Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2024, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 628-638.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.07.002
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Manli( ), CHEN Hui(
), CHEN Hui( ), DUAN Zhi, XU Qimei, LI Zhen
), DUAN Zhi, XU Qimei, LI Zhen
Received:2023-11-17
Revised:2024-02-27
Online:2024-07-30
Published:2024-08-08
Contact:
CHEN Hui
Share article
CLC Number:
WANG Manli, CHEN Hui, DUAN Zhi, XU Qimei, LI Zhen. A study on communication mechanism of lung cancer cells in tumor microenvironment mediated by pleckstrin-2/miR-196a signal axis[J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 628-638.
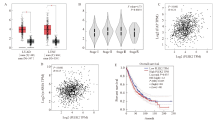
Fig. 1
The expression of plek2 is related to CAFs based on GEPIA A: PLEK2 expression is present in LUAD (including 483 tumor samples and 347 normal samples) and LUSC (including 486 tumor samples and 338 normal samples). The red box chart represents tumor tissue, while the gray box chart represents normal tissue. The vertical axis represents the logarithmic value of PLEK2 per million transcripts [log2 (PLEK2 TPM)]. B: The relative expression of PLEK2 in different pathological stages of lung cancer (LUAD+LUSC) showed significant differences (F = 4.73, P = 0.002 8). The vertical axis represents the logarithmic value of the copy number of the PLEK2 transcript [log2 (PLEK2 TPM)]. C: The expression of PLEK2 (log2 PLEK2 TPM) in lung cancer (LUAD+LUSC) was positively correlated with the expression of α-SMA (log2-SMA TPM) (R = 0.24, P<0.001). D: The expression of PLEK2 (log2 PLEK2 TPM) in lung cancer (LUAD+LUSC) was positively correlated with the expression of FAP (log2 FAP TPM) (R = 0.15, P<0.001). TPM stands for every million transcripts. E: Using the TCGA data set of lung cancer patients (LUAD+LUSC), the correlation between the expression of PLEK2 and the overall survival was analyzed by GEPIA. Patients were divided into high (red, n = 481) and low (blue, n = 481) gene expression levels by using the median cut-off value, and the log-rank P = 0.035 was displayed, indicating that the difference was statistically significant."
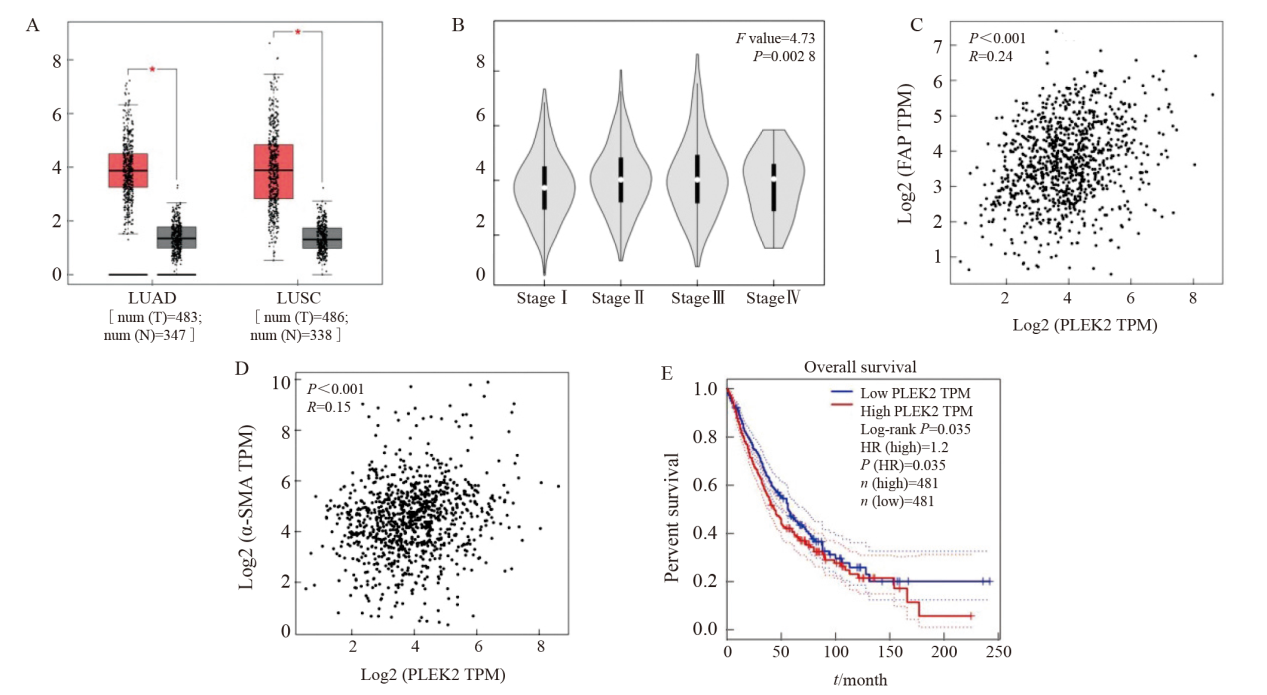
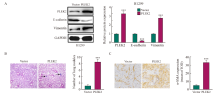
Fig. 2
PLEK2 overexpression promotes EMT in lung cancer cells A: The expression of PLEK2, E-cadherin and vimentin in H1299 cells transfected with Vector control and PLEK2 overexpression lentivirus was analyzed by protein blot. B: H-E staining of lung tissue and quantitative analysis of metastatic nodules. C: Immunohistochemical analysis of α-SMA in lung tissue metastases. IOD: Integral optical density. ***: P<0.001, compared with Vector group."

Tab. 1
miRNA analysis of significantly different expression in PLEK2 up-regulated lung cancer cells and their exosomes"
| Gene ID | Log2 (PLEK2/Vector) | P value (PLEK2/Vector) | Log2 (PLEK2_exo/Vector_exo) | P value (PLEK2_exo/Vector_exo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-196a | 5.129 28 | 0 | 11.598 05 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | 2.711 72 | 0 | 6.990 58 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-425-3p | 0.854 52 | 0 | 3.906 89 | <0.01 |
| hsa-let-7a-3p | 0.690 35 | <0.01 | 3.087 46 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-451a | -2.369 67 | 0 | 2.935 87 | 0 |
| hsa-let-7g-5p | 0.407 17 | 0 | 2.681 13 | 0 |
| hsa-let-7f-5p | 0.461 73 | 0 | 2.594 83 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-3529-3p | -7.313 86 | 0 | 2.546 97 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-98-5p | 0.552 27 | 0 | 2.451 70 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-34a-5p | 0.481 45 | 0 | 1.257 98 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | 0.459 64 | 0 | 1.224 56 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-26b-5p | 0.539 63 | 0 | 1.222 39 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | -0.485 63 | 0 | 1.015 60 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-374c-3p | -16.431 76 | 0 | 0.584 96 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-10a-5p | 0.598 08 | 0 | -0.654 86 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | 0.467 65 | 0 | -1.075 66 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-4488 | -1.643 86 | <0.01 | -1.165 31 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-21-3p | -0.473 92 | 0 | -1.514 57 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-19b-3p | 0.520 33 | 0 | -1.777 61 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-4516 | -2.584 96 | <0.01 | -2.036 84 | 0 |
| hsa-miR-128-3p | 0.474 44 | 0 | -2.321 93 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-3184-3p | -2.525 28 | 0 | -3.807 35 | <0.01 |
| hsa-miR-363-3p | 2.369 23 | 0 | -10.344 30 | <0.01 |
Fig. 4
Exosomes miR-196a derived from tumor cells are taken up by fibroblasts and promote the activation of CAFs A: Transmission electron micrographs of Vector_exo and PLEK2_exo (scale = 100 nm). B: Western blot analysis of the expression of CD9, CD63, CD81 and calnexin in exosomes. C: After co-culture for 48 h, the internalization of Vector_exo and PLEK2_exo labeled with PKH26 by MRC-5 cells was examined by confocal microscope. D: RT-qPCR analysis of miR-196a, α-SMA, FAP in MRC-5 cells treated with Vector_exo, PLEK2_exo. E, F: Western blot and RT-qPCR were used to determine the protein and mRNA levels of α-SMA and FAP in MRC-5 cells transfected with miR-196a mimetic (miR-196a) and NC. G, H: Western blot and RT-qPCR were used to determine the protein and mRNA levels of α-SMA and FAP in MRC-5 cells transfected with miR-196a inhibitors (si-miR-196a#1 and si-miR-196a#) and control (si-NC). *: P<0.05, compared with the Vector_exo group; **: P<0.01, compared with the Vector_exo group or si-NC group; ***: P<0.001, compared with the Vector_exo group, NC group or si-NC group."

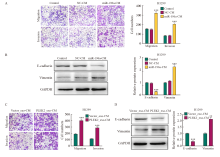
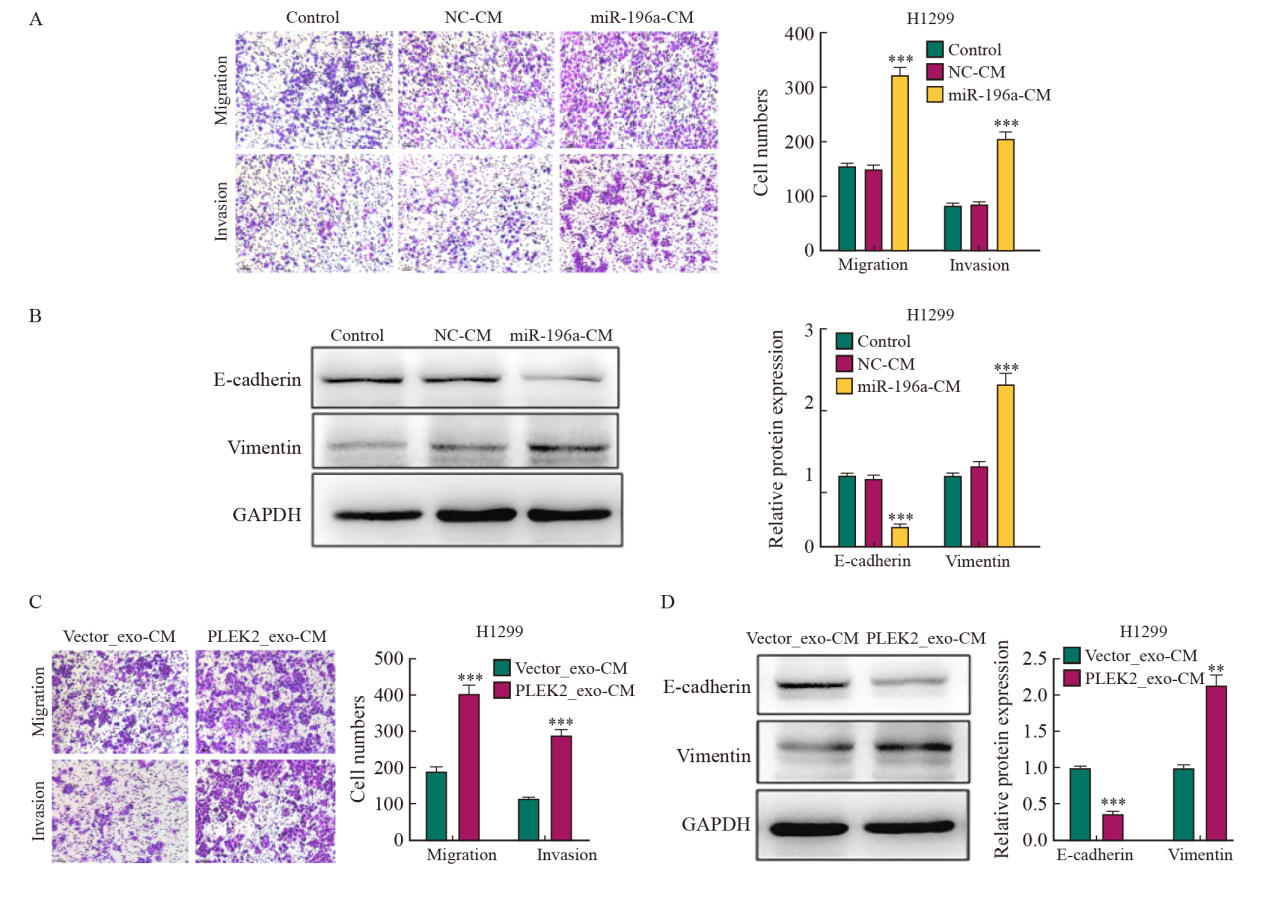
Fig. 5
CAFs activation promotes the invasion and metastasis of lung cancer A: The metastatic and invasive ability of H1299 cells treated with miR-196a-CM was determined by transwell test. B: the expression level of EMT-related proteins in H1299 cells treated with miR-196a-CM. C: The metastatic and invasive ability of H1299 cells co-cultured with Vector_exo-CM and PLEK2_exo-CM was determined by transwell test. D: The expression level of EMT-related proteins in H1299 cells co-cultured with Vector_exo-CM and PLEK2_exo-CM. **: P<0.01, compared with Vector_exo-CM group; ***: P<0.001, compared with NC-CM group or Vector_exo-CM group."
| [1] | SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249. |
| [2] | MILLER K D, NOGUEIRA L, DEVASIA T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72(5): 409-436. |
| [3] | CHAFT J E, RIMNER A, WEDER W, et al. Evolution of systemic therapy for stagesⅠ-Ⅲ non-metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(9): 547-557. |
| [4] | ENTEZARI M, GHANBARIRAD M, TAHERIAZAM A, et al. Long non-coding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: potential functions in lung cancer progression, drug resistance and tumor microenvironment remodeling[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2022, 150: 112963. |
| [5] | WANG G C, ZHOU Q, XU Y, et al. Emerging roles of pleckstrin-2 beyond cell spreading[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 768238. |
| [6] | WEN Y S, GUO G R, YANG L J, et al. A tumor microenvironment gene set-based prognostic signature for non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2022, 9: 849108. |
| [7] |
HU S C, MA J H, SU C, et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis[J]. Acta Biomater, 2021, 135: 567-581.
doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.09.003 pmid: 34506976 |
| [8] | PATHANIA A S, PRATHIPATI P, CHALLAGUNDLA K B. New insights into exosome mediated tumor-immune escape: clinical perspectives and therapeutic strategies[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1876(2): 188624. |
| [9] | NIU L R, YANG W L, DUAN L L, et al. Biological implications and clinical potential of metastasis-related miRNA in colorectal cancer[J]. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids, 2021, 23: 42-54. |
| [10] | TAN Z F, XUE H B, SUN Y L, et al. The role of tumor inflammatory microenvironment in lung cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 688625. |
| [11] | XU K H, ZHANG C P, DU T T, et al. Progress of exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2021, 134: 111111. |
| [12] | ZHAO X Y, SHU D L, SUN W J, et al. PLEK2 promotes cancer stemness and tumorigenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via the c-Myc-mediated positive feedback loop[J]. Cancer Commun, 2022, 42(10): 987-1007. |
| [13] | LIU J H, CHEN H, QIAO G B, et al. PLEK2 and IFI6, representing mesenchymal and immune-suppressive microenvironment, predicts resistance to neoadjuvant immunotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2023, 72(4): 881-893. |
| [14] |
SHAO W, AZAM Z, GUO J T, et al. Oncogenic potential of PIK3CD in glioblastoma is exerted through cytoskeletal proteins PAK3 and PLEK2[J]. Lab Invest, 2022, 102(12): 1314-1322.
doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00821-8 pmid: 35851857 |
| [15] | WU D M, DENG S H, ZHOU J, et al. PLEK2 mediates metastasis and vascular invasion via the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of SHIP2 in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2020, 146(9): 2563-2575. |
| [16] | XIA Q L, HE X M, MA Y, et al. 5-mRNA-based prognostic signature of survival in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. World J Clin Oncol, 2023, 14(1): 27-39. |
| [17] |
WANG F, ZHANG C Q, CHENG H, et al. TGF-β-induced PLEK2 promotes metastasis and chemoresistance in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating LCN2[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(10): 901.
doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04155-z pmid: 34601488 |
| [18] | WU C X, GU J M, GU H B, et al. The recent advances of cancer associated fibroblasts in cancer progression and therapy[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1008843. |
| [19] | SHELTON M, ANENE C A, NSENGIMANA J, et al. The role of CAF derived exosomal microRNAs in the tumour microenvironment of melanoma[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2021, 1875(1): 188456. |
| [20] | MA Y N, WANG S S, LIEBE R, et al. Crosstalk between hepatic stellate cells and tumor cells in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Chin Med J, 2021, 134(21): 2544-2546. |
| [21] |
CUI J Z, YUAN Y, SHANMUGAM M K, et al. MicroRNA-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting BRAM1 to regulate SMAD and MAPK signaling pathways[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(15): 4254-4270.
doi: 10.7150/ijbs.60805 pmid: 34803496 |
| [22] | QIU H, XIE Z Q, TANG W F, et al. Association between microRNA-146a, -499a and-196a-2 SNPs and non-small cell lung cancer: a case-control study involving 2249 subjects[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(2): BSR20201158. |
| [23] |
QIN X, GUO H Y, WANG X N, et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5[J]. Genome Biol, 2019, 20(1): 12.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1604-0 pmid: 30642385 |
| [24] | LIU E C, LEE T T, WU S L, et al. Abstract 1035: PLEK2 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition through increasing Snail1 in lung cancer cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(13_Supplement): 1035. |
| [25] | HAN X, MEI Y, MISHRA R K, et al. Targeting pleckstrin-2/Akt signaling reduces proliferation in myeloproliferative neoplasm models[J]. J Clin Invest, 2023, 133(6): e159638. |
| [1] | WANG Zifei, DING Yahui, LI Yan, LUAN Xin, TANG Min. Application of 3D bioprinting in cancer research and tissue engineering [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 814-826. |
| [2] | WANG Xiaocong, LI Ming. The value of single-cell sequencing in oral squamous cell carcinoma research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 501-508. |
| [3] | ZHANG Shaoqiu, YAN Li, LI Ruichen, ZHAO Yang, WANG Xiaoshen, YANG Xuguang, ZHU Yi. Recent advances and prospect in immune microenvironment and its mechanisms of function in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(6): 629-636. |
| [4] | CAI Jialuo, ZHU Ruiqiu, LI Sen, CAO Yijun, HUANG Fang. Mechanism of inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated drug resistance in colorectal cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(12): 1065-1072. |
| [5] | XUE Ying, MAO Yunyu, XU Jianqing. Progress in construction of hypoxia-sensitive CAR-T cell for solid tumor therapy [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(1): 71-77. |
| [6] | LIU Qiang, FANG Yi, WANG Jing. Application progress of single-cell sequencing technology in breast cancer research [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(7): 635-642. |
| [7] | SU Jiaqi, XU Wenhao, TIAN Xi, ANWAIE Aihetaimujiang, QU Yuanyuan, SHI Guohai, ZHANG Hailiang, YE Dingwei. New strategies for combined with immunotherapy of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: advances in aerobic glycolysis [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(4): 287-297. |
| [8] | ZHOU Shukui, ZHANG Dongliang, WANG Xiang, LIU Lei, LI Zeng, YANG Shengke, LIAO Hong. Developing a new animal model of subcutaneous transplanted prostate cancer with cell sheet technology [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 200-206. |
| [9] | LI Wei, ZHANG Shanling, TAO Yingjie, WANG Xudong. Research status and progress of mechanism of T cell immune metabolism and its application combined with immune checkpoint inhibitor [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 640-646. |
| [10] | QIAO Tingting , GE Shujing , LUO Yuan , LU Chengrong , DUAN Lianning . Mechanism of inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by phosphorylated H2AX in lung cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(4): 277-284. |
| [11] | HAN Xiangchen, LI Xiaoguang, HU Xin. Single-cell RNA sequencing and its application in breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(11): 1110-1114. |
| [12] | WEI Lirong , TENG Xiaoyan , XIA Qianlin , DU Yuzhen . STC1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote invasion and migration of lung cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(7): 497-504. |
| [13] | JIANG Mengyi , LU Yanqiao , WANG Hongxia . Research progress and clinical significance of breast cancer heterogeneity [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(5): 394-400. |
| [14] | FAN Shouren , WU Shuhua , LI Yangyang , XU Xiaoyang , HE Shuang , WEN Feifei , LIU Liu , GUO Ningjie , JIA Zhenzhen . The correlation between LC3 and tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(11): 849-857. |
| [15] | JIN Yujuan, HU Liang, JI Hongbin. Advances in molecular mechanism of lung cancer: from rational to practice [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(10): 759-769. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
