |
| [20] |
MCCABE E M, RASMUSSEN T P. lncRNA involvement in cancer stem cell function and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2021, 75: 38-48.
doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.012 pmid: 33346133 |
| [21] |
LIU H, LI D X, SUN L N, et al. Interaction of lncRNA MIR100HG with hnRNPA2B1 facilitates m6A-dependent stabilization of TCF7L2 mRNA and colorectal cancer progression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 74.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01555-3 |
| [22] |
LI Z, LANG Z Q, WANG T, et al. LncRNA SNHG22 promotes gastric cancer progression by regulating the miR-101-3p/e2f2 axis[J]. Cell Cycle, 2023, 22(3): 347-360.
doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2119515 |
| [23] |
LIN Z H, SONG J L, GAO Y K, et al. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/lncRNA-PMAN inhibits ferroptosis by promoting the cytoplasmic translocation of ELAVL1 in peritoneal dissemination from gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102312.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102312 |
| [24] |
MANGEAT P, ROY C, MARTIN M. ERM proteins in cell adhesion and membrane dynamics[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 1999, 9(5): 187-192.
pmid: 10322453 |
| [25] |
DEGRYSE B, BRITTO M, SHAN C X, et al. Moesin and merlin regulate urokinase receptor-dependent endothelial cell migration, adhesion and angiogenesis[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2017, 88: 14-22.
doi: S1357-2725(17)30090-0 pmid: 28473293 |
| [26] |
LI Y Q, ZHENG Z, LIU Q X, et al. Moesin as a prognostic indicator of lung adenocarcinoma improves prognosis by enhancing immune lymphocyte infiltration[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2021, 19(1): 109.
doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02229-y |
| [27] |
SUN X, LI K X, HASE M, et al. Suppression of breast cancer-associated bone loss with osteoblast proteomes via Hsp90ab1/moesin-mediated inhibition of TGFβ/FN1/CD44 signaling[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(2): 929-943.
doi: 10.7150/thno.66148 pmid: 34976221 |
| [28] |
YU L F, ZHAO L, WU H Z, et al. Moesin is an independent prognostic marker for ER-positive breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2019, 17(2): 1921-1933.
doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9799 pmid: 30675256 |
| [29] |
KAMIOKA H, TOMONO T, FUJITA A, et al. Moesin-mediated P-glycoprotein activation during snail-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells[J]. J Pharm Sci, 2020, 109(7): 2302-2308.
doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2020.03.008 |
| [1] | WEN Ziqiang, LAN Junliang, ZHOU Bo, XU Qiwei. PARP1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating expression of POU2F2 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 848-856. |
| [2] | CAO Fei, YU Wenhao, TANG Xiaonan, MA Zidong, CHANG Tingmin, GONG Yabin, LIAO Mingjuan, KANG Xiaohong. Mechanism of LINC01410 promoting proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 753-762. |
| [3] | LIU Shuai, ZHANG Kai, ZHANG Xiaoqing, LUAN Wei. An exploratory study on the perioperative treatment of locally advanced gastric cancer with combination of penpulimab, anlotinib and chemotherapy [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 659-668. |
| [4] | CHEN Xun, ZHENG Zhenxia, RUAN Xueru. Effects of TMCO1 on proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 571-580. |
| [5] | SUN Rongqi, SONG Ning, ZHENG Wentian, ZHANG Xinyue, LI Minmin, GONG Hui, JIANG Yingying. Effect of long noncoding RNA FLJ30679 on proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 439-450. |
| [6] | XIONG Jiayan, LEI Wei, YOU Bo, ZHANG Zhenxin, XIE Haijing, SHAN Ying, XIA Tian, ZHOU Yong. Study on the mechanism of DDX6 promoting proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by regulating stability of CKMT1A mRNA [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 451-459. |
| [7] | ZHOU Xueqin, LUAN Yanchao, ZHAO Li, RONG Chaochao, YANG Na. Expression of CDC20 in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and its effect on the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 460-472. |
| [8] | GUAN Ruirui, HAO Qian, ZHANG Yaqi, SUN Qinggang, CHEN Yitian, LI Xiumin, ZHOU Xiang, HAN Tao. CDC20 facilitates the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cell by stabilizing NLRP3 expression [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 473-484. |
| [9] | WANG Fei, LIU Pei, HU Nan. Effect of bevacizumab assisted PD-1 inhibitor on serum miR-20a-5p and miR-515-3p in the treatment of gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 493-500. |
| [10] | Professional Committee on Gastric Cancer of Shanghai Anticancer Association , Professional Committee on Gastrointestinal Cancer of China Association for Promotion of Health Science and Technology . Chinese expert consensus on clinical practice of locally advanced gastric cancer invading adjacent organs (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 517-526. |
| [11] | XU Yonghu, XU Dazhi. Progress and prospects of gastric cancer treatment in the 21st century [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 239-249. |
| [12] | WANG Xuefei, ZHOU Peng, TANG Zhaoqing. New progress and development trend of surgical treatment for gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 250-258. |
| [13] | XUE Chi, GAO Peng, ZHU Zhi, WANG Zhenning. Application and challenge of immunotherapy in perioperative therapy of gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 259-267. |
| [14] | SHEN Jie, WANG Jiangli, WANG Zezhou, MO Miao, ZHOU Changming, YUAN Jing, XU Dazhi, ZHENG Ying. Survival analysis of 6 737 surgically resected gastric cancer cases in China from a large single institution hospital-based cancer registry database [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 268-277. |
| [15] | LI Jing, ZHENG Lei, GAO Yu. Analysis of effects of trastuzumab assisted modified DOF fortnightly regimen on serum tumor markers and survival rate in patients with cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 286-292. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
