Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2022, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 134-141.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.02.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Bingni1, LIU Xiaohang1, GU Bingxin2, ZHOU Liangping1, GU Yajia1( )
)
Received:2021-11-03
Revised:2022-01-07
Online:2022-02-28
Published:2022-03-08
Contact:
GU Yajia
E-mail:cjr.guyajia@vip.163.com
Share article
CLC Number:
ZHOU Bingni, LIU Xiaohang, GU Bingxin, ZHOU Liangping, GU Yajia. The value of mpMRI combined with 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT in the detection of significant residual prostate cancer after neoadjuvant androgen deprivation therapy[J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(2): 134-141.
Tab. 1
Assessment categories by magnetic resonance imaging sequence after radiation therapy"
| Sequence | Score | Pattern changes |
|---|---|---|
| T2WI | 1 | No abnormal signal intensity compared to the background |
| 2 | Linear, wedge-shaped, or diffuse moderate hypointensity or residual benign prostatic hyperplasia nodules | |
| 3 | Focal or mass-like mild hypointensity not at the primary tumor site; includes others that do not qualify as 2, 4, or 5 | |
| 4 | Focal or mass-like moderate hypointensity not at the same site as the primary tumor, or location of primary tumor not known | |
| 5 | Focal or mass-like marked hypointensity at the same site as the primary tumor | |
| DWI | 1 | No abnormality on high b-value DWI and apparent diffusion coeffecient (ADC) map |
| 2 | Diffuse moderate hyperintensity on high b-value DWI and/or diffuse moderate hypointensity on the ADC map | |
| 3 | Focal marked hyperintensity on high b-value DWI or focal marked hypointensity on the ADC map, but not on both | |
| 4 | Focal marked hyperintensity on high b-value DWI and marked hypointensity on the ADC map not at the same site as the primary tumor, or site of the primary tumor not known | |
| 5 | Focal marked hyperintensity on high b-value DWI and marked hypointensity on the ADC map at the same site as the primary tumor | |
| DCE | 1 | No enhancement |
| 2 | Diffuse or heterogeneous enhancement | |
| 3 | Focal or mass-like late enhancement | |
| 4 | Focal or mass-like early enhancement not at the same site as the primary tumor, or tumor site not known | |
| 5 | Focal or mass-like early enhancement at the same site as the primary tumor |
Tab. 2
Comparison of general information between the significant residual group and complete response or minimum residual disease group"
| Average age | Initial PSA | PSA after neoadjuvant ADT | Gleason score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR group | 66.84±7.76 | 82.56 (21.39, 218.42) | 0.236 (0.06, 2.50) | 9 (8, 9) |
| CR/MRD group | 67.08±8.26 | 138.00 (8.23, 200.00) | 0.086 (0.01, 0.35) | 8 (7, 9) |
| P value | 0.854 | 0.514 | 0.021 | 0.073 |
Fig. 2
mpMRI combined with 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT to detect significant residual prostate cancer after neoadjuvant androgen deprivation treatment A 73-year-old patient received 3 months of neoadjuvant ADT with Gleason score 5+4=9, initial PSA was 82.56 ng/mL, PSA after neoadjuvant ADT was 5.73 ng/mL. Pathology diagnosis after RP confirmed the presence of significant residual lesion. A: The prostate showed heterogeneous signal intensity on T2WI, and the bilateral peripheral zone were diffuse moderate hypointensity; B, C: No obvious abnormal signal intensity on DWI and ADC images; D: No obvious abnormal enhancement lesion on DCE, PI-RR score 1; E: Cross-sectional view of the prostate on CT; F: Positive lesion was detected by SPECT; G: Fusion image of SPECT and CT; H: Maximum intensity projection image."
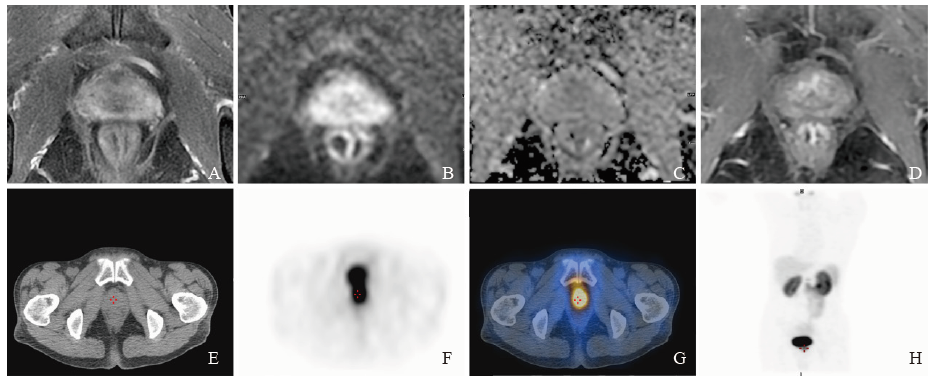
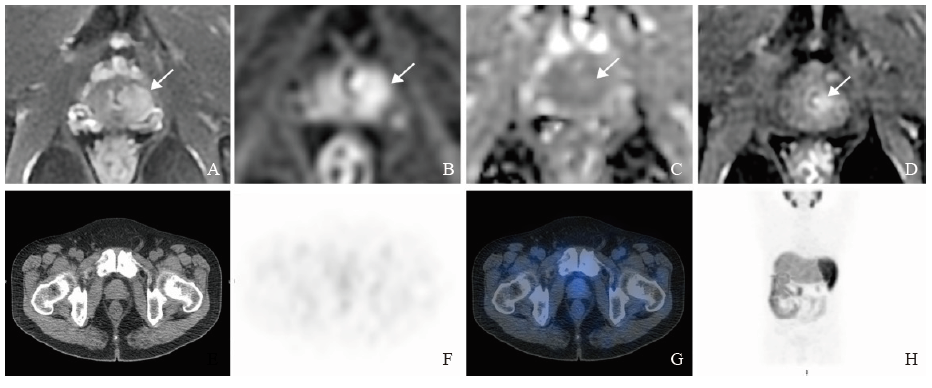
Fig. 3
mpMRI combined with 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT to detect significant residual prostate cancer after neoadjuvant androgen deprivation treatment A 58-year-old patient received transuerthral resection of prostate and 3 months of neoadjuvant ADT with Gleason score 10, initial PSA was 8.23 ng/mL, PSA after neoadjuvant ADT was 0.685 ng/mL. Pathology after RP confirmed the presence of significant residual lesion. A: Foucal hyperintensity on T2WI of the left peripheral zone (arrow); B, C: The lesion showed hyperintensity on DWI and isointensity-mild hyperintensity on ADC image (arrow); D: Foucal mass-like early enhancement on DCE (arrow), PI-RR score 5; E: Cross-sectional view of the prostate on CT; F: Negative result on SPECT; G: Fusion image of SPECT and CT; H: Maximum intensity projection image."
| [1] | SIEGEL R L,, MILLER K D,, FUCHS H E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021,71(1):7-33. |
| [2] | HEDGIRE S,, KILCOYNE A,, TONYUSHKIN A, et al. Effect of androgen deprivation and radiation therapy on MRI fiber tractography in prostate cancer: can we assess treatment response on imaging?[J]. Br J Radiol, 2019,92(1093):20170170. |
| [3] | COAKLEY F V,, TEH H S,, QAYYUM A, et al. Endorectal MR imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging for locally recurrent prostate cancer after external beam radiation therapy: preliminary experience[J]. Radiology, 2004,233(2):441-448. |
| [4] | HOFMAN M S,, LAWRENTSCHUK N,, FRANCIS R J, et al. Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET-CT in patients with high-risk prostate cancer before curative-intent surgery or radiotherapy (proPSMA): a prospective, randomised, multicentre study[J]. Lancet, 2020,395(10231):1208-1216. |
| [5] | FENDLER W P,, FERDINANDUS J,, CZERNIN J, et al. Impact of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET on the management of recurrent prostate cancer in a prospective single-arm clinical trial [J]. J Nucl Med, 2020,61(12):1793-1799. |
| [6] | AFSHAR-OROMIEH A,, HABERKORN U,, SCHLEMMER H P, et al. Comparison of PET/CT and PET/MRI hybrid systems using a 68Ga-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer: initial experience [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2014,41(5):887-897. |
| [7] | EIBER M,, MAURER T,, SOUVATZOGLOU M, et al. Evaluation of hybrid 68Ga-PSMA ligand PET/CT in 248 patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy [J]. J Nucl Med, 2015,56(5):668-674. |
| [8] | MORIGI J J,, STRICKER P D,, VAN LEEUWEN P J, et al. Prospective comparison of 18F-fluoromethylcholine versus 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in prostate cancer patients who have rising PSA after curative treatment and are being considered for targeted therapy [J]. J Nucl Med, 2015,56(8):1185-1190. |
| [9] | LAWAL I O,, ANKRAH A O,, MOKGORO N P, et al. Diagnostic sensitivity of Tc- 99m hynic PSMA SPECT/CT in prostate carcinoma: a comparative analysis with Ga-68 PSMA PET/CT [J]. Prostate, 2017,77(11):1205-1212. |
| [10] | ONAL C,, GULER O C,, TORUN N, et al. The effect of androgen deprivation therapy on 68Ga-PSMA tracer uptake in non-metastatic prostate cancer patients [J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2020,47(3):632-641. |
| [11] | PANEBIANCO V,, VILLEIRS G,, WEINREB J C, et al. Prostate magnetic resonance imaging for local recurrence reporting (PI-RR): international consensus-based guidelines on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer recurrence after radiation therapy and radical prostatectomy[J]. Eur Urol Oncol, 2021,4(6):868-876. |
| [12] | 胡四龙,, 许晓平,, 朱耀, 等. 99mTc标记PSMA小分子抑制剂靶向前列腺癌分子影像初步临床研究 [J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2016,26(7):608-615. |
| HU S L,, XU X P,, ZHU Y, et al. Preliminary clinical study of 99mTc-labelled small molecules against PSMA for prostate cancer imaging [J]. China Oncol, 2016,26(7):608-615. | |
| [13] | 许晓平,, 张建平,, 何思敏, 等. 前列腺特异性膜抗原小分子抑制剂显像研究[J]. 肿瘤影像学, 2015,24(3):173-178. |
| XU X P,, ZHANG J P,, HE S M, et al. The imaging study of a small-molecular inhibitor targeting prostate specific membrane antigen[J]. Oncoradiology, 2015,24(3):173-178. | |
| [14] | MCKAY R R,, MONTGOMERY B,, XIE W L, et al. Post prostatectomy outcomes of patients with high-risk prostate cancer treated with neoadjuvant androgen blockade[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis, 2018,21(3):364-372. |
| [15] | PETRAKI C D,, SFIKAS C P. Histopathological changes induced by therapies in the benign prostate and prostate adenocarcinoma[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2007,22(1):107-118. |
| [16] | STABILE A,, GIGANTI F,, ROSENKRANTZ A B, et al. Multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer diagnosis: current status and future directions[J]. Nat Rev Urol, 2020,17(1):41-61. |
| [17] | KATELARIS N C,, BOLTON D M,, WEERAKOON M, et al. Current role of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in the management of prostate cancer[J]. Korean J Urol, 2015,56(5):337-345. |
| [18] | PADHANI A R,, MACVICAR A D,, GAPINSKI C J, et al. Effects of androgen deprivation on prostatic morphology and vascular permeability evaluated with MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 2001,218(2):365-374. |
| [19] | MURPHY W M,, SOLOWAY M S,, BARROWS G H. Pathologic changes associated with androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer[J]. Cancer, 1991,68(4):821-828. |
| [20] | JOSEPH I B,, NELSON J B,, DENMEADE S R, et al. Androgens regulate vascular endothelial growth factor content in normal and malignant prostatic tissue[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 1997,3(12 Pt 1):2507-2511. |
| [21] | BARRETT T,, GILL A B,, KATAOKA M Y, et al. DCE and DW MRI in monitoring response to androgen deprivation therapy in patients with prostate cancer: a feasibility study[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2012,67(3):778-785. |
| [22] | RØE K,, SEIERSTAD T,, KRISTIAN A, et al. Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging-based assessment of vascular changes and radiation response in androgen-sensitive prostate carcinoma xenografts under androgen-exposed and androgen-deprived conditions[J]. Neoplasia, 2010,12(10):818-825. |
| [23] | RØE K,, KAKAR M,, SEIERSTAD T, et al. Early prediction of response to radiotherapy and androgen-deprivation therapy in prostate cancer by repeated functional MRI: a preclinical study[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2011,6:65. |
| [24] | CHRISTIE D R,, SHARPLEY C F,, MITINA N, et al. Is prospective MRI mapping of the changes in the volume of the prostate gland in prostate cancer patients undergoing 6 months of neo-adjuvant androgen deprivation therapy a step towards a trial to determine those who may benefit from treatment intensification or extended duration?[J]. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol, 2020,64(2):287-292. |
| [25] | 胡四龙,, 许晓平,, 朱耀, 等. 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT探测前列腺癌病灶的临床应用价值 [J]. 肿瘤影像学, 2016,25(3):272-278. |
| HU S L,, XU X P,, ZHU Y, et al. Clinical value of 99mTc-PSMA SPECT/CT in detection of prostate cancer [J]. Oncoradiology, 2016,25(3):272-278. | |
| [26] | REINFELDER J,, KUWERT T,, BECK M, et al. First experience with SPECT/CT using a 99mTc-labeled inhibitor for prostate-specific membrane antigen in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer [J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2017,42(1):26-33. |
| [27] | GARCÍA-PÉREZ F O,, DAVANZO J,, LÓPEZ-BUENROSTRO S, et al. Head to head comparison performance of 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-iPSMA SPECT/CT and 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT a prospective study in biochemical recurrence prostate cancer patients [J]. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2018,8(5):332-340. |
| [28] | KWAK C,, JEONG S J,, PARK M S, et al. Prognostic significance of the nadir prostate-specific antigen level after hormone therapy for prostate cancer[J]. J Urol, 2002,168(3):995-1000. |
| [29] | EVANS M J,, SMITH-JONES P M,, WONGVIPAT J, et al. Noninvasive measurement of androgen receptor signaling with a positron-emitting radiopharmaceutical that targets prostate-specific membrane antigen[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011,108(23):9578-9582. |
| [30] | VAZ S,, HADASCHIK B,, GABRIEL M, et al. Influence of androgen deprivation therapy on PSMA expression and PSMA-ligand PET imaging of prostate cancer patients[J]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2020,47(1):9-15. |
| [1] | Committee of Integrated Rehabilitation for Urogenital Tumors, Chinese Anti-Cancer Association. Chinese expert consensus on perioperative integrated rehabilitation for radical prostatectomy (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 890-902. |
| [2] | PAN Jian, YE Dingwei, ZHU Yao, WANG Beihe. Correlation analysis of PSMA PET/CT-derived parameters and circulating tumor DNA features in patients with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 680-685. |
| [3] | Cancer Nuclear Medicine Committee of China Anti-Cancer Association, Chinese Association of Nuclear Medicine Physicians. Expert consensus of 177Lu-labeled PSMA radioligand therapy for clinical practice of prostate cancer (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 702-714. |
| [4] | MA Fenghua, JIANG Anqi, CHEN Yiqing, XU Congjian, KANG Yu. Magnetic resonance imaging for distinguishing gastric-type endocervical adenocarcinoma from lobular endocervical glandular hyperplasia [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(4): 380-388. |
| [5] | LIU Qi, CHANG Cai, LI Jiawei. Research progress on the correlation between imaging features and the molecular subtype, histopathology, clinical prognosis of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 201-209. |
| [6] | WANG Yan, SU Yue, HU Tu, LIU Qiying, YAO Weiqiang, CHEN Yong, YAN Wangjun, ZHANG Zhen. Retrospective analysis of short-term efficacy and safety of preoperative radiotherapy for 33 cases of locally high-risk soft tissue sarcoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 693-700. |
| [7] | PAN Jian, ZHU Yao, DAI Bo, YE Dingwei. Advances in basic research, clinical diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer in 2022 [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 210-217. |
| [8] | CHEN Ruchuan, LIU Wei, ZHOU Bingni, LIU Xiaohang, ZHOU Liangping. The value of VI-RADS combined with tumor contact length in the detection of muscle-invasive bladder cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(3): 260-266. |
| [9] | Society of Male Reproductive System Oncology, China Anti-Cancer Association. Expert consensus on perioperative comprehensive treatment for high risk prostate cancer (2023 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(12): 1204-1214. |
| [10] | YANG Wenbo, ZHANG Bin, WU Jiahui, CUI Jie. Current status and treatment direction of the immune microenvironment of castration-resistant prostate cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(10): 945-953. |
| [11] | ZHOU Shukui, ZHANG Dongliang, WANG Xiang, LIU Lei, LI Zeng, YANG Shengke, LIAO Hong. Developing a new animal model of subcutaneous transplanted prostate cancer with cell sheet technology [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 200-206. |
| [12] | Chinese Prostate Cancer Consortium (CPCC), YE Dingwei, HUANG Jian. Chinese Prostate Cancer Consortium (CPCC) Chinese expert consensus on advanced prostate cancer: clinical management of patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer treated by initial novel hormone therapy (2022 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1242-1258. |
| [13] | XU Wenhao, TIAN Xi, Aihetaimujiang·Anwaier , QU Yuanyuan, SHI Guohai, ZHANG Hailiang, YE Dingwei. A systematic review of current advancements of artificial intelligence in genitourinary cancers [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(1): 68-74. |
| [14] | LUO Rong , HU Peian , XIE Tiansong , ZHANG Zehua , ZHOU Liangping , ZHOU Zhengrong , CHEN Lei . The correlation of imaging, clinical features and pathology of myxoid fibrosarcoma [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(8): 734-739. |
| [15] | WEI Yu , ZHANG Tingwei , HE Yi , LI Jun , BI Jianbin , ZENG Yu , WAN Lijun , WU Gaoliang , WANG Huansheng , ZHANG Jun , ZHU Wei , QU Yuanyuan , ZHU Yao , YE Dingwei . Preliminary study on efficacy and safety of fluzoparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 561-566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
