Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2024, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 1090-1099.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.12.003
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
REN Jiaqiang1( ), WU Shuai1, SU Tong2, LI Jie1, HAN Liang1, WU Zheng1(
), WU Shuai1, SU Tong2, LI Jie1, HAN Liang1, WU Zheng1( )
)
Received:2024-08-30
Online:2024-12-30
Published:2025-01-21
Share article
REN Jiaqiang, WU Shuai, SU Tong, LI Jie, HAN Liang, WU Zheng. An exploratory study of INPP4B, a biomarker of gemcitabine chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer[J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(12): 1090-1099.
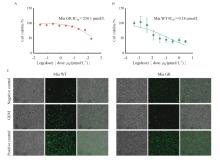
Fig. 1
Identification of gemcitabine resistant pancreatic cancer cell strain A: IC50 quantitative efficacy curves of Mia GR; B: IC50 quantitative efficacy curves of Mia WT against gemcitabine; C: Levels of reactive oxygen species production in response to gemcitabine by Mia WT and Mia GR cell lines."
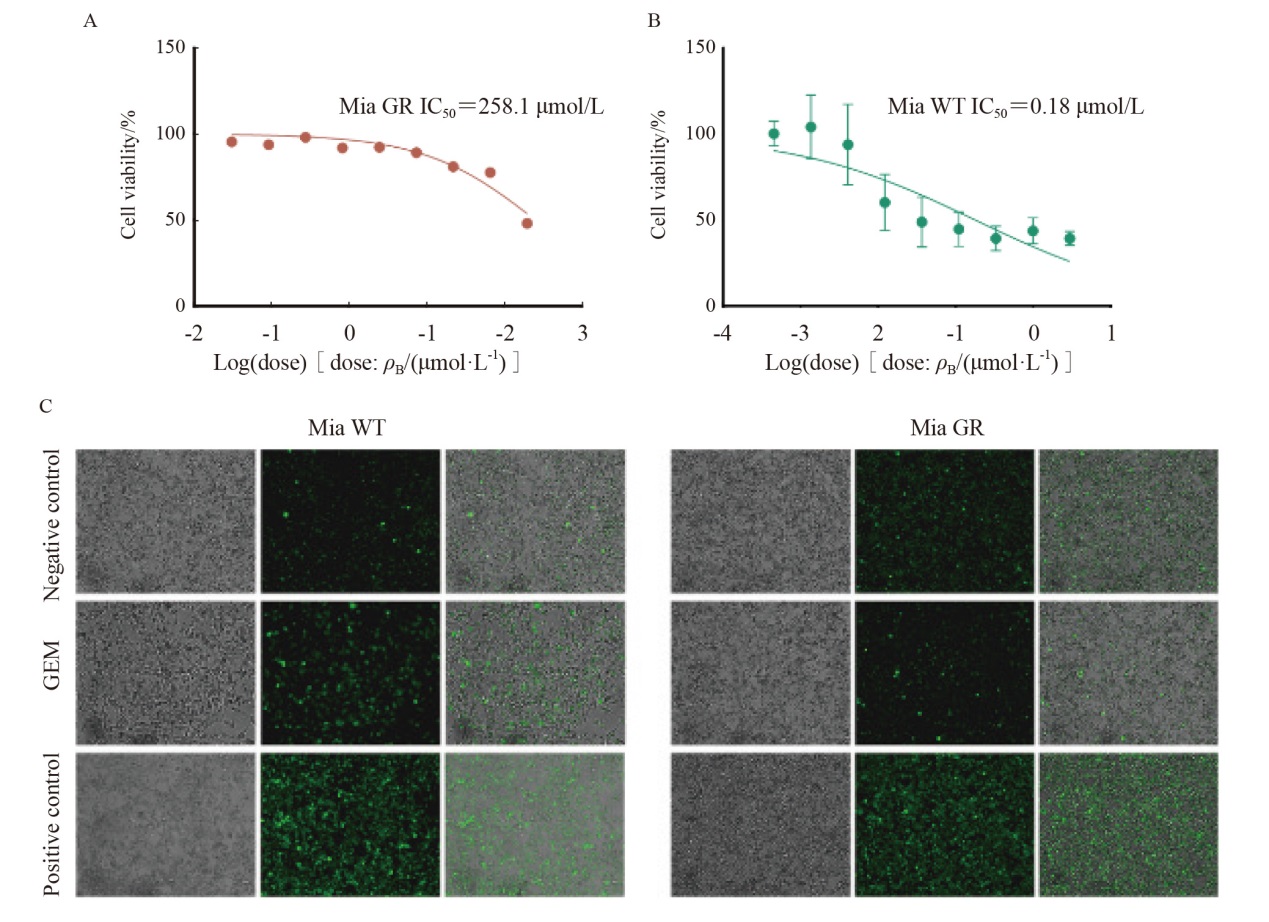
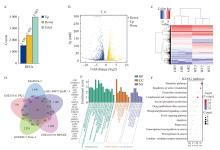
Fig. 2
Sequencing of gemcitabine resistant cell strain in pancreatic cancer and analysis of the results A: Differentially expressed genes of Mia GR and Mia WT; B: Volcano plots; C: Heat maps of differentially expressed genes; D: Common differentially expressed genes in different cell lines in the online database of isoform studies; E: Gene ontology terms of common differentially expressed genes; F: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis."
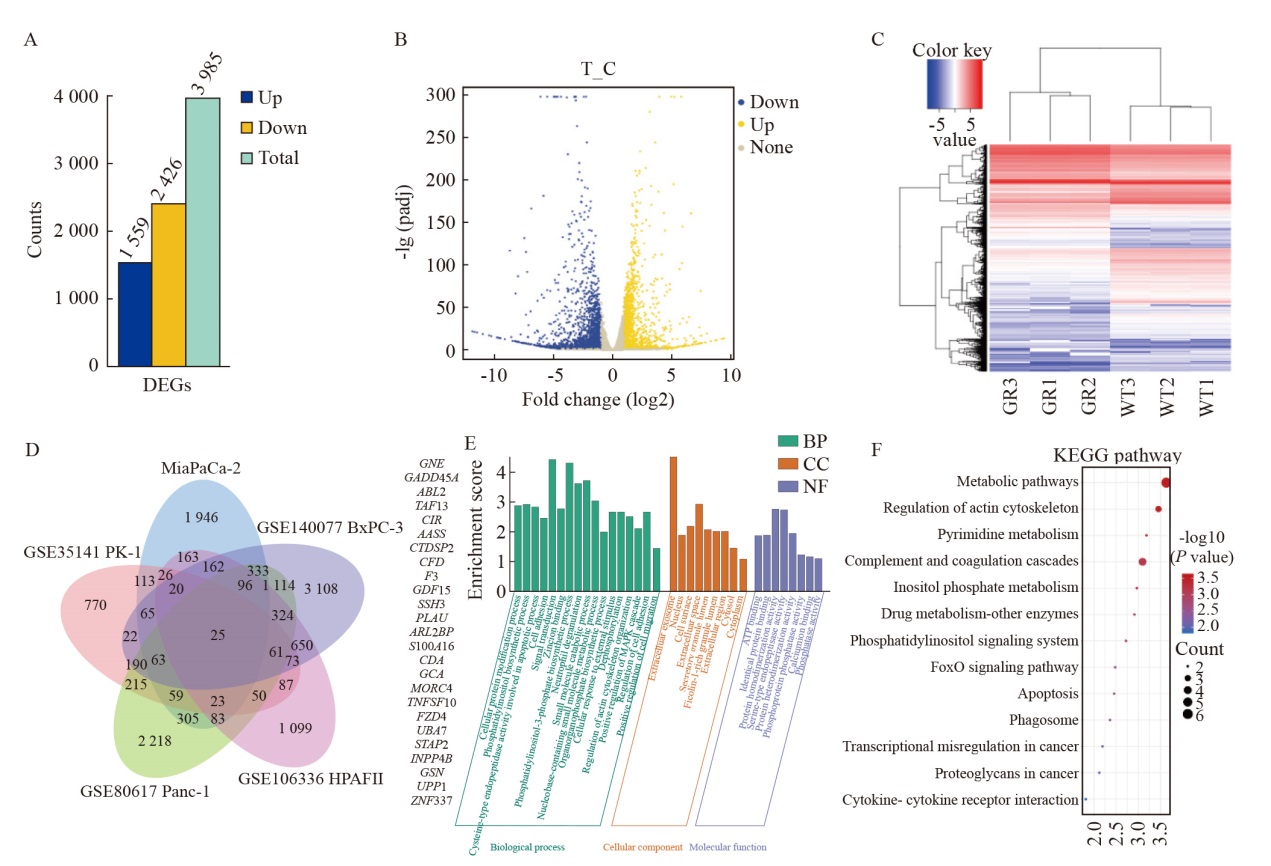
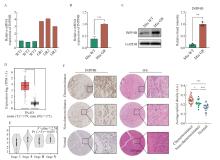
Fig. 3
Identification of INPP4B expression levels in pancreatic cancer cells and tissues A: The mRNA expression level of INPP4B in each group of samples from sequencing results; B: RTFQ-PCR to verify the mRNA level of INPP4B in Mia GR and Mia WT; C: Western blot to detect the expression level of INPP4B in Mia WT and Mia GR and statistics; D: Difference in expression levels of INPP4B between tumor patients and control group; E: Distribution of expression levels of INPP4B in patients with different stages of pancreatic cancer in TCGA database; F: Immunohistochemical analysis of INPP4B expression levels in drug resistant pancreatic cancer tissues, non-drug resistant pancreatic cancer tissues, and para-cancerous tissues. *: P<0.05, compared with each other; **: P<0.01, compared with each other; ***: P<0.001, compared with each other."
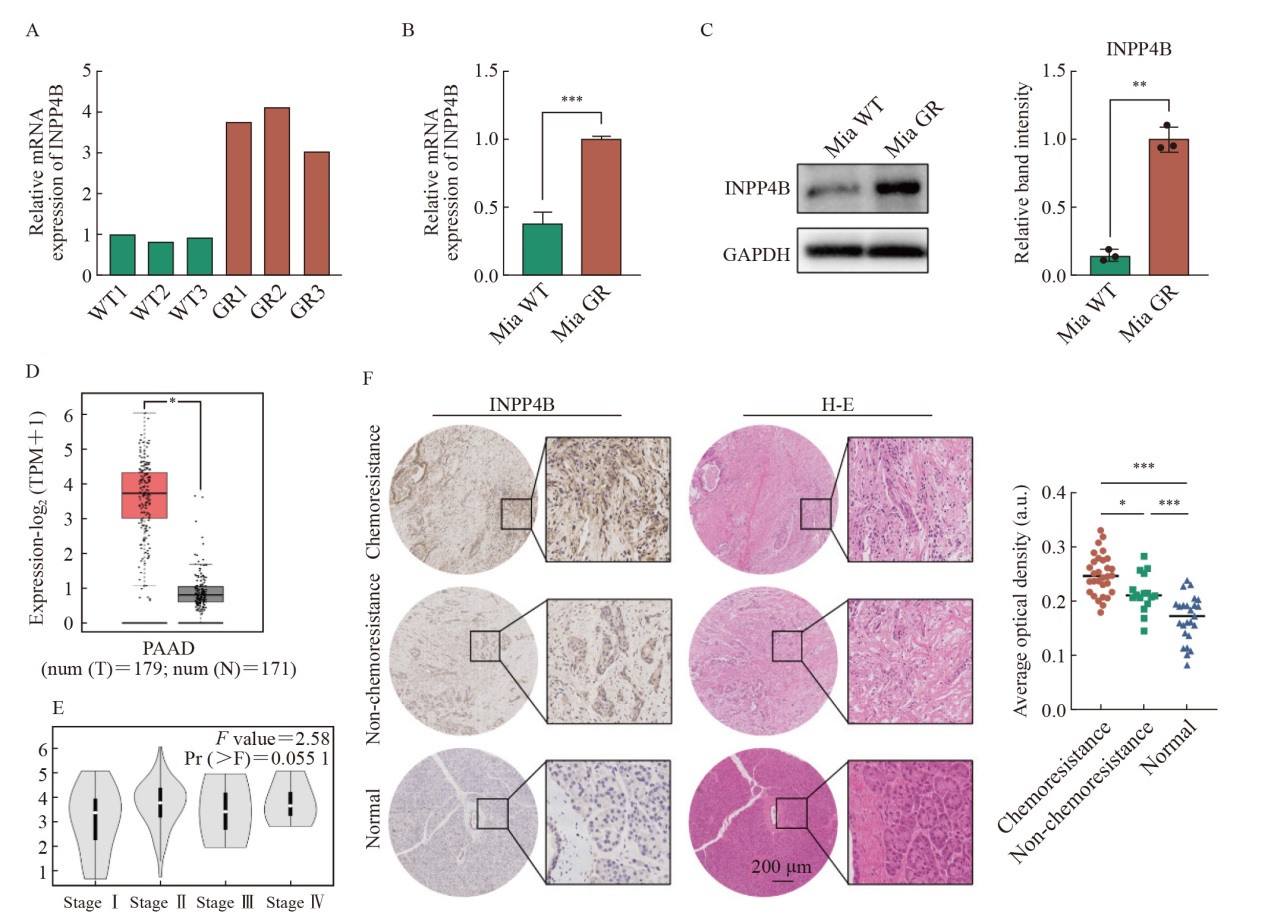
Tab. 1
Baseline characteristics and prognosis information of patients with pancreatic cancer"
| Item | Group | |
|---|---|---|
| Chemoresistance(n=30) | Non-chemoresistance (n=16) | |
| Gender n (%) | ||
| Male | 17 (56.7) | 11 (68.8) |
| Female | 13 (43.3) | 5 (31.2) |
| Age/year | ||
| Median (range) | 59 (35-79) | 58 (46-80) |
| OS t/month | ||
| Median (range) | 9.9 (2.0-26.9) | 17.7 (5.2-31.0) |
| PFS t/month | ||
| Median (range) | 7.8 (1.6-26.9) | 15.0 (1.3-31.0) |
| [1] | SIEGEL R, MILLER K D, WAGLE N S, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73: 17-48. |
| [2] |
MOORE A, DONAHUE T. Pancreatic cancer[J]. JAMA, 2019, 322(14): 1426.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.14699 pmid: 31593274 |
| [3] |
ZHANG L F, WU J H, LING M T, et al. The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway in human cancers induced by infection with human papillomaviruses[J]. Mol Cancer, 2015, 14: 87.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0361-x pmid: 26022660 |
| [4] | TEMPERO M A, MALAFA M P, AL-HAWARY M, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2017, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2017, 15(8): 1028-1061. |
| [5] | VO T T T, FRUMAN D A. INPP4B is a tumor suppressor in the context of PTEN deficiency[J]. Cancer Discov, 2015, 5(7): 697-700. |
| [6] | GEWINNER C, WANG Z C, RICHARDSON A, et al. Evidence that inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase type Ⅱ is a tumor suppressor that inhibits PI3K signaling[J]. Cancer Cell, 2009, 16(2): 115-125. |
| [7] | DZNELADZE I, WOOLLEY J F, ROSSELL C, et al. SubID, a non-median dichotomization tool for heterogeneous populations, reveals the pan-cancer significance of INPP4B and its regulation by EVI1 in AML[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(2): e0191510. |
| [8] | ZHAI S Y, LIU Y B, LU X X, et al. INPP4B as a prognostic and diagnostic marker regulates cell growth of pancreatic cancer via activating AKT[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 8287-8299. |
| [9] | ZHANG B, WANG W D, LI C H, et al. Inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase type Ⅱ plays critical roles in the modulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion dynamics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2018, 12(6): 548-563. |
| [10] |
FARRELL A S, JOLY M M, ALLEN-PETERSEN B L, et al. MYC regulates ductal-neuroendocrine lineage plasticity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma associated with poor outcome and chemoresistance[J]. Nat Commun, 2017, 8(1): 1728.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01967-6 pmid: 29170413 |
| [11] |
SHAO F, HUANG M, MENG F T, et al. Circular RNA signature predicts gemcitabine resistance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 584.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00584 pmid: 29922161 |
| [12] | SAIKI Y, YOSHINO Y, FUJIMURA H, et al. DCK is frequently inactivated in acquired gemcitabine-resistant human cancer cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 421(1): 98-104. |
| [13] | ZHOU J R, ZHANG L S, ZHENG H L, et al. Identification of chemoresistance-related mRNAs based on gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cell lines[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(3): 1115-1130. |
| [14] |
SCHWARTZ L H, LITIÈRE S, DE VRIES E, et al. RECIST 1.1-Update and clarification: from the RECIST committee[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2016, 62: 132-137.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.03.081 pmid: 27189322 |
| [15] |
ZHANG X, ZHENG S Y, HU C H, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-induced lncRNA UPK1A-AS1 confers platinum resistance in pancreatic cancer via efficient double-strand break repair[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(16): 2372-2389.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02253-6 pmid: 35264742 |
| [16] |
BILIMORIA K Y, BENTREM D J, KO C Y, et al. Validation of the 6th edition AJCC pancreatic cancer staging system: report from the National Cancer Database[J]. Cancer, 2007, 110(4): 738-744.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.22852 pmid: 17580363 |
| [17] |
RODGERS S J, OOMS L M, OORSCHOT V M J, et al. INPP4B promotes PI3Kα-dependent late endosome formation and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in breast cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 3140.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23241-6 pmid: 34035258 |
| [18] |
CHEN Y, SUN Z Y, QI M, et al. INPP4B restrains cell proliferation and metastasis via regulation of the PI3K/AKT/SGK pathway[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(5): 2935-2943.
doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13595 pmid: 29516642 |
| [19] | TEMPERO M A, MALAFA M P, AL-HAWARY M, et al. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2021, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2021, 19(4): 439-457. |
| [20] |
GROOT V P, REZAEE N, WU W C, et al. Patterns, timing, and predictors of recurrence following pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2018, 267(5): 936-945.
doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002234 pmid: 28338509 |
| [21] |
KANDA M, MATTHAEI H, WU J, et al. Presence of somatic mutations in most early-stage pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 142(4): 730-733.e9.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.042 pmid: 22226782 |
| [22] | WADDELL N, PAJIC M, PATCH A M, et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 495-501. |
| [23] |
DAUER P, NOMURA A, SALUJA A, et al. Microenvironment in determining chemo-resistance in pancreatic cancer: neighborhood matters[J]. Pancreatology, 2017, 17(1): 7-12.
doi: S1424-3903(16)31256-X pmid: 28034553 |
| [24] |
BEATTY G L, EGHBALI S, KIM R. Deploying immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer: defining mechanisms of response and resistance[J]. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book, 2017, 37: 267-278.
doi: 10.14694/EDBK_175232 pmid: 28561678 |
| [25] | GOLAN T, HAMMEL P, RENI M, et al. Maintenance olaparib for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic pancreatic cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 381(4): 317-327. |
| [26] |
PISHVAIAN M J, BLAIS E M, BRODY J R, et al. Overall survival in patients with pancreatic cancer receiving matched therapies following molecular profiling: a retrospective analysis of the Know Your Tumor registry trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(4): 508-518.
doi: S1470-2045(20)30074-7 pmid: 32135080 |
| [27] | MINI E, NOBILI S, CACIAGLI B, et al. Cellular pharmacology of gemcitabine[J]. Ann Oncol, 2006, 17(Suppl 5): v7-v12. |
| [28] | ASLEH K, LYCK CARSTENSEN S, TYKJAER JØRGENSEN C L, et al. Basal biomarkers nestin and INPP4B predict gemcitabine benefit in metastatic breast cancer: samples from the phase Ⅲ SBG0102 clinical trial[J]. Int J Cancer, 2019, 144(10): 2578-2586. |
| [1] | WANG Ting, QIN Yi, XU Xiaowu, YU Xianjun. New advances in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in 2024 [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 1-11. |
| [2] | LIN Qiuyu, WANG Yuxin, LIN Chenghe. Application and prospect of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 58-67. |
| [3] | WU Wen, ZHANG Ruoxin, WENG Junyong, MA Yanlei, CAI Guoxiang, LI Xinxiang, YANG Yongzhi. Exploring the prognostic value of positive lymph node ratio in stage Ⅲ colorectal cancer patients and establishing a predictive model [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 873-880. |
| [4] | XIAO Feng, XU Tonglin, ZHU Lin, XIAO Jingwen, WU Tianqi, GU Chunyan. Significance of infiltration of M1 tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 726-733. |
| [5] | CHEN Hong, CAO Zhiyun. Recent progress in the construction and application of patient-derived pancreatic cancer organoid models [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 590-597. |
| [6] | ZHANG Ruoxin, YE Zilan, WENG Junyong, LI Xinxiang. Correlation study between advanced age and inferior prognosis in stage Ⅱ colorectal cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 485-492. |
| [7] | LI Jun, LU Tingwei, FANG Xuqian. Impact of MSI-H/dMMR on clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of patients with BRAF V600E-mutated resectable colorectal cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(11): 1061-1066. |
| [8] | TAN Xiaolang, YAO Sha, WANG Guihua, PENG Luogen. Research on uPAR promoting proliferation, migration, and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting autophagy via MAPK signaling [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(10): 944-956. |
| [9] | LI Tianjiao, YE Longyun, JIN Kaizhou, WU Weiding, YU Xianjun. Advances in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(1): 1-12. |
| [10] | JIN Yizi, LIN Mingxi, ZHANG Jian. Receptor discordance between primary breast cancer and liver metastases [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 834-843. |
| [11] | WU Han, YANG Zhangru, FENG Wen, ZENG Wanqin, GUO Jindong, LI Hongxuan, WANG Changlu, WANG Jiaming, LÜ Changxing, ZHANG Qin, YU Wen, CAI Xuwei, FU Xiaolong. The efficacy and prognosis analysis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for multiple primary early-stage lung cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 844-856. |
| [12] | CHEN Jinjuan, WANG Xingran, LI Wenzhi, CHENG Yu, SUN Yihua, TAO Xiang, MA Fenghua, SUN Li, ZHAO Hongbo, LU Xin. Conservative surgery in stage I placental site trophoblastic tumor: a report of 10 cases and literature review [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 857-865. |
| [13] | SUN Yang, WANG Lian, ZHAO Meng, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GENG Zhijun, WANG Yueyue, SONG Xue, ZUO Lugen, LI Jing, HU Jianguo. The prognostic value of high expression of FKBP1A in gastric cancer and the regulatory effect of targeted PI3K/AKT on glucose metabolism [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 726-739. |
| [14] | JIANG Lin, LIU Qiying, JIA Liqing, ZHANG Jing, CHANG Heng, XUE Tian, REN Min, BAI Qianming, ZHU Xiaoli, ZHOU Xiaoyan. Retrospective study on MGMT methylation status and its clinical significance in gliomas [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 740-750. |
| [15] | WANG Ruoxi, JI Peng, GONG Yue, CHEN Sheng. Response rate and clinical outcome of HER2-low breast cancer after neoadjuvant therapy: a single-center retrospective study [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 686-692. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
