Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 469-477.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.05.007
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Lijun( ), WANG Yichen, ZHENG Qiang, WANG Yue, JIN Yan, LI Yuan(
), WANG Yichen, ZHENG Qiang, WANG Yue, JIN Yan, LI Yuan( )
)
Received:2022-10-17
Revised:2023-03-21
Online:2023-05-30
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
LI Yuan
Share article
CLC Number:
CHEN Lijun, WANG Yichen, ZHENG Qiang, WANG Yue, JIN Yan, LI Yuan. Consistency analysis of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry antibodies in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 469-477.
Tab. 1
Number of positive cases of ESCC under different cut-off for CPS or TPS using PD-L1 22C3, SP263 and 28-8 antibodies [n (%)]"
| PD-L1 antibody clone | Positive case (n=78) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS≥10 | CPS≥1 | TPS≥10% | TPS≥1% | |
| 22C3 | 38 (48.7) | 68 (87.2) | 25 (32.1) | 41 (52.6) |
| SP263 | 41 (52.6) | 73 (93.6) | 28 (35.9) | 48 (61.5) |
| 28-8 | 40 (51.3) | 70 (89.7) | 27 (34.6) | 43 (55.1) |
Tab. 2
Number of positive cases of ESCC under different cut-off for CPS or TPS using PD-L1 22C3, E1L3N XP, CST E1L3N, BP6099, MXR006 antibodies[n (%)]"
| PD-L1 antibody clone | Positive case (n=68) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS≥10 | CPS≥1 | TPS≥10% | TPS≥1% | |
| 22C3 | 33 (48.4) | 62 (91.2) | 20 (29.3) | 43 (63.2) |
| E1L3N XP | 29 (42.6) | 64 (94.1) | 17 (25.0) | 46 (67.6) |
| CST E1L3N | 31 (45.6) | 63 (92.6) | 18 (26.5) | 57 (83.8) |
| BP6099 | 22 (32.4) | 61 (89.7) | 16 (23.5) | 51 (75.0) |
| MXR006 | 29 (42.6) | 62 (91.2) | 19 (27.9) | 48 (70.6) |
Tab. 3
Number of consistent cases in ESCC with CPS, TPS and IPS at cut-off value of 1 or 10 using PD-L1 22C3 and SP263, 28-8 antibody assays [n (%)]"
| PD-L1 antibody clone | Concordant case (n=78) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS≥10 | CPS≥1 | TPS≥10% | TPS≥1% | |
| 22C3 vs SP263 | 69 (88.5) | 73 (93.6) | 73 (93.6) | 69 (88.5) |
| 22C3 vs 28-8 | 72 (92.3) | 76 (97.4) | 74 (94.9) | 68 (87.2) |
| SP263 vs 28-8 | 67 (85.9) | 75 (96.2) | 75 (96.2) | 73 (93.6) |
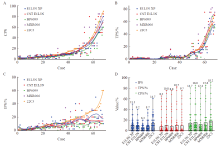
Fig. 3
Comparison of interpretation results in ESCC using PD-L1 22C3 with four domestic clone number antibodies under three scoring systems A-C: Comparison of CPS, TPS and IPS interpretation results using PD-L1 22C3, E1L3N XP, CST E1L3N, BP6099 and MXR006 antibodies in each case. D: Distribution and median comparison of CPS, TPS and IPS interpretation results using PD-L1 22C3, E1L3N XP, CST E1L3N, BP6099 and MXR006 antibodies in 68 cases."
Tab. 4
Number of consistent cases in ESCC with CPS, TPS and IPS at cut-off value of 1 or 10 using PD-L1 22C3 and E1L3N XP, CST E1L3N, BP6099, MXR006 antibody assay [n (%)]"
| PD-L1 antibody clone | Concordant case (n=68) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPS≥10 | CPS≥1 | TPS≥10% | TPS≥1% | IPS≥10% | IPS≥1% | |
| 22C3 vs E1L3N XP | 64 (94.1) | 66 (97.0) | 65 (95.6) | 65 (95.6) | 57 (83.8) | 47 (69.1) |
| 22C3 vs CST E1L3N | 64 (94.1) | 65 (95.6) | 64 (94.1) | 65 (95.6) | 52 (76.5) | 50 (73.5) |
| 22C3 vs BP6099 | 57 (83.8) | 63 (92.6) | 64 (94.1) | 63 (92.6) | 49 (72.0) | 57 (83.8) |
| 22C3 vs MXR006 | 60 (88.2) | 64 (94.1) | 65 (95.6) | 64 (94.1) | 50 (73.5) | 54 (79.4) |
| E1L3N XP vs CST E1L3N | 62 (91.2) | 67 (98.5) | 65 (95.6) | 66 (97.0) | 57 (83.8) | 55 (80.9) |
| E1L3N XP vs BP6099 | 51 (75.0) | 65 (95.6) | 65 (95.6) | 64 (94.1) | 56 (82.3) | 56 (82.3) |
| E1L3N XP vs MXR006 | 60 (88.2) | 66 (97.0) | 66 (97.0) | 65 (95.6) | 55 (80.9) | 57 (83.8) |
| CST E1L3N vs BP6099 | 59 (86.8) | 66 (97.0) | 66 (97.0) | 66 (97.0) | 61 (89.7) | 53 (77.9) |
| CST E1L3N vs MXR006 | 60 (88.2) | 65 (95.6) | 67 (98.5) | 65 (95.6) | 60 (88.2) | 58 (85.3) |
| BP6099 XP vs MXR006 | 61 (89.7) | 63 (92.6) | 65 (95.6) | 63 (92.6) | 57 (83.8) | 53 (77.9) |
| [1] | 李琦, 李涛, 范羽, 等. PD-1/PD-L1在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及临床意义[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗, 2018, 31(4)248-257 |
| LI Q, LI T, FAN Y, et al. Expression of PD-1/PD-L1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance[J]. J Cancer Control Treat, 2018, 31(4)248-257 | |
| [2] | 王程浩, 韩泳涛. 2020年中国临床肿瘤学会《食管癌诊疗指南》解读[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗, 2020, 33(4): 285-290. |
| WANG C H, HAN Y T. Interpretation of the 2020 guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal cancer by Chinese society of clinical oncology[J]. J Cancer Control Treat, 2020, 33(4): 285-290. | |
| [3] |
SHAH M A, KOJIMA T, HOCHHAUSER D, et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab for heavily pretreated patients with advanced, metastatic adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: the phase 2 KEYNOTE-180 study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5(4): 546-550.
doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5441 pmid: 30570649 |
| [4] |
KOJIMA T, SHAH M A, MURO K, et al. Randomized phase Ⅲ KEYNOTE-181 study of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in advanced esophageal cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(35): 4138-4148.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01888 |
| [5] |
HUANG Z L, JIN Y, CAI X, et al. Association of the programmed death ligand-1 combined positive score in tumors and clinicopathological features in esophageal cancer[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2022, 13(4): 523-532.
doi: 10.1111/tca.v13.4 |
| [6] |
GUO W, WANG P, LI N, et al. Prognostic value of PD-L1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(17): 13920-13933.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23810 pmid: 29568405 |
| [7] |
BANG Y J, RUIZ E Y, VAN CUTSEM E, et al. Phase Ⅲ, randomised trial of avelumab versus physician’s choice of chemotherapy as third-line treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: primary analysis of JAVELIN Gastric 300[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29(10): 2052-2060.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy264 |
| [8] |
MURO K, CHUNG H C, SHANKARAN V, et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-012): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(6): 717-726.
doi: S1470-2045(16)00175-3 pmid: 27157491 |
| [9] |
JANJIGIAN Y Y, BENDELL J, CALVO E, et al. CheckMate-032 study: efficacy and safety of nivolumab and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic esophagogastric cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(28): 2836-2844.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.6212 pmid: 30110194 |
| [10] |
LEONE A G, PETRELLI F, GHIDINI A, et al. Efficacy and activity of PD-1 blockade in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis with focus on the value of PD-L1 combined positive score[J]. ESMO Open, 2022, 7(1): 100380.
doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100380 |
| [11] |
HIRSCH F R, MCELHINNY A, STANFORTH D, et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry assays for lung cancer: results from phase 1 of the blueprint PD-L1 IHC assay comparison project[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2017, 12(2): 208-222.
doi: S1556-0864(16)33536-5 pmid: 27913228 |
| [12] |
TSAO M S, KERR K M, KOCKX M, et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry comparability study in real-life clinical samples: results of blueprint phase 2 project[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2018, 13(9): 1302-1311.
doi: S1556-0864(18)30626-9 pmid: 29800747 |
| [13] | KRIGSFELD G S, ZERBA K, NOVOTNY J Jr, et al. A comparative study of the PD-L1 IHC 22C3 and 28-8 assays on lung cancer samples[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol, 2019, 104(1): 236-237. |
| [14] |
WATANABE T, OKUDA K, MURASE T, et al. Four immunohistochemical assays to measure the PD-L1 expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(29): 20769-20780.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25100 pmid: 29755688 |
| [15] |
DE RUITER E J, MULDER F J, KOOMEN B M, et al. Comparison of three PD-L1 immunohistochemical assays in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)[J]. Mod Pathol, 2021, 34(6): 1125-1132.
doi: 10.1038/s41379-020-0644-7 |
| [16] | KRIGSFELD G S, PRINCE E, ZERBA K, et al. Analysis of real-world PD-L1 testing in patients with urothelial carcinoma[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(7_suppl): 447. |
| [17] |
KARNIK T, KIMLER B F, FAN F, et al. PD-L1 in breast cancer: comparative analysis of 3 different antibodies[J]. Hum Pathol, 2018, 72: 28-34.
doi: S0046-8177(17)30281-2 pmid: 28843709 |
| [18] |
ADAM J, LE STANG N, ROUQUETTE I, et al. Multicenter harmonization study for PD-L1 IHC testing in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2018, 29(4): 953-958.
doi: S0923-7534(19)45464-1 pmid: 29351573 |
| [19] |
BÜTTNER R, GOSNEY J R, SKOV B G, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 immunohistochemistry testing: a review of analytical assays and clinical implementation in non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(34): 3867-3876.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.7642 pmid: 29053400 |
| [20] |
UDALL M, RIZZO M, KENNY J, et al. PD-L1 diagnostic tests: a systematic literature review of scoring algorithms and test-validation metrics[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2018, 13(1): 12.
doi: 10.1186/s13000-018-0689-9 pmid: 29426340 |
| [1] | CAO Fei, YU Wenhao, TANG Xiaonan, MA Zidong, CHANG Tingmin, GONG Yabin, LIAO Mingjuan, KANG Xiaohong. Mechanism of LINC01410 promoting proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 753-762. |
| [2] | LIAO Ziyi, PENG Yang, ZENG Beilei, MA Yingying, ZENG Li, GAN Kelun, MA Daiyuan. Analysis of pathological remission degree and influencing factors of radical surgery after neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 669-679. |
| [3] | ZHANG Haoting, ZHENG Jing, FU Mengjiao, ZHOU Jianying. Research progress on thyroid dysfunction induced by immunotherapy for lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 701-706. |
| [4] | CD-Positive Lymphoma Pathology Expert Group. The standardization of immunohistochemical detection and interpretation of CD30 expression in lymphomas [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 228-234. |
| [5] | MA Xiao, XIANG Jiaqing, MA Longfei. Surgical treatment of esophagotracheal fistula caused by neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer: a case report [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(6): 542-544. |
| [6] | DUAN Yuqing, XIA Ning, JIA Yunlong, ZHENG Wenya, LIU Lihua. SRSF1 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Eca9706 cells by regulating VEGFA mRNA alternative splicing [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 191-199. |
| [7] | WU Quan, GUO Jingwei, LEI Yuxin, HU Xiaoru, WANG Zhe. Expression of MMR in 515 cases of endometrioid adenocarcinoma and its correlation with clinicopathological features [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1190-1198. |
| [8] | XU Ran , WANG Xinyue , FENG Linyuan , HAN Anna , WANG Yixuan , YANG Wanshan , LIU Chao . Expression and biological significance of NCAPD2 in glioma [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(9): 789-798. |
| [9] | CHEN Jie, WANG Yan, ZHANG Weimin, ZHAO Di, ZHANG Lingyuan, ZHAN Qimin. Hypoxia induces expression of IL-7 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to promote tumor progression [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(5): 361-367. |
| [10] | XIAO Feng , XIAO Jingwen , SHAO Jianguo , CHEN Liyan , GU Chunyan . The expression of programmed death 1 in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes of hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(5): 419-427. |
| [11] | FENG Runlin , HUA Jie , KUI Xiang , LI Ruyi , YI Xiaojia , WANG Yan , TAO Yanping . A case report of metastatic pericardial myxoid liposarcoma and literature review [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(3): 227-230. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jinzhong , LI Yueqi , SHI Ke , YANG Liang , GUO Dan . Expression and clinical significance of PLK4 gene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on cell proliferation, invasion and migration [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(12): 1185-1193. |
| [13] | LIU Wei , WANG Xiaojiang , ZHANG Jing , ZHU Weifeng , PENG Fengying , WANG Jianchao , XIAO Weijin , HU Dan . Clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic analysis of medullary thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(11): 1096-1103. |
| [14] | HUANG Ling , ZOU Yourui , MA Yue , LI Zhuoqi , GAO Xinyi , ABU Lagu , MA Hui . Expression difference and clinical significance of CHKα in different grades of gliomas [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(10): 892-898. |
| [15] | FENG Bo, WANG Gaoyan, LIANG Xiaoliang, WU Zheng, GUO Yanli, SHEN Supeng, GUO Wei. The expression level of FAM83H in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its effect on biological characteristics of esophageal cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(9): 674-681. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
