Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 517-526.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.05.012
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Jing( ), ZHOU Juan, SU Chunxia(
), ZHOU Juan, SU Chunxia( )
)
Received:2022-06-21
Revised:2022-09-05
Online:2023-05-30
Published:2023-06-16
Contact:
SU Chunxia
Share article
CLC Number:
WU Jing, ZHOU Juan, SU Chunxia. Advances in fatty acid metabolism reprogramming of lung cancer[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(5): 517-526.
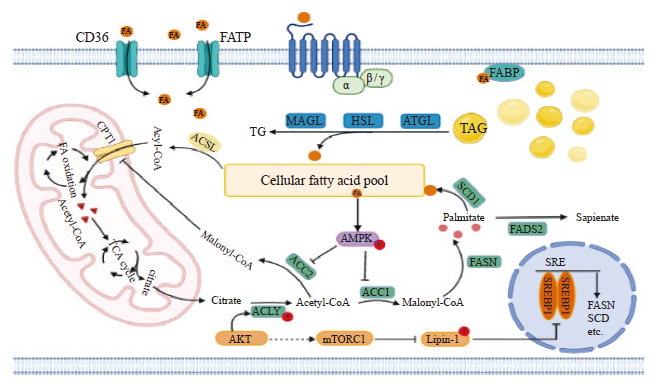
Fig. 1
Fatty acid metabolism in lung cancer Lung cancer cells obtain fatty acids from exogenous uptake and de novo lipogenesis. Exogenous uptake of fatty acids from the microenvironment is facilitated by CD36, FATP and FABP. De novo fatty acid synthesis mainly refers to the generation of palmitate from citrate under the enzymatic activities of ACLY, ACC and FASN enzymes, and then can be desaturated and elongated to form diverse lipidomic species. SREBP1 regulates fatty acid synthesis by regulating the expression of fatty acid synthesis-related enzymes at the transcriptional level. When nutrients are sufficient, fatty acids are stored as lipid droplets.And when energy is stressed, these fatty acids are released from lipid dropletsthrough lipolysis, and energy is generated through fatty acid oxidation. In addition to providing energy, free fatty acids, as important signaling molecules, participate in intracellular signaling through FFAR, thereby affecting various physiological processes of cells. FFAR: Free fatty acid receptor; ACLY: ATP-citrate lyase; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FASN: Fatty acid synthase; SCD1: Stearyl coenzyme A desaturated enzyme 1; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; HSL: Hormone-sensitive lipase; MAGL: Monoacylglycerol lipase; ACSL: Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; CPT1: Carnitine palmitoyl transferase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; SREBP1: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins; SRE: Sterol regulatory element."
Tab. 1
Inhibitors targeting fatty acid synthesis-related enzymes in lung cancer"
| Target | Agent | Mechanism of action | Drug development stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | ND-646 | ACC inhibitor binding to the BC domain of ACC[ | Preclinical |
| FASN | Cerulenin | Non-competitive FASN inhibitor[ | Preclinical |
| FASN | Orlistat | Irreversible FASN inhibitor; Induction of ferroptosis in lung cancer cells[ | Preclinical |
| FASN | C75 | Cytotoxicity; Side effects of anorexia and weight loss[ | Preclinical |
| FASN | TVB-3166 | Reversible FASN inhibitor; Inhibition of β-catenin signaling and induction of apoptosis[ | Preclinical |
| FASN | TVB-2640 | Reversible FASN inhibitor[ | Phase Ⅱ Clinical Trial (NCT03808558) |
| ACLY | SB-204990 | Specific ACLY inhibitor; Inhibition of proliferation in lung tumor growth[ | Preclinical |
| SCD1 | MF-438 | Specific SCD1 inhibitor; Induction of apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma stem cells[ | Preclinical |
| [1] |
THAI A A, SOLOMON B J, SEQUIST L V, et al. Lung cancer[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10299): 535-554.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00312-3 pmid: 34273294 |
| [2] |
SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, FUCHS H E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(1): 7-33.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v72.1 |
| [3] |
CONWAY E M, PIKOR L A, KUNG S H Y, et al. Macrophages, inflammation, and lung cancer[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2016, 193(2): 116-130.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.201508-1545CI |
| [4] |
HANAHAN D, WEINBERG R A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-674.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 pmid: 21376230 |
| [5] |
WARBURG O. On the origin of cancer cells[J]. Science, 1956, 123(3191): 309-314.
doi: 10.1126/science.123.3191.309 pmid: 13298683 |
| [6] |
KUMAGAI S, KOYAMA S, ITAHASHI K, et al. Lactic acid promotes PD-1 expression in regulatory T cells in highly glycolytic tumor microenvironments[J]. Cancer Cell, 2022, 40(2): 201-218.e9.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2022.01.001 |
| [7] | ALI A, LEVANTINI E, TEO J T, et al. Fatty acid synthase mediates EGFR palmitoylation in EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancer[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2018, 10(3): e8313. |
| [8] | CONTAT C, ANCEY P B, ZANGGER N, et al. Combined deletion of Glut1 and Glut3 impairs lung adenocarcinoma growth[J]. Elife, 2020, 9: e53618. |
| [9] |
BROADFIELD L A, PANE A A, TALEBI A, et al. Lipid metabolism in cancer: new perspectives and emerging mechanisms[J]. Dev Cell, 2021, 56(10): 1363-1393.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.04.013 pmid: 33945792 |
| [10] |
SNAEBJORNSSON M T, JANAKI-RAMAN S, SCHULZE A. Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31(1): 62-76.
doi: S1550-4131(19)30617-5 pmid: 31813823 |
| [11] |
BENSAAD K, FAVARO E, LEWIS C A, et al. Fatty acid uptake and lipid storage induced by HIF-1α contribute to cell growth and survival after hypoxia-reoxygenation[J]. Cell Rep, 2014, 9(1): 349-365.
doi: S2211-1247(14)00732-3 pmid: 25263561 |
| [12] |
CORBET C, BASTIEN E, SANTIAGO DE JESUS J P, et al. TGFβ2-induced formation of lipid droplets supports acidosis-driven EMT and the metastatic spreading of cancer cells[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 454.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14262-3 pmid: 31974393 |
| [13] |
ABUMRAD N A, CABODEVILLA A G, SAMOVSKI D, et al. Endothelial cell receptors in tissue lipid uptake and metabolism[J]. Circ Res, 2021, 128(3): 433-450.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.318003 pmid: 33539224 |
| [14] |
WANG J C, LI Y S. CD36 tango in cancer: signaling pathways and functions[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(17): 4893-4908.
doi: 10.7150/thno.36037 pmid: 31410189 |
| [15] |
PASCUAL G, AVGUSTINOVA A, MEJETTA S, et al. Targeting metastasis-initiating cells through the fatty acid receptor CD36[J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7635): 41-45.
doi: 10.1038/nature20791 |
| [16] |
FENG W W, WILKINS O, BANG S, et al. CD36-mediated metabolic rewiring of breast cancer cells promotes resistance to HER2-targeted therapies[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 29(11): 3405-3420.e5.
doi: S2211-1247(19)31479-2 pmid: 31825825 |
| [17] |
NI K W, WANG D M, XU H Y, et al. miR-21 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cells growth by regulating fatty acid metabolism[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 219.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0941-8 pmid: 31462892 |
| [18] |
SUN Q, ZHANG W, WANG L, et al. Hypermethylated CD36 gene affected the progression of lung cancer[J]. Gene, 2018, 678: 395-406.
doi: S0378-1119(18)30764-9 pmid: 29969695 |
| [19] |
MA X Z, XIAO L L, LIU L T, et al. CD36-mediated ferroptosis dampens intratumoral CD8+ T cell effector function and impairs their antitumor ability[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(5): 1001-1012.e5.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.015 |
| [20] |
WANG H P, FRANCO F, TSUI Y C, et al. CD36-mediated metabolic adaptation supports regulatory T cell survival and function in tumors[J]. Nat Immunol, 2020, 21(3): 298-308.
doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0589-5 pmid: 32066953 |
| [21] |
FHU C W, ALI A. Fatty acid synthase: an emerging target in cancer[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(17): 3935.
doi: 10.3390/molecules25173935 |
| [22] |
NIEMAN K M, KENNY H A, PENICKA C V, et al. Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth[J]. Nat Med, 2011, 17(11): 1498-1503.
doi: 10.1038/nm.2492 pmid: 22037646 |
| [23] | 刘倩, 王世凤, 徐缓, 等. CRABPII和E-FABP在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及其意义[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2013, 16(1): 12-19. |
| LIU Q, WANG S F, XU H, et al. Expressions and significances of CRABPII and E-FABP in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chin J Lung Cancer, 2013, 16(1): 12-19. | |
| [24] |
YANG S H, KOBAYASHI S, SEKINO K, et al. Fatty acid-binding protein 5 controls lung tumor metastasis by regulating the maturation of natural killer cells in the lung[J]. FEBS Lett, 2021, 595(13): 1797-1805.
doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14106 pmid: 33982279 |
| [25] |
KIMURA I, ICHIMURA A, OHUE-KITANO R, et al. Free fatty acid receptors in health and disease[J]. Physiol Rev, 2020, 100(1): 171-210.
doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2018 pmid: 31487233 |
| [26] |
WANG X, HE S B, GU Y T, et al. Fatty acid receptor GPR120 promotes breast cancer chemoresistance by upregulating ABC transporters expression and fatty acid synthesis[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 40: 251-262.
doi: S2352-3964(18)30614-5 pmid: 30738829 |
| [27] |
LIU Z, HOPKINS M M, ZHANG Z H, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids and other FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate cancer cells[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2015, 352(2): 380-394.
doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.218974 pmid: 25491146 |
| [28] |
BARTOSZEK A, FICHNA J, TARASIUK A, et al. Free fatty acid receptors as new potential targets in colorectal cancer[J]. Curr Drug Targets, 2020, 21(14): 1397-1404.
doi: 10.2174/1389450120666191112141901 |
| [29] |
MUNKARAH A, MERT I, CHHINA J, et al. Targeting of free fatty acid receptor 1 in EOC: a novel strategy to restrict the adipocyte-EOC dependence[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2016, 141(1): 72-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.02.026 pmid: 27016232 |
| [30] |
BACCI M, LORITO N, SMIRIGLIA A, et al. Fat and furious: lipid metabolism in antitumoral therapy response and resistance[J]. Trends Cancer, 2021, 7(3): 198-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.10.004 pmid: 33281098 |
| [31] |
RÖHRIG F, SCHULZE A. The multifaceted roles of fatty acid synthesis in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2016, 16(11): 732-749.
doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.89 pmid: 27658529 |
| [32] |
MOSSMANN D, PARK S, HALL M N. mTOR signalling and cellular metabolism are mutual determinants in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2018, 18(12): 744-757.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0074-8 pmid: 30425336 |
| [33] |
WILLIAMS K J, ARGUS J P, ZHU Y, et al. An essential requirement for the SCAP/SREBP signaling axis to protect cancer cells from lipotoxicity[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(9): 2850-2862.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0382-T pmid: 23440422 |
| [34] |
EZZEDDINI R, TAGHIKHANI M, SOMI M H, et al. Clinical importance of FASN in relation to HIF-1α and SREBP-1c in gastric adenocarcinoma[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 224: 169-176.
doi: S0024-3205(19)30220-6 pmid: 30914315 |
| [35] |
PETERSON T R, SENGUPTA S S, HARRIS T E, et al. mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1 localization to control the SREBP pathway[J]. Cell, 2011, 146(3): 408-420.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.034 pmid: 21816276 |
| [36] |
MA L, CHEN Z B, ERDJUMENT-BROMAGE H, et al. Phosphorylation and functional inactivation of TSC2 by ERK implications for tuberous sclerosis and cancer pathogenesis[J]. Cell, 2005, 121(2): 179-193.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.031 pmid: 15851026 |
| [37] |
GOUW A M, EBERLIN L S, MARGULIS K, et al. Oncogene KRAS activates fatty acid synthase, resulting in specific ERK and lipid signatures associated with lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2017, 114(17): 4300-4305.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1617709114 pmid: 28400509 |
| [38] |
TALEBI A, DEHAIRS J, RAMBOW F, et al. Sustained SREBP-1-dependent lipogenesis as a key mediator of resistance to BRAF-targeted therapy[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 2500.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04664-0 pmid: 29950559 |
| [39] |
DAI M, YANG B K, CHEN J, et al. Nuclear-translocation of ACLY induced by obesity-related factors enhances pyrimidine metabolism through regulating histone acetylation in endometrial cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 513: 36-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.024 pmid: 33991616 |
| [40] |
MIGITA T, NARITA T, NOMURA K, et al. ATP citrate lyase: activation and therapeutic implications in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2008, 68(20): 8547-8554.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1235 pmid: 18922930 |
| [41] | CSANADI A, KAYSER C, DONAUER M, et al. Prognostic value of malic enzyme and ATP-citrate lyase in non-small cell lung cancer of the young and the elderly[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(5): e0126357. |
| [42] |
GUO W N, MA J Y, YANG Y Q, et al. ATP-citrate lyase epigenetically potentiates oxidative phosphorylation to promote melanoma growth and adaptive resistance to MAPK inhibition[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26(11): 2725-2739.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1359 pmid: 32034077 |
| [43] |
HAN Q, CHEN C A, YANG W, et al. ATP-citrate lyase regulates stemness and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2021, 20(3): 251-261.
doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2020.05.010 |
| [44] | BIAN X, LIU R, MENG Y, et al. Lipid metabolism and cancer[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(1): e20201606. |
| [45] |
SVENSSON R U, PARKER S J, EICHNER L J, et al. Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer in preclinical models[J]. Nat Med, 2016, 22(10): 1108-1119.
doi: 10.1038/nm.4181 pmid: 27643638 |
| [46] |
RIOS GARCIA M, STEINBAUER B, SRIVASTAVA K, et al. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1-dependent protein acetylation controls breast cancer metastasis and recurrence[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 26(6): 842-855.e5.
doi: S1550-4131(17)30570-3 pmid: 29056512 |
| [47] |
GU L, ZHU Y H, LIN X, et al. Stabilization of FASN by ACAT1-mediated GNPAT acetylation promotes lipid metabolism and hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(11): 2437-2449.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1156-0 pmid: 31974474 |
| [48] |
BASTOS D C, RIBEIRO C F, AHEARN T, et al. Genetic ablation of FASN attenuates the invasive potential of prostate cancer driven by Pten loss[J]. J Pathol, 2021, 253(3): 292-303.
doi: 10.1002/path.v253.3 |
| [49] |
CHANG L G, FANG S R, CHEN Y B, et al. Inhibition of FASN suppresses the malignant biological behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells via deregulating glucose metabolism and AKT/ERK pathway[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2019, 18(1): 118.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1058-8 pmid: 31122252 |
| [50] |
JIANG L, XIAO L, SUGIURA H, et al. Metabolic reprogramming during TGFβ1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Oncogene, 2015, 34(30): 3908-3916.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.321 pmid: 25284588 |
| [51] |
LEWIS C A, BRAULT C, PECK B, et al. SREBP maintains lipid biosynthesis and viability of cancer cells under lipid- and oxygen-deprived conditions and defines a gene signature associated with poor survival in glioblastoma multiforme[J]. Oncogene, 2015, 34(40): 5128-5140.
doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.439 pmid: 25619842 |
| [52] |
YOUNG R M, ACKERMAN D, QUINN Z L, et al. Dysregulated mTORC1 renders cells critically dependent on desaturated lipids for survival under tumor-like stress[J]. Genes Dev, 2013, 27(10): 1115-1131.
doi: 10.1101/gad.198630.112 |
| [53] |
ZHANG J Q, SONG F, ZHAO X J, et al. EGFR modulates monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis through phosphorylation of SCD1 in lung cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2017, 16(1): 127.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0704-x pmid: 28724430 |
| [54] |
HUANG Q F, WANG Q G, LI D, et al. Co-administration of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol (g-PPT) and EGFR-TKI overcomes EGFR-TKI resistance by decreasing SCD1 induced lipid accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 129.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1120-4 |
| [55] |
LI Z, LIU H, LUO X. Lipid droplet and its implication in cancer progression[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(12): 4112-4122.
pmid: 33414989 |
| [56] |
EL-MASHTOLY S F, YOSEF H K, PETERSEN D, et al. Label-free Raman spectroscopic imaging monitors the integral physiologically relevant drug responses in cancer cells[J]. Anal Chem, 2015, 87(14): 7297-7304.
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01431 pmid: 26075314 |
| [57] |
ZECHNER R, ZIMMERMANN R, EICHMANN T O, et al. FAT SIGNALS: lipases and lipolysis in lipid metabolism and signaling[J]. Cell Metab, 2012, 15(3): 279-291.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.12.018 |
| [58] |
PRÜSER J L, RAMER R, WITTIG F, et al. The monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor JZL184 inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis via the CB1 cannabinoid receptor[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2021, 20(5): 787-802.
doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0589 pmid: 33632876 |
| [59] |
KIENZL M, HASENOEHRL C, MAITZ K, et al. Monoacylglycerol lipase deficiency in the tumor microenvironment slows tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2021, 10(1): 1965319.
doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1965319 |
| [60] |
LIU R Y, WANG X, CURTISS C, et al. Monoglyceride lipase gene knockout in mice leads to increased incidence of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(2): 36.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0188-z pmid: 29348400 |
| [61] |
MA Y B, TEMKIN S M, HAWKRIDGE A M, et al. Fatty acid oxidation: an emerging facet of metabolic transformation in cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 435: 92-100.
doi: S0304-3835(18)30518-4 pmid: 30102953 |
| [62] |
PADANAD M S, KONSTANTINIDOU G, VENKATESWARAN N, et al. Fatty acid oxidation mediated by acyl-CoA synthetase long chain 3 is required for mutant KRAS lung tumorigenesis[J]. Cell Rep, 2016, 16(6): 1614-1628.
doi: S2211-1247(16)30895-6 pmid: 27477280 |
| [63] |
WANG T Y, FAHRMANN J F, LEE H, et al. JAK/STAT3-regulated fatty acid β-oxidation is critical for breast cancer stem cell self-renewal and chemoresistance[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(6): 1357.
doi: S1550-4131(18)30302-4 pmid: 29874570 |
| [64] |
HOY A J, NAGARAJAN S R, BUTLER L M. Tumour fatty acid metabolism in the context of therapy resistance and obesity[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2021, 21(12): 753-766.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00388-4 pmid: 34417571 |
| [65] |
SCHLAEPFER I R, JOSHI M. CPT1A-mediated fat oxidation, mechanisms, and therapeutic potential[J]. Endocrinology, 2020, 161(2): bqz046.
doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqz046 |
| [66] |
WANG Y N, ZENG Z L, LU J H, et al. CPT1A-mediated fatty acid oxidation promotes colorectal cancer cell metastasis by inhibiting anoikis[J]. Oncogene, 2018, 37(46): 6025-6040.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0384-z |
| [67] | 贾建博, 王涛, 辛向兵, 等. CPT1A促进肺癌转移的调控作用[J]. 海南医学, 2019, 30(1): 5-8. |
| JIA J B, WANG T, XIN X B, et al. Roles of CPT1A promoting lung cancer metastasis[J]. Hainan Med J, 2019, 30(1): 5-8. | |
| [68] |
KOUNDOUROS N, POULOGIANNIS G. Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer[J]. Br J Cancer, 2020, 122(1): 4-22.
doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0650-z |
| [69] |
RELAT J, BLANCAFORT A, OLIVERAS G, et al. Different fatty acid metabolism effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and C75 in adenocarcinoma lung cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 280.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-280 pmid: 22769244 |
| [70] |
ZHOU W J, ZHANG J, YAN M K, et al. Orlistat induces ferroptosis-like cell death of lung cancer cells[J]. Front Med, 2021, 15(6): 922-932.
doi: 10.1007/s11684-020-0804-7 |
| [71] |
BUCKLEY D, DUKE G, HEUER T S, et al. Fatty acid synthase-modern tumor cell biology insights into a classical oncology target[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 177: 23-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.021 |
| [72] |
FALCHOOK G, INFANTE J, ARKENAU H T, et al. First-in-human study of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of first-in-class fatty acid synthase inhibitor TVB-2640 alone and with a taxane in advanced tumors[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2021, 34: 100797.
doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100797 |
| [73] |
GRANCHI C. ATP citrate lyase (ACLY) inhibitors: an anti-cancer strategy at the crossroads of glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2018, 157: 1276-1291.
doi: S0223-5234(18)30773-6 pmid: 30195238 |
| [74] |
YANG L, ZHANG F Q, WANG X, et al. A FASN-TGF-β1-FASN regulatory loop contributes to high EMT/metastatic potential of cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(34): 55543-55554.
doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10837 pmid: 27765901 |
| [75] |
VENTURA R, MORDEC K, WASZCZUK J, et al. Inhibition of de novo palmitate synthesis by fatty acid synthase induces apoptosis in tumor cells by remodeling cell membranes, inhibiting signaling pathways, and reprogramming gene expression[J]. EBioMedicine, 2015, 2(8): 808-824.
doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.06.020 pmid: 26425687 |
| [76] |
LOOMBA R, MOHSENI R, LUCAS K J, et al. TVB-2640 (FASN inhibitor) for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: FASCINATE-1, a randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a trial[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161(5): 1475-1486.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.025 |
| [77] |
ZHANG C, LIU J, HUANG G, et al. Cullin3-KLHL25 ubiquitin ligase targets ACLY for degradation to inhibit lipid synthesis and tumor progression[J]. Genes Dev, 2016, 30(17): 1956-1970.
doi: 10.1101/gad.283283.116 |
| [78] |
HANAI J, DORO N, SASAKI A T, et al. Inhibition of lung cancer growth: ATP citrate lyase knockdown and statin treatment leads to dual blockade of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathways[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2012, 227(4): 1709-1720.
doi: 10.1002/jcp.22895 |
| [79] |
HATZIVASSILIOU G, ZHAO F P, BAUER D E, et al. ATP citrate lyase inhibition can suppress tumor cell growth[J]. Cancer Cell, 2005, 8(4): 311-321.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.09.008 pmid: 16226706 |
| [80] |
PISANU M E, NOTO A, DE VITIS C, et al. Blockade of stearoyl-CoA-desaturase 1 activity reverts resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer stem cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 406: 93-104.
doi: S0304-3835(17)30463-9 pmid: 28797843 |
| [81] |
SHE K L, FANG S H, DU W, et al. SCD1 is required for EGFR-targeting cancer therapy of lung cancer via re-activation of EGFR/PI3K/AKT signals[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2019, 19: 103.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0809-y pmid: 31019378 |
| [82] | HESS D, CHISHOLM J W, IGAL R A. Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA-desaturase activity blocks cell cycle progression and induces programmed cell death in lung cancer cells[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(6): e11394. |
| [83] |
VRIENS K, CHRISTEN S, PARIK S, et al. Evidence for an alternative fatty acid desaturation pathway increasing cancer plasticity[J]. Nature, 2019, 566(7744): 403-406.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0904-1 |
| [84] |
LIEN E C, WESTERMARK A M, ZHANG Y, et al. Low glycaemic diets alter lipid metabolism to influence tumour growth[J]. Nature, 2021, 599(7884): 302-307.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04049-2 |
| [85] |
DIERGE E, DEBOCK E, GUILBAUD C, et al. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the acidic tumor environment leads to ferroptosis-mediated anticancer effects[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(8): 1701-1715.e5.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.016 pmid: 34118189 |
| [1] | FENG Xinying, WANG Bing, LIU Peifeng. Innovations and challenges in intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal metastatic carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 827-837. |
| [2] | CAO Xiaoshan, YANG Beibei, CONG Binbin, LIU Hong. The progress of treatment for brain metastases of triple-negative breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 777-784. |
| [3] | WANG Manli, CHEN Hui, DUAN Zhi, XU Qimei, LI Zhen. A study on communication mechanism of lung cancer cells in tumor microenvironment mediated by pleckstrin-2/miR-196a signal axis [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 628-638. |
| [4] | HUANG Sijie, KANG Xun, LI Wenbin. Clinical research progress of intrathecal therapy in the treatment of leptomeningeal metastasis [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 695-701. |
| [5] | QIAN Bin, CHEN Haiquan. Important progress in surgical treatment of lung cancer in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(4): 335-339. |
| [6] | LIN Yicong, WANG Yue, XUE Qianqian, ZHENG Qiang, JIN Yan, HUANG Ziling, LI Yuan. Clinical pathological characteristics and immune microenvironment significance of EGFR T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients and its prognostic implications [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(4): 368-379. |
| [7] | XU Yonghu, XU Dazhi. Progress and prospects of gastric cancer treatment in the 21st century [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 239-249. |
| [8] | CHEN Yifan, LI Ting, WANG Biyun. Research progress of CCR8 in tumor immunotherapy [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 299-305. |
| [9] | JIANG Mengqi, HAN Yuchen, FU Xiaolong. Research progress on H-E stained whole slide image analysis by artificial intelligence in lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 306-315. |
| [10] | JIN Yizi, LIN Mingxi, ZENG Cheng, GUO Qing, ZHANG Jian. Research advances in estrogen receptor low positive early breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 972-978. |
| [11] | LIU Xuerou, YANG Yumei, ZHAO Qian, RONG Xiangyu, LIU Wei, ZHENG Ruijie, PANG Jinlong, LI Xian, LI Shanshan. Research progress on the role of glutamine metabolism-related proteins in tumor metastasis [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(1): 97-103. |
| [12] | WU Han, YANG Zhangru, FENG Wen, ZENG Wanqin, GUO Jindong, LI Hongxuan, WANG Changlu, WANG Jiaming, LÜ Changxing, ZHANG Qin, YU Wen, CAI Xuwei, FU Xiaolong. The efficacy and prognosis analysis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for multiple primary early-stage lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 844-856. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lingling, WANG Xiangyi, WEI Xing, LIN Li, TANG Chuanhao, LIANG Jun. A study on prevention and treatment of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting in non-small cell lung cancer patients with low-frequency electrical stimulator for antiemesis [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 776-781. |
| [14] | KANG Yinnan, CHEN Shun, XIE Youcheng, ZHENG Ying, HE Yujing, LI Chuyi, YU Xiaohui. Application and research progress of antibody drug conjugates in HER2 positive advanced gastric cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 790-800. |
| [15] | ZHANG Haoting, ZHENG Jing, FU Mengjiao, ZHOU Jianying. Research progress on thyroid dysfunction induced by immunotherapy for lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 701-706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
