Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2022, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (10): 948-959.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.10.003
• Specialists'Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qingling( ), ZHANG Yunpeng, ZHOU Zandong, ZHANG Yue, LIU Tong(
), ZHANG Yunpeng, ZHOU Zandong, ZHANG Yue, LIU Tong( )
)
Received:2022-08-08
Revised:2022-10-18
Online:2022-10-30
Published:2022-11-29
Share article
CLC Number:
ZHANG Qingling, ZHANG Yunpeng, ZHOU Zandong, ZHANG Yue, LIU Tong. Construction of a mouse model of adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(10): 948-959.
Tab. 1
Summary of doxorubicin mouse model in document literature"
| Reference | Cumulative dose | Mode of administration |
|---|---|---|
| [ | 7 mg | 1 mg/kg, once a day for continued 7 days |
| [ | 15 mg | 15 mg/kg, once |
| [ | 2.5 mg/kg, every other day, six times in a row | |
| [ | 5 mg /kg, once a week for 3 weeks | |
| [ | 7.5 mg/kg, twice on alternate days | |
| [ | 16 mg | 4 mg/kg, once a week for 4 weeks |
| [ | 18 mg | 6 mg/kg, via tail vein at day 0, 2, and 4 |
| [ | 20 mg | 5 mg/kg, once a week for 4 weeks |
| [ | 20 mg/kg, once | |
| [ | 24 mg | 6 mg/kg, once a week for 4 weeks |
| [ | 25 mg | 5 mg/kg, once a week for 5 weeks |
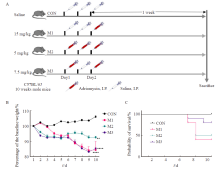
Fig. 1
Mice general condition monitoring A: Grouping and treatment; B: Change trend of percentage of body weight relative to baseline body weight in control group and model group; C: Survival curves of mice in control group and model group. CON: Control group; M1: Model group 1; M2: Model group 2; M3: Model group 3; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with each other; Data were expressed as x±s."
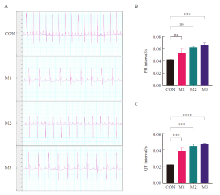
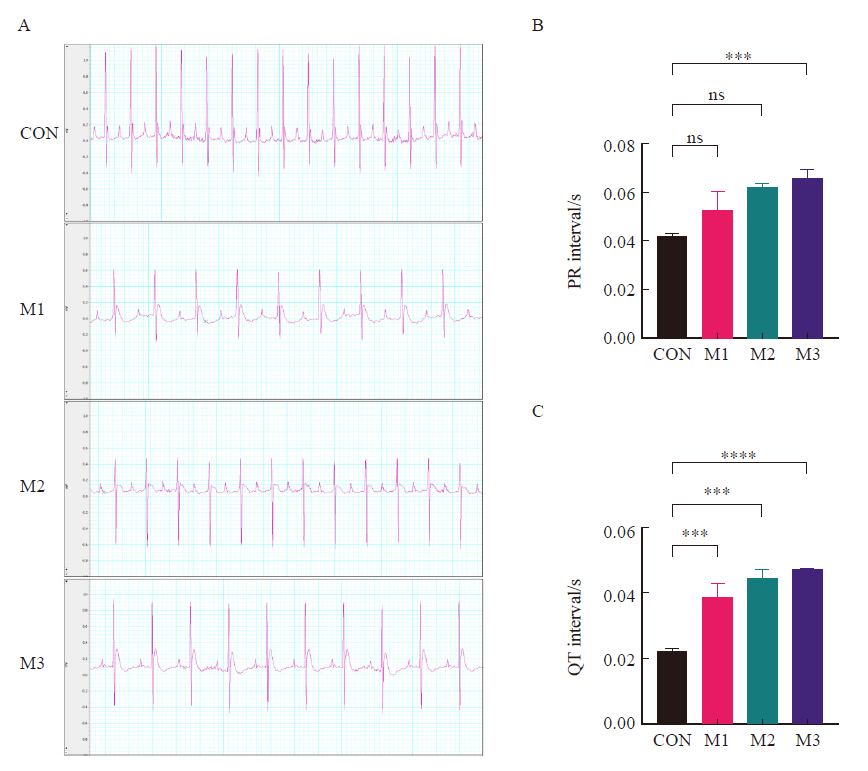
Fig. 2
Electrocardiogram and statistical results of each group A: Typical electrocardiogram; Arrows showed: T-wave flattening and duration extension in each model group; B-C: Statistical results of PR interval and QT interval; CON: Control group; M1: Model group 1; M2: Model group 2; M3: Model group 3; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with each other; Data were expressed as x±s. ns: No statistical significance."
Tab. 2
Comparison of echocardiography and electrocardiogram parameters in each group"
| Item | CON | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVIDd/mm | 3.752 4±0.133 9 | 3.738 9±0.152 0 | 3.427 8±0.157 4 | 3.247 3±0.229 8 |
| LVIDs/mm | 2.706 6±0.104 7 | 2.707 0±0.142 0 | 2.470 1±0.124 2 | 2.486 2±0.180 3 |
| LVPWd/mm | 0. 715 0±0.045 7 | 0.639 3±0.056 6 | 0.710 2±0.013 1 | 0.717 2±0.048 3 |
| LVPWs/mm | 0.990 9±0.027 5 | 0.686 3±0.019 6 | 0.916 1±0.030 3 | 0.927 0±0.071 7 |
| IVSd/mm | 0.787 2±0.075 6 | 0.822 8±0.100 7 | 0.778 2±0.049 9 | 0.727 3±0.053 9 |
| IVSs/mm | 1.200 4±0.039 3 | 1.130 3±0.182 4 | 0.951 7±0.027 9 | 0.940 5±0.046 2 |
| LVEF/% | 54.722 9±1.635 1 | 46.009 3±4.413 7 | 54.684 3±3.375 4 | 40.396 6±2.240 7* |
| LVFS/% | 27.880 8±1.050 3 | 22.568 3±2.503 1 | 27.857 9±2.202 7 | 19.395 5±1.207 5* |
| P wave duration/s | 0.014 0±0.001 3 | 0.012 0±0.000 7 | 0.012 1±0.000 3 | 0.015 3±0.001 2 |
| PR interval/s | 0.042 3±0.000 9 | 0.052 7±0.007 9 | 0.062 0±0.001 2 | 0.064 2±0.003 8** |
| QRS duration/s | 0.011 2±0.001 0 | 0.010 5±0.000 8 | 0.010 5±0.000 1 | 0.010 3±0.000 6 |
| QT interval/s | 0.022 0±0.000 9 | 0.038 6±0.004 4* | 0.044 4±0.003 0** | 0.047 5±0.000 2** |
| QTc interval/s | 0.041 9±0.002 0 | 0.072 1±0.007 5* | 0.848 1±0.003 4** | 0.637 7±0.004 2* |
| RR intervals/s | 0.148 5±0.008 6 | 0.152 2±0.007 6 | 0.143 3±0.011 7 | 0.164 8±0.017 5 |
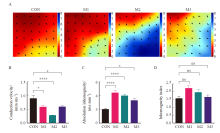
Fig. 3
Ventricular epicardial electrical conduction images and statistical results of mice in each group A: Mapping diagram; B-D: Mapping statistical results; CON: Control group; M1: Model group 1; M2: Model group 2; M3: Model group 3; *: P<0.05, compared with each other; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with each other; Data were expressed as x±s. ns: No statistical significance."
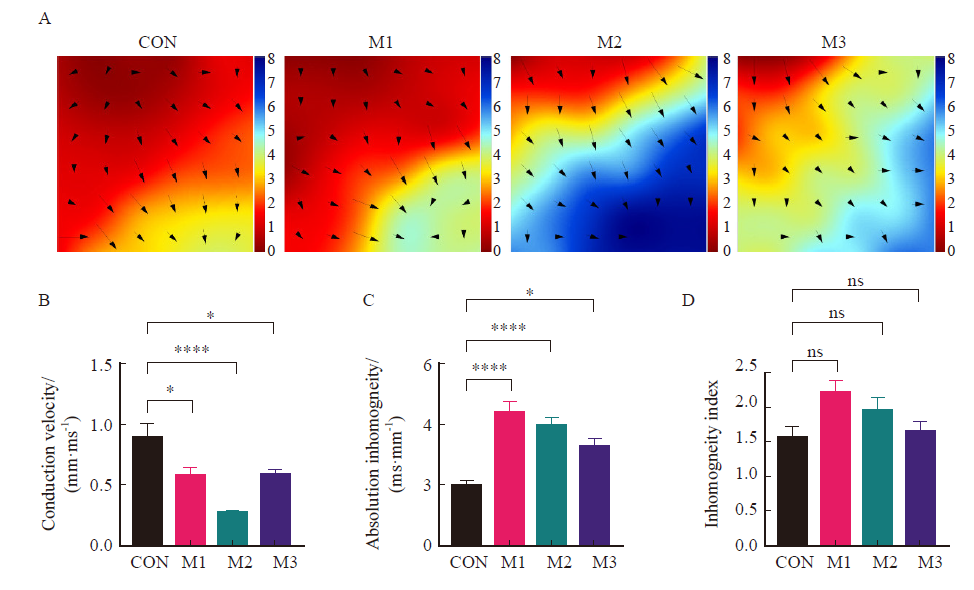
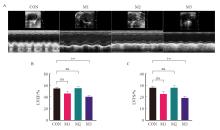
Fig. 4
M-model ultrasound images and statistical results of parasternal left ventricle in short axis section of mice in each group A: M-model ultrasound images of parasternal left ventricle in short axis section in each group; B-C: The statistical results of LVEF and LVFS; CON: Control group; M1: Model group 1; M2: Model group 2; M3: Model group 3; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; Data were expressed as x±s. ns: No statistical significance."
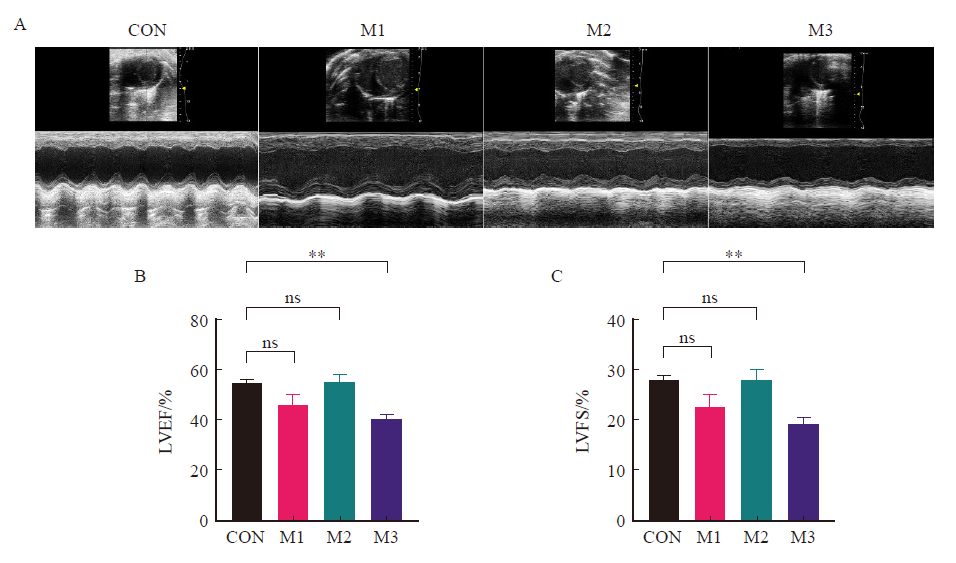
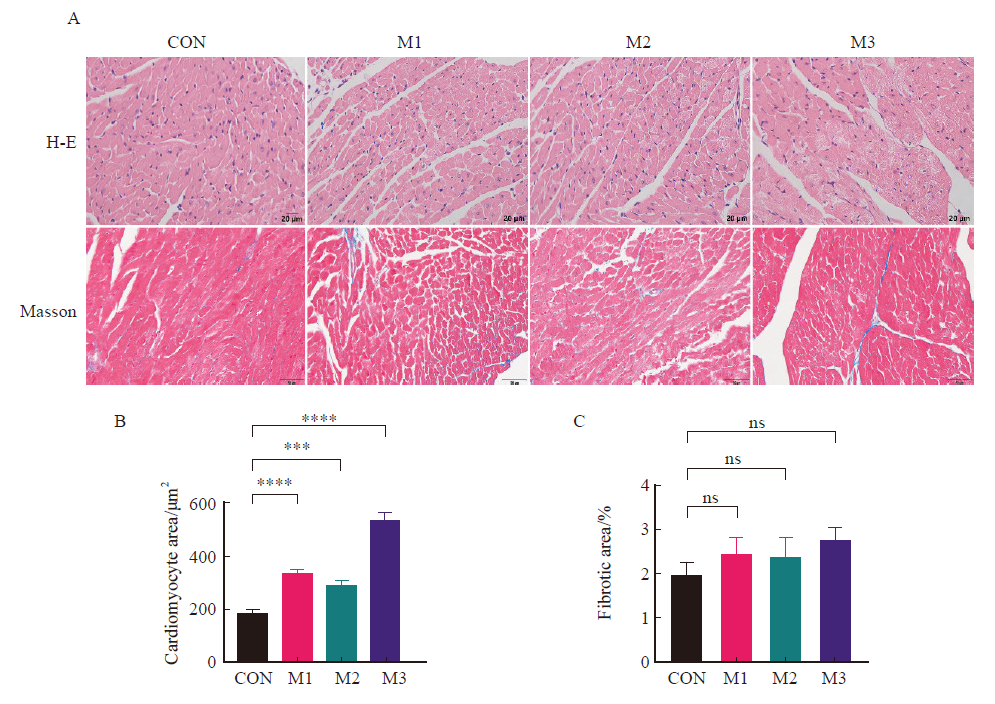
Fig. 6
H-E staining and Masson staining of left ventricular tissue in each group A: H-E staining and Masson staining; B: Cardiomyocyte vacuoles number; C: Fibrotic condition; CON: Control group; M1: Model group 1; M2: Model group 2; M3: Model group 3; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other; ****: P<0.000 1, compared with each other; Data were expressed as x±s. ns: No statistical significance."
| [1] | WILD C P, WEIDERPASS E, STEWART B W, et al. World cancer report: cancer research for cancer prevention. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer[R], 2020. |
| [2] |
SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, FUCHS H E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21654 |
| [3] | ZHENG R S, ZHANG S W, ZENG H M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2022, 2(1): 1-9. |
| [4] |
ARMENIAN S H, LACCHETTI C, BARAC A, et al. Prevention and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(8): 893-911.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.70.5400 pmid: 27918725 |
| [5] |
ARMENIAN S H, ROBISON L L. Childhood cancer survivorship: an update on evolving paradigms for understanding pathogenesis and screening for therapy-related late effects[J]. Curr Opin Pediatr, 2013, 25(1): 16-22.
doi: 10.1097/MOP.0b013e32835b0b6a |
| [6] |
GUDMUNDSDOTTIR T, WINTHER J F, DE FINE LICHT S, et al. Cardiovascular disease in adult life after childhood cancer in Scandinavia: a population-based cohort study of 32 308 one-year survivors[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 137(5): 1176-1186.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.29468 |
| [7] |
HARVEY V J, SLEVIN M L, PONDER B A, et al. Chemotherapy of diffuse malignant mesothelioma. Phase Ⅱ trials of single-agent 5-fluorouracil and adriamycin[J]. Cancer, 1984, 54(6): 961-964.
doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840915)54:6<961::AID-CNCR2820540602>3.0.CO;2-B |
| [8] |
SØRENSEN P G, BACH F, BORK E, et al. Randomized trial of doxorubicin versus cyclophosphamide in diffuse malignant pleural mesothelioma[J]. Cancer Treat Rep, 1985, 69(12): 1431-1432.
pmid: 3907825 |
| [9] |
SCHERPEREEL A, BERGHMANS T, LAFITTE J J, et al. Valproate-doxorubicin: promising therapy for progressing mesothelioma. A phase Ⅱ study[J]. Eur Respir J, 2011, 37(1): 129-135.
doi: 10.1183/09031936.00037310 |
| [10] |
BUIKHUISEN W A, HIDDINGA B I, BAAS P, et al. Second line therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: a systematic review[J]. Lung Cancer, 2015, 89(3): 223-231.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.06.018 pmid: 26162564 |
| [11] |
DIMARCO A, GAETANI M, OREZZI P, et al. “Daunomycin”, a new antibiotic of the rhodomycin group[J]. Nature, 1964, 201: 706-707.
doi: 10.1038/201706a0 |
| [12] | CHABNER B A, LONGO D L. Cancer chemotherapy and biotherapy: principles and practice[M]. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2011. |
| [13] | COUFAL N, FARNAES L. Anthracyclines and anthraceneodiones[M]//Cancer management in man:chemotherapy, biological therapy, hyperthermia and supporting measures. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 2010: 87-102. |
| [14] | CURIGLIANO G, CARDINALE D, SUTER T, et al. Cardiovascular toxicity induced by chemotherapy, targeted agents and radiotherapy: ESMO clinical practice guidelines[J]. Ann Oncol, 2012, 23(Suppl 7): Ⅶ155-166. |
| [15] |
ZHANG X, HU C, KONG C Y, et al. FNDC5 alleviates oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via activating AKT[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(2): 540-555.
doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0372-z pmid: 31209361 |
| [16] |
SANGOMLA S, SAIFI M A, KHURANA A, et al. Nanoceria ameliorates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity: possible mitigation via reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. J Trace Elem Med Biol, 2018, 47: 53-62.
doi: S0946-672X(17)30771-X pmid: 29544808 |
| [17] |
RUSSO M, GUIDA F, PAPARO L, et al. The novel butyrate derivative phenylalanine-butyramide protects from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2019, 21(4): 519-528.
doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1439 pmid: 30843309 |
| [18] |
ZHAO L S, QI Y, XU L N, et al. microRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2[J]. Redox Biol, 2018, 15: 284-296.
doi: S2213-2317(17)30910-2 pmid: 29304479 |
| [19] |
ZHANG H W, XU A D, SUN X, et al. Self-maintenance of cardiac resident reparative macrophages attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy through the SR-A1-c-Myc axis[J]. Circ Res, 2020, 127(5): 610-627.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.316428 pmid: 32466726 |
| [20] |
HU C, ZHANG X, WEI W Y, et al. Matrine attenuates oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via maintaining AMPKα/UCP2 pathway[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2019, 9(4): 690-701.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.03.003 |
| [21] | TADOKORO T, IKEDA M, IDE T, et al. Mitochondria-dependent ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity[J]. JCI Insight, 2020, 5(9): 132747. |
| [22] | WANG C Y, CHEN C C, LIN M H, et al. TLR9 binding to beclin 1 and mitochondrial SIRT3 by a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor protects the heart from doxorubicin toxicity[J]. Biology (Basel), 2020, 9(11): E369. |
| [23] |
WANG A J, TANG Y F, ZHANG J J, et al. Cardiac SIRT1 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting sestrin 2[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102310.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102310 |
| [24] |
FANG X X, WANG H, HAN D, et al. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy[J]. PNAS, 2019, 116(7): 2672-2680.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821022116 pmid: 30692261 |
| [25] |
CHAN B Y H, ROCZKOWSKY A, CHO W J, et al. MMP inhibitors attenuate doxorubicin cardiotoxicity by preventing intracellular and extracellular matrix remodelling[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2021, 117(1): 188-200.
doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa017 pmid: 31995179 |
| [26] |
GUPTA S K, GARG A, BÄR C, et al. Quaking inhibits doxorubicin-mediated cardiotoxicity through regulation of cardiac circular RNA expression[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 122(2): 246-254.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311335 pmid: 29133306 |
| [27] |
WU X T, WANG L J, WANG K, et al. ADAR2 increases in exercised heart and protects against myocardial infarction and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Mol Ther, 2022, 30(1): 400-414.
doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.07.004 |
| [28] |
SOKER M, KERVANCIOGLU M. Plasma concentrations of NT-pro-BNP and cardiac troponin-I in relation to doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and cardiac function in childhood malignancy[J]. Saudi Med J, 2005, 26(8): 1197-1202.
pmid: 16127512 |
| [29] |
SAWICKI K T, SALA V, PREVER L, et al. Preventing and treating anthracycline cardiotoxicity: new insights[J]. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, 2021, 61: 309-332.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-030620-104842 pmid: 33022184 |
| [30] |
FERRANS V J. Overview of cardiac pathology in relation to anthracycline cardiotoxicity[J]. Cancer Treat Rep, 1978, 62(6): 955-961.
pmid: 352510 |
| [31] |
SHAN K, LINCOFF A M, YOUNG J B. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1996, 125(1): 47-58.
pmid: 8644988 |
| [32] |
BERRY G J, JORDEN M. Pathology of radiation and anthracycline cardiotoxicity[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2005, 44(7): 630-637.
pmid: 15825155 |
| [33] |
SWAIN S M, WHALEY F S, EWER M S. Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: a retrospective analysis of three trials[J]. Cancer, 2003, 97(11): 2869-2879.
pmid: 12767102 |
| [34] |
JONES L W, HAYKOWSKY M, PEDDLE C J, et al. Cardiovascular risk profile of patients with HER2/neu-positive breast cancer treated with anthracycline-taxane-containing adjuvant chemotherapy and/or trastuzumab[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2007, 16(5): 1026-31.
doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0870 |
| [35] |
AMIOKA M, SAIRAKU A, OCHI T, et al. Prognostic significance of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma treated with anthracyclines[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2016, 118(9): 1386-1389.
doi: S0002-9149(16)31319-4 pmid: 27600461 |
| [36] |
MAZUR M, WANG F L, HODGE D O, et al. Burden of cardiac arrhythmias in patients with anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2017, 3(2): 139-150.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2016.08.009 |
| [37] |
KILICKAP S, BARISTA I, AKGUL E, et al. Early and late arrhythmogenic effects of doxorubicin[J]. South Med J, 2007, 100(3): 262-265.
pmid: 17396729 |
| [38] |
FRADLEY M G, VIGANEGO F, KIP K, et al. Rates and risk of arrhythmias in cancer survivors with chemotherapy-induced cardiomyopathy compared with patients with other cardiomyopathies[J]. Open Heart, 2017, 4(2): e000701.
doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2017-000701 |
| [39] |
QIN Y, GUO T, WANG Z, et al. The role of iron in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: recent advances and implication for drug delivery[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2021, 9(24): 4793-4803.
doi: 10.1039/d1tb00551k pmid: 34059858 |
| [40] |
IKEDA S, MATSUSHIMA S, OKABE K, et al. Blockade of L-type Ca2 + channel attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via suppression of CaMKⅡ-NF-κB pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 9850.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46367-6 |
| [41] |
ZHANG Y S, KNIGHT W, CHEN S, et al. Multiprotein complex with TRPC (transient receptor potential-canonical) channel, PDE1C (phosphodiesterase 1C), and A2R (adenosine A2 receptor) plays a critical role in regulating cardiomyocyte cAMP and survival[J]. Circulation, 2018, 138(18): 1988-2002.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034189 pmid: 29871977 |
| [42] |
HU C, ZHANG X, SONG P, et al. Meteorin-like protein attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via activating cAMP/PKA/SIRT1 pathway[J]. Redox Biol, 2020, 37: 101747.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101747 |
| [43] |
PAN J A, ZHANG H, LIN H, et al. Irisin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiac perivascular fibrosis through inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by regulating ROS accumulation and autophagy disorder in endothelial cells[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 46: 102120.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102120 |
| [44] |
GRATIA S, KAY L, POTENZA L, et al. Inhibition of AMPK signalling by doxorubicin: at the crossroads of the cardiac responses to energetic, oxidative, and genotoxic stress[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2012, 95(3): 290-299.
doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs134 pmid: 22461523 |
| [45] |
ANJOS M, FONTES-OLIVEIRA M, COSTA V M, et al. An update of the molecular mechanisms underlying doxorubicin plus trastuzumab induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 280: 119760.
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119760 |
| [46] |
EBRAHIM N, AL SAIHATI H A, MOSTAFA O, et al. Prophylactic evidence of MSCs-derived exosomes in doxorubicin/trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: beyond mechanistic target of NRG-1/erb signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 5967.
doi: 10.3390/ijms23115967 |
| [47] | MODESTO P N, POLEGATO B F, DOS SANTOS P P, et al. Green tea (camellia sinensis) extract increased topoisomerase Ⅱ β, improved antioxidant defense, and attenuated cardiac remodeling in an acute doxorubicin toxicity model[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021, 2021: 8898919. |
| [48] |
VEJPONGSA P, YEH E. Topoisomerase 2β: a promising molecular target for primary prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 95(1): 45-52.
doi: 10.1038/clpt.2013.201 pmid: 24091715 |
| [49] |
BEJI S, D'AGOSTINO M, GAMBINI E, et al. Doxorubicin induces an alarmin-like TLR4-dependent autocrine/paracrine action of nucleophosmin in human cardiac mesenchymal progenitor cells[J]. BMC Biol, 2021, 19(1): 124.
doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01058-5 pmid: 34134693 |
| [50] |
LIU P, BAO H Y, JIN C C, et al. Targeting extracellular heat shock protein 70 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced heart failure through resolution of toll-like receptor 2-mediated myocardial inflammation[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2019, 8(20): e012338.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012338 |
| [51] |
MA Z G, KONG C Y, WU H M, et al. Toll-like receptor 5 deficiency diminishes doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity in mice[J]. Theranostics, 2020, 10(24): 11013-11025.
doi: 10.7150/thno.47516 |
| [52] |
SENEVIRATNE A K, XU M J, HENAO J J A, et al. The mitochondrial transacylase, tafazzin, regulates for AML stemness by modulating intracellular levels of phospholipids[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2019, 24(4): 621-636.e16.
doi: S1934-5909(19)30072-4 pmid: 30930145 |
| [53] |
WANG P X, WANG M H, HU Y H, et al. Isorhapontigenin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via increasing YAP1 expression[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(3): 680-693.
doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.017 |
| [54] |
XIAO M J, TANG Y F, WANG J (, et al. A new FGF1 variant protects against adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity via modulating p53 activity[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 49: 102219.
doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102219 |
| [55] |
SHAIKH F, DUPUIS L L, ALEXANDER S, et al. Cardioprotection and second malignant neoplasms associated with dexrazoxane in children receiving anthracycline chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2016, 108(4): djv357.
doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv357 |
| [56] |
JIRKOVSKÁ A, KARABANOVICH G, KUBEŠ J, et al. Structure-activity relationship study of dexrazoxane analogues reveals ICRF-193 as the most potent bisdioxopiperazine against anthracycline toxicity to cardiomyocytes due to its strong topoisomerase Ⅱβ interactions[J]. J Med Chem, 2021, 64(7): 3997-4019.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02157 |
| [57] |
TEBBI C K, LONDON W B, FRIEDMAN D, et al. Dexrazoxane-associated risk for acute myeloid leukemia/myelodysplastic syndrome and other secondary malignancies in pediatric Hodgkin's disease[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(5): 493-500.
pmid: 17290056 |
| [58] |
HORACEK J M, JAKL M, HORACKOVA J, et al. Assessment of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity with electrocardiography[J]. Exp Oncol, 2009, 31(2): 115-117.
pmid: 19550402 |
| [59] |
ARBEL Y, SWARTZON M, JUSTO D. QT prolongation and Torsades de Pointes in patients previously treated with anthracyclines[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2007, 18(4): 493-498.
doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e328012d023 |
| [60] |
TAKEMURA G, FUJIWARA H. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy from the cardiotoxic mechanisms to management[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2007, 49(5): 330-352.
pmid: 17329180 |
| [61] | KUNO A, HOSODA R, TSUKAMOTO M, et al. SIRT1 in the cardiomyocyte counteracts doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via regulating histone H2AX[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2022: cvac026. |
| [62] |
SINGAL P K, ILISKOVIC N. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 1998, 339(13): 900-5.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199809243391307 |
| [63] |
SHEN Y H, ZHANG H, NI Y Y, et al. Tripartite motif 25 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by degrading p85α[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(7): 643.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05100-4 pmid: 35871160 |
| [1] | WU Wen, ZHANG Ruoxin, WENG Junyong, MA Yanlei, CAI Guoxiang, LI Xinxiang, YANG Yongzhi. Exploring the prognostic value of positive lymph node ratio in stage Ⅲ colorectal cancer patients and establishing a predictive model [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 873-880. |
| [2] | WENG Junyong, YE Zilan, ZHANG Ruoxin, LIU Qi, LI Xinxiang. Exploring the guiding role of the number of adverse pathological features in risk stratification for recurrence of stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ colorectal cancer: a retrospective cohort study of 9 875 cases [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 527-536. |
| [3] | TANG Nan, HUANG Huixia, LIU Xiaojian. Integrated single-cell sequencing and transcriptome sequencing to reveal a 9-gene prognostic signature of immune cells in colorectal cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 548-560. |
| [4] | HAO Xian, HUANG Jianjun, YANG Wenxiu, LIU Jinting, ZHANG Junhong, LUO Yubei, LI Qing, WANG Dahong, GAO Yuwei, TAN Fuyun, BO Li, ZHENG Yu, WANG Rong, FENG Jianglong, LI Jing, ZHAO Chunhua, DOU Xiaowei. Establishment of primary breast cancer cell line as new model for drug screening and basic research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 561-570. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ruoxin, YE Zilan, WENG Junyong, LI Xinxiang. Correlation study between advanced age and inferior prognosis in stage Ⅱ colorectal cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 485-492. |
| [6] | OUYANG Fei, WANG Yang, CHEN Yu, PEI Guoqing, WANG Ling, ZHANG Yang, SHI Lei. Construction of the prediction model of breast cancer bone metastasis based on machine learning [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 903-914. |
| [7] | DONG Hao, QIU Yonggang, WANG Xinbin, YANG Junjie, LOU Cuncheng, YIN Lekang, YE Xiaodan. Predictive value of logistic regression model based on high-resolution CT signs for high-grade pattern in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 768-775. |
| [8] | ZHONG Yang, YANG Yanju, ZHAO Jun, HU Weigang. The feasibility and implementation of a golden beam model in Monaco treatment planning system [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 452-459. |
| [9] | YANG Wenxiao, GUO Linwei, LING Hong, HU Xin. Characterization of immune microenvironment identifies prognostic and immunotherapy benefit for trastuzumab-based therapy [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 484-498. |
| [10] | LIU Jialin, ZHANG Xianyu, PANG Da. Research progress of adaptive therapy strategy based on Darwinian dynamics in tumor therapy [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(4): 397-402. |
| [11] | LU Yu, XI Yumeng, HE Xiaoming, YANG Shaokun, ZHANG Jia, WANG Lei, HE Chaoxing, XIANG Bai. Advances in the application of co-culture strategies in organoids [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 293-302. |
| [12] | FU Qingsheng, JIN Lei, ZHANG Xudong, XU Yingchen, ZHU Chunfu, QIN Xihu, WU Baoqiang. Effect of tRF-Pro-CGG on the biological behavior of mouse pancreatic cancer cells and its molecular mechanism [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 241-249. |
| [13] | CHEN Yingyao, CHU Xiangling, YU Xin, SU Chunxia. Advances in models predicting efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 61-70. |
| [14] | CUI Lingjun, TIAN Chao, CHENG Zixuan, ZHENG Jiabin, SU Fei, TAN Huangying. Advances in preclinical research models for gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(9): 779-785. |
| [15] | XU Yuchen, CHENG Leilei, WANG Yan, LIN Jinyi, CHEN Jiahui, CHEN Yifan, ZHOU Yuhong, LIU Tianshu, GE Junbo. Predictive value of sST2 level in immune-related adverse events [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(8): 712-718. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
