Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 908-919.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.10.003
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHE Youjun1( ), GUO Zihan1, ZHANG Zhongwei2, DU Qiong1(
), GUO Zihan1, ZHANG Zhongwei2, DU Qiong1( )
)
Received:2023-07-19
Revised:2023-10-18
Online:2023-10-30
Published:2023-10-31
Contact:
DU Qiong.
Share article
CLC Number:
SHE Youjun, GUO Zihan, ZHANG Zhongwei, DU Qiong. Evaluation of adverse events of CDK4/6 inhibitors: a real-world study based on the FAERS database[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(10): 908-919.
Tab. 2
Population characteristics of CDK4/6 inhibitor-related reports in the FAERS database"
| Item | Palbociclib | Abemaciclib | Ribociclib |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of reports | 66 250 | 7 573 | 11 739 |
| Gender n (%) | |||
| Female | 61 977 (93.55) | 6 775 (89.46) | 10 823 (92.2) |
| Male | 1 521 (2.30) | 130 (1.72) | 234 (1.99) |
| Missing | 2 752 (4.15) | 668 (8.82) | 682 (5.81) |
| Median age (Q1, Q3) | 66 (57, 74) | 64 (56, 72) | 61 (51, 71) |
| Year of report n (%) | |||
| Before 2019 | 30 432 (45.94) | 2 346 (30.98) | 3 140 (26.75) |
| 2020 | 9 951 (15.02) | 1 522 (20.10) | 1 962 (16.71) |
| 2021 | 8 909 (13.45) | 1 368 (18.06) | 2 255 (19.21) |
| 2022 | 12 852 (19.40) | 1 850 (24.43) | 3 202 (27.28) |
| 2023 | 4 106 (6.20) | 487 (6.43) | 1 180 (10.05) |
| Reporter n (%) | |||
| Consumer | 28 344 (42.78) | 3 355 (44.30) | 6 021 (51.29) |
| Pharmacist | 19 203 (28.99) | 1 850 (24.43) | 1 724 (14.69) |
| Physician | 8 867 (13.38) | 1 098 (14.50) | 2 970 (25.30) |
| Others | 9 836 (14.85) | 1 270 (16.77) | 1024 (8.73) |
| Country n (%) | |||
| China | 542 (0.81) | 176 (2.32) | 66 (0.56) |
| Unknown | 2 473 (3.74) | 743 (9.81) | 238 (2.03) |
| Others | 63 777 (96.21) | 6 830 (90.20) | 11 501 (97.97) |
| Type of reports | |||
| Non-serious | 35 561 (53.68) | 4 108 (54.25) | 8 855 (75.43) |
| Serious | 30 689 (46.32) | 3 465 (45.75) | 2 884 (24.57) |
| Outcome | |||
| Life-threatening | 347 (0.52) | 106 (1.40) | 359 (3.06) |
| Hospitalization | 8 708 (13.14) | 1 612 (21.29) | 2 608 (22.22) |
| Disability | 178 (0.27) | 42 (0.55) | 89 (0.76) |
| Death | 8 250 (12.45) | 664 (8.77) | 2 489 (21.20) |
| Others | 48 767 (73.62) | 5 149 (67.99) | 6 194 (52.76) |
| Median of onset time (Q1, Q3) | 79 (20, 276) | 32 (11, 102) | 63 (16, 253) |
Tab. 3
Top 30 adverse events with the highest frequency of occurrence in signaling assays for CDK4/6 inhibitors"
| No. | Palbociclib | Abemaciclib | Ribociclib | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred term (PT) | n | ROR | Preferred term (PT) | n | ROR | Preferred term (PT) | n | ROR | |||
| 1 | Fatigue | 11 391 | 4.59 | Diarrhoea | 2 027 | 13.54 | Nausea | 1 278 | 1.98 | ||
| 2 | Alopecia | 4 848 | 7.28 | Nausea | 569 | 2.70 | Fatigue | 1 259 | 2.03 | ||
| 3 | Neutropenia | 3 460 | 8.29 | Fatigue | 509 | 2.51 | Neutropenia | 875 | 8.56 | ||
| 4 | Decreased appetite | 2 544 | 3.12 | Vomiting | 402 | 3.24 | Vomiting | 770 | 2.02 | ||
| 5 | Platelet count decreased | 1 643 | 4.58 | Decreased appetite | 281 | 4.36 | White blood cell count decreased | 720 | 8.21 | ||
| 6 | Hot flush* | 1 323 | 5.61 | Dehydration | 254 | 6.86 | Diarrhoea | 681 | 1.33 | ||
| 7 | Haemoglobin decreased | 1 145 | 3.15 | White blood cell count decreased | 226 | 7.80 | Pain | 629 | 1.20 | ||
| 8 | Epistaxis | 1 007 | 3.84 | Neutropenia | 170 | 4.99 | Malaise | 576 | 1.52 | ||
| 9 | Bone pain | 842 | 4.13 | Anaemia | 169 | 3.18 | Dyspnoea | 566 | 1.20 | ||
| 10 | Leukopenia | 784 | 4.67 | Weight decreased | 159 | 2.09 | Asthenia | 508 | 1.63 | ||
| 11 | Oral pain | 618 | 7.92 | Alopecia | 153 | 2.81 | Alopecia | 496 | 3.00 | ||
| 12 | Hypoacusis* | 618 | 3.81 | Abdominal pain upper * | 147 | 2.68 | Rash | 475 | 1.29 | ||
| 13 | Laboratory test abnormal | 382 | 3.81 | Blood creatinine increased | 142 | 7.74 | Decreased appetite | 455 | 2.30 | ||
| 14 | Blood test abnormal | 369 | 8.43 | Abdominal pain | 140 | 2.21 | Pruritus | 431 | 1.44 | ||
| 15 | Lacrimation increased | 320 | 3.43 | Interstitial lung disease | 119 | 9.58 | Cough | 430 | 1.94 | ||
| 16 | Taste disorder | 304 | 6.40 | Constipation | 119 | 2.14 | Constipation | 375 | 2.22 | ||
| 17 | Myelosuppression | 295 | 5.38 | Platelet count decreased | 107 | 3.73 | Pyrexia | 370 | 1.28 | ||
| 18 | Immune system disorder* | 246 | 5.65 | Myelosuppression | 102 | 23.51 | Back pain | 351 | 1.79 | ||
| 19 | Cytopenia | 229 | 7.54 | Drug intolerance | 86 | 3.62 | Pain in extremity | 350 | 1.37 | ||
| 20 | Lymphoedema* | 207 | 9.40 | Haemoglobin decreased | 85 | 2.95 | Anaemia | 336 | 2.07 | ||
| 21 | Onychoclasis* | 199 | 8.79 | Pulmonary embolism | 83 | 2.99 | Decreased immune responsiveness* | 301 | 45.56 | ||
| 22 | Nail disorder* | 187 | 7.38 | Hepatic function abnormal | 79 | 8.29 | Feeling abnormal* | 286 | 1.34 | ||
| 23 | Musculoskeletal chest pain* | 185 | 3.36 | Pneumonitis | 75 | 11.24 | Electrocardiogram QT prolonged | 284 | 9.57 | ||
| 24 | Pulmonary thrombosis | 139 | 3.85 | Thrombosis | 67 | 2.96 | Haemoglobin decreased | 267 | 3.04 | ||
| 25 | Oral mucosal blistering | 135 | 6.06 | Thrombocytopenia | 66 | 2.21 | Weight decreased | 265 | 1.14 | ||
| 26 | Gingival pain | 119 | 4.33 | Neutrophil count decreased | 62 | 6.10 | Neutrophil count decreased | 258 | 8.40 | ||
| 27 | Nasal dryness | 96 | 4.51 | Red blood cell count decreased | 59 | 7.60 | Peripheral swelling | 250 | 2.10 | ||
| 28 | White blood cell disorder | 93 | 10.15 | Full blood count decreased | 55 | 10.71 | Pleural effusion* | 246 | 4.74 | ||
| 29 | Appetite disorder | 92 | 4.51 | Renal impairment | 54 | 2.44 | Leukopenia | 242 | 5.97 | ||
| 30 | Red cell distribution width increased* | 87 | 6.73 | Stomatitis * | 50 | 3.15 | Platelet count decreased | 238 | 2.72 | ||
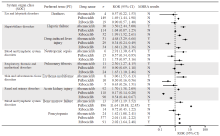
Fig. 7
Detection of CDK4/6 inhibitor designated medical event (DME) signals A lower limit of the 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of the ROR value greater than 1 generated a signal of an adverse reaction. A PT with signals under both the MHRA and the ROR methods was considered a signal of a DME; N: No; Y: Yes."
| [1] |
HUPPERT L A, GUMUSAY O, IDOSSA D, et al. Systemic therapy for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early stage and metastatic breast cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(5): 480-515.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v73.5 |
| [2] |
WU Y M, ZHANG Y, PI H, et al. Current therapeutic progress of CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 3477-3487.
doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S250632 pmid: 32523378 |
| [3] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 乳腺癌诊疗指南(2022年版)[J]. 中国合理用药探索, 2022, 19(10): 51. |
| National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer (2022 edition)[J]. China Licens Pharm, 2022, 19(10): 51. | |
| [4] |
GRADISHAR W J, MORAN M S, ABRAHAM J, et al. Breast cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2022, 20(6): 691-722.
doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.0030 |
| [5] |
ONESTI C E, JERUSALEM G. CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: differences in toxicity profiles and impact on agent choice. A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2021, 21(3): 283-298.
doi: 10.1080/14737140.2021.1852934 |
| [6] |
GRINSHPUN A, TOLANEY S M, BURSTEIN H J, et al. The dilemma of selecting a first line CDK4/6 inhibitor for hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer[J]. NPJ Breast Cancer, 2023, 9(1): 15.
doi: 10.1038/s41523-023-00520-7 pmid: 36949066 |
| [7] |
GAO J J, CHENG J, BLOOMQUIST E, et al. CDK4/6 inhibitor treatment for patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced or metastatic breast cancer: a US Food and Drug Administration pooled analysis[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(2): 250-260.
doi: S1470-2045(19)30804-6 pmid: 31859246 |
| [8] |
SCHETTINI F, GIUDICI F, GIULIANO M, et al. Overall survival of CDK4/6-inhibitor-based treatments in clinically relevant subgroups of metastatic breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2020, 112(11): 1089-1097.
doi: 10.1093/jnci/djaa071 pmid: 32407488 |
| [9] | THILL M, SCHMIDT M. Management of adverse events during cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor-based treatment in breast cancer[J]. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 2018, 10: 1758835918793326. |
| [10] | 国家肿瘤质控中心乳腺癌专家委员会, 中国抗癌协会肿瘤药物临床研究专业委员会, 徐兵河, 等. CDK4/6抑制剂治疗激素受体阳性人表皮生长因子受体2阴性晚期乳腺癌的临床应用共识[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2021, 43(4): 405-413. |
| Breast Cancer Expert Committee of National Cancer Quality Control Center, Cancer Drug Clinical Research Professional Committee of China Anti-Cancer Association, XU B H, et al. Consensus recommendations for the clinical application of CDK4/6 inhibitors in patients with hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative advanced breast cancer[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2021, 43(4): 405-413. | |
| [11] |
DESNOYERS A, NADLER M B, KUMAR V, et al. Comparison of treatment-related adverse events of different cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer: a network meta-analysis[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2020, 90: 102086.
doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102086 |
| [12] |
RASCHI E, FUSAROLI M, ARDIZZONI A, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors and interstitial lung disease in the FDA adverse event reporting system: a pharmacovigilance assessment[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 186(1): 219-227.
doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-06001-w |
| [13] |
RASCHI E, FUSAROLI M, LA PLACA M, et al. Skin toxicities with cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: signals from disproportionality analysis of the FDA adverse event reporting system[J]. Am J Clin Dermatol, 2022, 23(2): 247-255.
doi: 10.1007/s40257-021-00645-0 |
| [14] |
SAKAEDA T, TAMON A, KADOYAMA K, et al. Data mining of the public version of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2013, 10(7): 796-803.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.6048 pmid: 23794943 |
| [15] | Administration USDO. FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) quarterly data extract files[EB/OL] (2023-04-27)[2023-7-14]. https://fis.fda.gov/extensions/FPD-QDE-FAERS/FPD-QDE-FAERS.html. |
| [16] |
CANDORE G, JUHLIN K, MANLIK K, et al. Comparison of statistical signal detection methods within and across spontaneous reporting databases[J]. Drug Saf, 2015, 38(6): 577-587.
doi: 10.1007/s40264-015-0289-5 |
| [17] | 尚鹏辉, 詹思延. 数据挖掘在药品不良反应信号检出和分析中的应用(下): 药物流行病学研究新方法系列讲座(三)[J]. 中国药物应用与监测, 2009, 6(3): 187-190. |
| HANG P H, ZHAN S Y. Application of data excavation in the signal detection and analysis of adverse drug reactions(third)[J]. Chin J Drug Appl Monit, 2009, 6(3): 187-190. | |
| [18] | Agency EM. Designated Medical Event (DME) list[EB/OL] (2020-06-15)[2023-7-14]. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/other/designated-medical-event-dme-list_en.xls. |
| [19] |
BRAAL C L, JONGBLOED E M, WILTING S M, et al. Inhibiting CDK4/6 in breast cancer with palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib: similarities and differences[J]. Drugs, 2021, 81(3): 317-331.
doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01461-2 pmid: 33369721 |
| [20] |
WANDER S A, O'BRIEN N, LITCHFIELD L M, et al. Targeting CDK4 and 6 in cancer therapy: emerging preclinical insights related to abemaciclib[J]. Oncologist, 2022, 27(10): 811-821.
doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyac138 pmid: 35917168 |
| [21] |
LI J, FU F M, YU L W, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative advanced breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 180(1): 21-32.
doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05528-2 |
| [22] |
THIBAULT S, HU W Y, HIRAKAWA B, et al. Intestinal toxicity in rats following administration of CDK4/6 inhibitors is independent of primary pharmacology[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2019, 18(2): 257-266.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0734 pmid: 30401694 |
| [23] |
CHAPPELL J C, TURNER P K, PAK Y A, et al. Abemaciclib inhibits renal tubular secretion without changing glomerular filtration rate[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 105(5): 1187-1195.
doi: 10.1002/cpt.1296 pmid: 30449032 |
| [24] |
VRANA E, MYLONA S, BOBOS M, et al. Ribociclib and palbociclib-induced erythema multiforme: a case report[J]. Oxf Med Case Reports, 2022, 2022(11): omac116.
doi: 10.1093/omcr/omac116 |
| [25] |
ZHANG P, ZHANG Q Y, TONG Z S, et al. Dalpiciclib plus letrozole or anastrozole versus placebo plus letrozole or anastrozole as first-line treatment in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer (DAWNA-2): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2023, 24(6): 646-657.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00172-9 |
| [26] |
XU B H, ZHANG Q Y, ZHANG P, et al. Dalpiciclib or placebo plus fulvestrant in hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: a randomized, phase 3 trial[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(11): 1904-1909.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01562-9 pmid: 34737452 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
