Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 768-775.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.08.005
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Hao1( ), QIU Yonggang1, WANG Xinbin1, YANG Junjie2, LOU Cuncheng1, YIN Lekang3(
), QIU Yonggang1, WANG Xinbin1, YANG Junjie2, LOU Cuncheng1, YIN Lekang3( ), YE Xiaodan3,4,5(
), YE Xiaodan3,4,5( )
)
Received:2023-02-03
Revised:2023-05-12
Online:2023-08-30
Published:2023-09-01
Contact:
YIN Lekang, YE Xiaodan
E-mail:yuanyxd@163.com
Share article
CLC Number:
DONG Hao, QIU Yonggang, WANG Xinbin, YANG Junjie, LOU Cuncheng, YIN Lekang, YE Xiaodan. Predictive value of logistic regression model based on high-resolution CT signs for high-grade pattern in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 768-775.
Tab. 1
Clinical and pathological characteristics of patients"
| Item | Total | HGP (n=88) | n-HGP (n=357) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age/year | 58±11 | 57±12 | 61±9 | 0.037△ |
| Gender | 0.015# | |||
| Male | 158 | 41 | 117 | |
| Female | 287 | 47 | 240 | |
| Smoking history | 0.003# | |||
| No | 390 | 69 | 321 | |
| Yes | 55 | 19 | 36 | |
| Location | 0.401# | |||
| Left upper lobe | 108 | 22 | 86 | |
| Left lower lobe | 69 | 17 | 52 | |
| Right upper lobe | 148 | 29 | 119 | |
| Right middle lobe | 36 | 9 | 27 | |
| Right lower lobe | 84 | 11 | 73 | |
| Clinical T staging | <0.001# | |||
| T1a | 121 | 10 | 111 | |
| T1b | 258 | 54 | 204 | |
| T1c | 66 | 24 | 42 | |
| Pure or mix pattern | 0.008* | |||
| Pure | 27 | 0 | 27 | |
| Mix | 418 | 88 | 330 | |
| Major histological patterns | <0.001* | |||
| Lepidic predominant | 52 | 1 | 51 | |
| Acinar predominant | 348 | 71 | 280 | |
| Papillary predominant | 32 | 6 | 26 | |
| Micropapillary | 4 | 4 | 0 | |
| Solid predominant | 9 | 9 | 0 |
Tab. 2
Observer consistency test results for CT features"
| Item | Case n | SE | Kappa value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 443 | 0.012 | 0.983 | 0.955-1.000 |
| Shape | 440 | 0.013 | 0.972 | 0.942-0.994 |
| Lobulation | 422 | 0.022 | 0.892 | 0.847-0.933 |
| Spiculation | 430 | 0.018 | 0.924 | 0.886-0.956 |
| Vacuole | 427 | 0.048 | 0.791 | 0.685-0.837 |
| Air bronchogram | 435 | 0.015 | 0.955 | 0.926-0.982 |
| Pleural indentation | 442 | 0.008 | 0.986 | 0.968-1.000 |
Tab. 3
Comparison of CT features of lesions between the HGP and n-HGP groups"
| Item | Total | HGP (n=88) | n-HGP (n=357) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor size D/mm | 14±5 | 17±5 | 14±5 | <0.001△ |
| Density | <0.001# | |||
| SSN | 377 | 45 | 332 | |
| SN | 68 | 43 | 25 | |
| Shape | 0.003# | |||
| Round or oval | 129 | 14 | 115 | |
| Irregular | 316 | 74 | 242 | |
| Lobulation | <0.001# | |||
| No | 287 | 25 | 262 | |
| Yes | 158 | 63 | 95 | |
| Spiculation | <0.001# | |||
| No | 296 | 32 | 264 | |
| Yes | 149 | 56 | 93 | |
| Vacuole | 0.764# | |||
| No | 406 | 81 | 325 | |
| Yes | 39 | 7 | 32 | |
| Air bronchogram | 0.162# | |||
| No | 242 | 42 | 200 | |
| Yes | 203 | 46 | 157 | |
| Pleural indentation | <0.001# | |||
| No | 256 | 33 | 223 | |
| Yes | 189 | 55 | 134 |

Fig. 1
CT and pathology images of SSN in the upper lobe of the left lung A 55-year-old male patient, no smoking history. A: HRCT transection lung window showed SSN in the upper lobe of the left lung, with a length diameter of about 15 mm and no lobes around it; B: Reconstructed image (coronal position), nodules did not show lobulation signs; C: Pathological diagram, the result was acinar predominant invasive adenocarcinoma (H-E, ×100)."
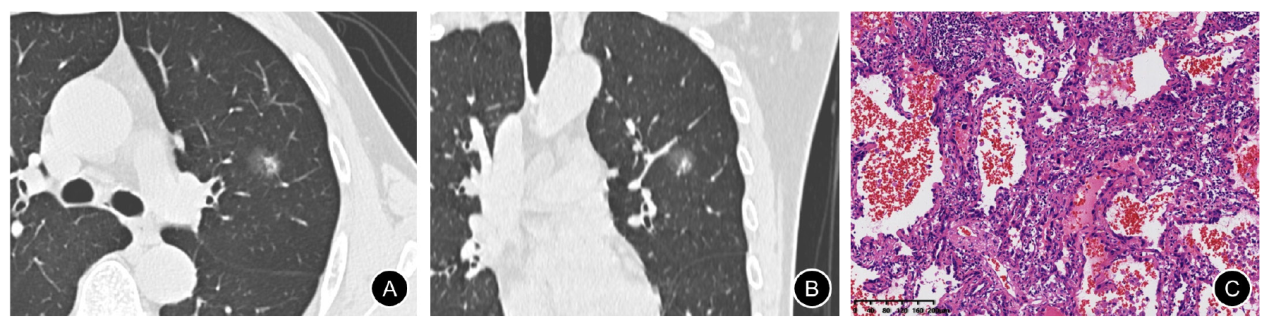

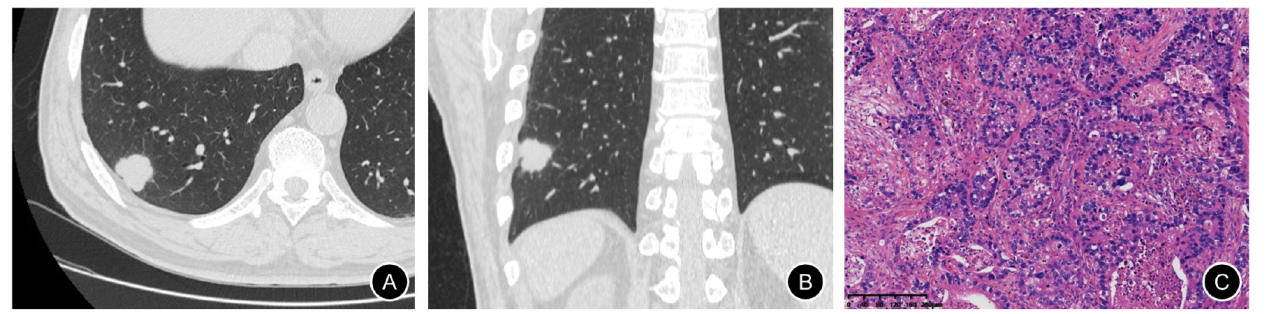
Fig. 2
CT and pathology images of SN in the lower lobe of the right lung A 58-year-old male patient with a smoking history of 30 years. A: HRCT transection lung window showed SN in the upper lobe of the left lung, with a long diameter of about 26 mm, and the lobulation sign was visible around the periphery; B: Reconstruction image (coronal position), nodules showed lobulation signs; C: Pathological diagram, the result was solid predominant invasive adenocarcinoma (H-E, ×100)."
Tab. 4
Comparison of diagnostic performance of CT model and univariate signs in predicting HGP"
| Item | AUC (95% CI) | Sensitivity/% | Specificity/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| CT model | 0.838 (0.788-0.889) | 70.5 | 84.9 |
| Tumor size | 0.695 (0.636-0.755) | 75.0 | 56.4 |
| Density | 0.709 (0.640-0.778) | 48.9 | 97.0 |
| Shape | 0.582 (0.519-0.644) | 84.1 | 32.2 |
| Lobulation | 0.725 (0.664-0.785) | 71.6 | 73.4 |
| Spiculation | 0.688 (0.624-0.752) | 63.6 | 73.9 |
| Pleural indentation | 0.625 (0.560-0.690) | 62.5 | 62.5 |
| [1] |
TRAVIS W D, BRAMBILLA E, NOGUCHI M, et al. International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2011, 6(2): 244-285.
doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 pmid: 21252716 |
| [2] |
TAKAHASHI Y, EGUCHI T, KAMEDA K, et al. Histologic subtyping in pathologic stage Ⅰ-ⅡA lung adenocarcinoma provides risk-based stratification for surveillance[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(87): 35742-35751.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.v9i87 |
| [3] |
YASUKAWA M, OHBAYASHI C, KAWAGUCHI T, et al. Analysis of histological grade in resected lung-invasive adenocarcinoma[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(3): 1491-1500.
doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13267 pmid: 30842187 |
| [4] |
JEON H W, KIM Y D, SIM S B, et al. Significant difference in recurrence according to the proportion of high grade patterns in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2021, 12(13): 1952-1958.
doi: 10.1111/tca.v12.13 |
| [5] |
VAN SCHIL P E, ASAMURA H, RUSCH V W, et al. Surgical implications of the new IASLC/ATS/ERS adenocarcinoma classification[J]. Eur Respir J, 2012, 39(2): 478-486.
doi: 10.1183/09031936.00027511 pmid: 21828029 |
| [6] |
HUNG J J, JENG W J, CHOU T Y, et al. Prognostic value of the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society lung adenocarcinoma classification on death and recurrence in completely resected stage Ⅰ lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2013, 258(6): 1079-1086.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31828920c0 |
| [7] | HUNG J J, YEH Y C, JENG W J, et al. Predictive value of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification of lung adenocarcinoma in tumor recurrence and patient survival[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(22): 2357-2364. |
| [8] |
CHOI Y, KIM J, PARK H, et al. Rethinking a non-predominant pattern in invasive lung adenocarcinoma: prognostic dissection focusing on a high-grade pattern[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(11): 2785.
doi: 10.3390/cancers13112785 |
| [9] |
TAKAHASHI Y, KURODA H, OYA Y, et al. Challenges for real-time intraoperative diagnosis of high risk histology in lung adenocarcinoma: a necessity for sublobar resection[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2019, 10(8): 1663-1668.
doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13133 pmid: 31287246 |
| [10] |
ANDRE L, MOREIRA, MD P, et al. A grading system for invasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma: a proposal from the international association for the study of lung cancer pathology committee[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2020, 15(10): 1599-1610.
doi: S1556-0864(20)30468-8 pmid: 32562873 |
| [11] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 |
| [12] |
KUHN E, MORBINI P, CANCELLIERI A, et al. Adenocarcinoma classification: patterns and prognosis[J]. Pathologica, 2018, 110(1): 5-11.
pmid: 30259909 |
| [13] |
ZHANG Y, QIANG J W, SHEN Y, et al. Using air bronchograms on multi-detector CT to predict the invasiveness of small lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2016, 85(3): 571-577.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.12.014 pmid: 26860669 |
| [14] | 金鑫, 赵绍宏, 高洁, 等. 纯磨玻璃密度肺腺癌病理分类及影像表现特点分析[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2014, 48(4): 283-287 |
| JIN X, ZHAO S H, GAO J, et al. Pathological classification and imaging characteristics of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma with pure ground-glass opacity[J]. Chin J Radiol, 2014, 48(4): 283-287 | |
| [15] | 蔡蒙婷, 纪晓微, 傅钢泽, 等. 含气腔型浸润性肺小腺癌的CT表现与病理分型的对照研究[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2019, 53(10): 886-891. |
| [16] |
ZHANG D G, CHEN X C, ZHU D X, et al. Intrapulmonary lymph node metastasis is common in clinically staged ⅠA adenocarcinoma of the lung[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2019, 10(2): 123-127.
doi: 10.1111/tca.2019.10.issue-2 |
| [17] |
YU Y, JIAN H, SHEN L, et al. Lymph node involvement influenced by lung adenocarcinoma subtypes in tumor size ≤3 cm disease: a study of 2 268 cases[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2016, 42(11): 1714-1719.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.02.247 |
| [18] |
MIKUBO M, NAITO M, MATSUI Y, et al. Relevance of intraoperative pleural lavage cytology and histologic subtype in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2018, 106(6): 1654-1660.
doi: S0003-4975(18)31256-6 pmid: 30227125 |
| [19] |
LEE G, CHOI E R, LEE H Y, et al. Pathologic heterogeneity of lung adenocarcinomas: a novel pathologic index predicts survival[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(43): 70353-70363.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11857 pmid: 27612421 |
| [20] |
SUNG Y E, LEE K Y, MOON Y. The prognostic utility of the histologic subtype of stage Ⅰ lung adenocarcinoma may be diminished when using only the invasive component to determine tumor size for tumor node metastasis (TNM) staging[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(5): 2910-2922.
doi: 10.21037/jtd |
| [21] |
CHEN L W, YANG S M, WANG H J, et al. Prediction of micropapillary and solid pattern in lung adenocarcinoma using radiomic values extracted from near-pure histopathological subtypes[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(7): 5127-5138.
doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07570-6 |
| [22] |
SUN F H, HUANG Y W, YANG X D, et al. Solid component ratio influences prognosis of GGO-featured ⅠA stage invasive lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Imaging, 2020, 20(1): 87.
doi: 10.1186/s40644-020-00363-6 |
| [23] |
MIYOSHI T, AOKAGE K, KATSUMATA S, et al. Ground-glass opacity is a strong prognosticator for pathologic stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 2019, 108(1): 249-255.
doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2019.01.079 |
| [24] |
MA X, ZHOU S, HUANG L, et al. Assessment of relationships among clinicopathological characteristics, morphological computer tomography features, and tumor cell proliferation in stage Ⅰ lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(5): 2844-2857.
doi: 10.21037/jtd |
| [1] | WENG Junyong, YE Zilan, ZHANG Ruoxin, LIU Qi, LI Xinxiang. Exploring the guiding role of the number of adverse pathological features in risk stratification for recurrence of stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ colorectal cancer: a retrospective cohort study of 9 875 cases [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 527-536. |
| [2] | ZHANG Ruoxin, YE Zilan, WENG Junyong, LI Xinxiang. Correlation study between advanced age and inferior prognosis in stage Ⅱ colorectal cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 485-492. |
| [3] | OUYANG Fei, WANG Yang, CHEN Yu, PEI Guoqing, WANG Ling, ZHANG Yang, SHI Lei. Construction of the prediction model of breast cancer bone metastasis based on machine learning [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 903-914. |
| [4] | JIA Liqing, GE Xiaolu, JIANG Lin, ZHOU Xiaoyan. Effects of lncRNA PKD2-2-3 on cell proliferation, clone formation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 717-725. |
| [5] | LIU Xiaoli, CHAI Wenjun, SUN Lei, YAN Mingxia, PAN Hongyu, SUN Yuexi. Analysis of differential splicing gene by regulation of splicing regulatory protein KHSRP in lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 637-645. |
| [6] | YANG Wenxiao, GUO Linwei, LING Hong, HU Xin. Characterization of immune microenvironment identifies prognostic and immunotherapy benefit for trastuzumab-based therapy [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 484-498. |
| [7] | CHEN Yingyao, CHU Xiangling, YU Xin, SU Chunxia. Advances in models predicting efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 61-70. |
| [8] | XU Yuchen, CHENG Leilei, WANG Yan, LIN Jinyi, CHEN Jiahui, CHEN Yifan, ZHOU Yuhong, LIU Tianshu, GE Junbo. Predictive value of sST2 level in immune-related adverse events [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(8): 712-718. |
| [9] | MU Jiaqian, TENG Xiaoyan, WEI Lirong, QIU Rong, GUI Pengcheng, DU Yuzhen. The role and application value of integrin β3 in bone metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(4): 351-356. |
| [10] | ZHU Haipeng, HU Jun, JIANG Min, CAI Ruonan, WANG Junqiao, LI Li. A study on mechanism of GOLM1 regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to promote proliferation, invasion and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 207-217. |
| [11] | HOU Qinghua, ZHONG Yanfeng, LIU Linzhuang, WU Liusheng, LIU Jixian. Expression, prognostic value of CBX3 in lung adenocarcinoma and its effect on biological behavior of cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(2): 152-160. |
| [12] | ZHANG Longfu, LIU Jie, NI Zheng, LU Xinyuan, HU Bin, WANG Hao, FENG Mingxiang, ZHANG Yong. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting spread through air spaces in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1210-1217. |
| [13] | HU Guannan , CHEN Lei , ZHOU Liangping , ZHOU Zhengrong . A case report of pulmonary malignant melanoma complicated with lung adenocarcinoma and literature review [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 647-650. |
| [14] | HU Yaqiong , BAI Jun , CHEN Lin , CHEN Xinlu , ZHANG Liping , ZHOU Dandan , WANG Yu , YIN Chonggao , LI Hongli , LIU Yuqing . miR-625-5p promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting PRKACA [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(6): 447-454. |
| [15] | PENG Zishan, KONG Hui, BAO Zhen, ZHAO Hongxing, LIU Xin, LU Shaohua. Clinicopathological analysis of 83 cases of multifocal lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(5): 408-418. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
