Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 637-645.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.07.001
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Xiaoli1( ), CHAI Wenjun1, SUN Lei1, YAN Mingxia1, PAN Hongyu1, SUN Yuexi2(
), CHAI Wenjun1, SUN Lei1, YAN Mingxia1, PAN Hongyu1, SUN Yuexi2( )
)
Received:2023-04-15
Revised:2023-06-27
Online:2023-07-30
Published:2023-08-10
Contact:
SUN Yuexi.
Share article
CLC Number:
LIU Xiaoli, CHAI Wenjun, SUN Lei, YAN Mingxia, PAN Hongyu, SUN Yuexi. Analysis of differential splicing gene by regulation of splicing regulatory protein KHSRP in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 637-645.
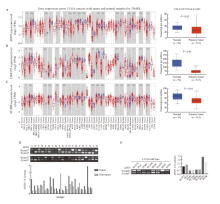
Fig. 3
Gene expression of different splicing transcript in lung adenocarcinoma Analysis of ADD3 (A), LIMCH1 (B) and NUMB (C) expression in lung adenocarcinoma tumor tissues and normal tissues using online TIMER and ULCAN database; D: Expression of ADD3 variable splicing isomers in 20 pairs of lung cancer tumor tissues and paired adjacent tissues;E: Expression of ADD3 variable splicing isomers in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001."
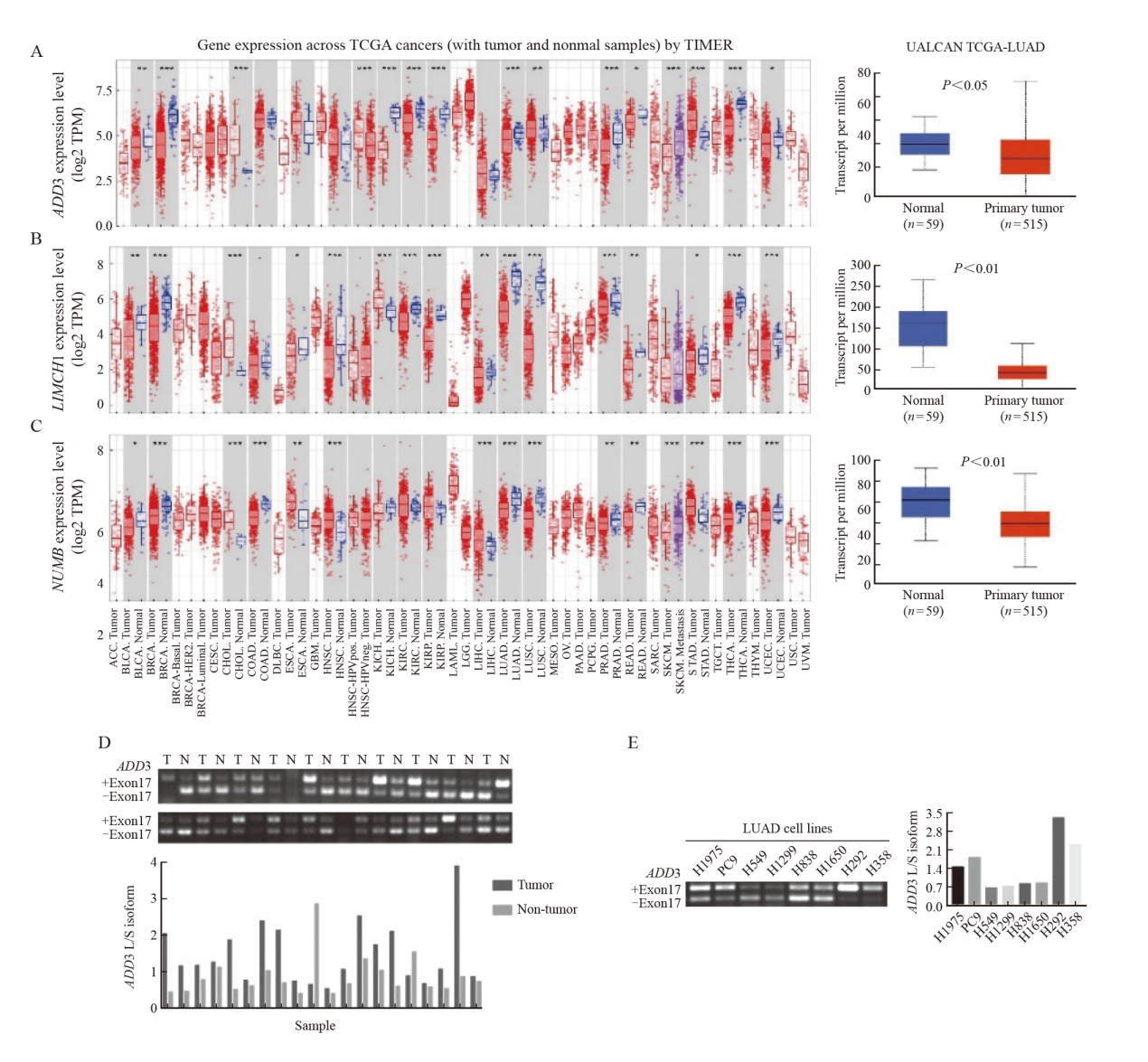
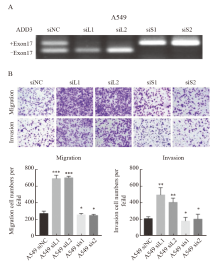
Fig. 6
The effect of ADD3 variable splicing isomers on migration and invasive potential in A549 cells A: Knockdown efficiency of ADD3 variable splicing isomer in A549 cells; B: Analysis of transwell migration and invasion experiment of knockdown ADD3 variable splicing isomer in A549 cells.*: P>0.05, compared with A549 siNC; **: P<0.01, compared with A549 siNC; ***: P<0.001, compared with A549 siNC."
| [1] |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v68.6 |
| [2] |
TIAN C H, WANG Y, YU H P, et al. A gene expression map of shoot domains reveals regulatory mechanisms[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 141.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08083-z pmid: 30635575 |
| [3] |
LI M M, WU P D, YANG Z C, et al. miR-193a-5p promotes pancreatic cancer cell metastasis through SRSF6-mediated alternative splicing of OGDHL and ECM1[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(1): 38-59.
pmid: 32064152 |
| [4] |
JBARA A, LIN K T, STOSSEL C, et al. RBFOX2 modulates a metastatic signature of alternative splicing in pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2023, 617(7959): 147-153.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05820-3 |
| [5] |
PELLARIN I, DALL’ACQUA A, GAMBELLI A, et al. Splicing factor proline- and glutamine-rich (SFPQ) protein regulates platinum response in ovarian cancer-modulating SRSF2 activity[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(22): 4390-4403.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1292-6 pmid: 32332923 |
| [6] |
HE Y T, OUYANG Z B, LIU W W, et al. TARDBP promotes ovarian cancer progression by altering vascular endothelial growth factor splicing[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(1): 49-61.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02539-9 |
| [7] |
HU X H, HARVEY S E, ZHENG R, et al. The RNA-binding protein AKAP8 suppresses tumor metastasis by antagonizing EMT-associated alternative splicing[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 486.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14304-1 pmid: 31980632 |
| [8] |
YADAV P, PANDEY A, KAKANI P, et al. Hypoxia-induced loss of SRSF2-dependent DNA methylation promotes CTCF-mediated alternative splicing of VEGFA in breast cancer[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(6): 106804.
doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106804 |
| [9] |
JIA R B, CHAI P W, WANG S Z, et al. m6A modification suppresses ocular melanoma through modulating HINT2 mRNA translation[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 161.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1088-x |
| [10] |
LOBAS A A, SOLOVYEVA E M, LEVITSKY L I, et al. Identification of alternative splicing in proteomes of human melanoma cell lines without RNA sequencing data[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2466.
doi: 10.3390/ijms24032466 |
| [11] |
SONG X, WAN X C, HUANG T Z, et al. SRSF3-regulated RNA alternative splicing promotes glioblastoma tumorigenicity by affecting multiple cellular processes[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(20): 5288-5301.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-1504 pmid: 31462429 |
| [12] |
LARIONOVA T D, BASTOLA S, AKSININA T E, et al. Alternative RNA splicing modulates ribosomal composition and determines the spatial phenotype of glioblastoma cells[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2022, 24(10): 1541-1557.
doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00994-w pmid: 36192632 |
| [13] |
KING P H, CHEN C Y. Role of KSRP in control of type Ⅰ interferon and cytokine expression[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2014, 34(4): 267-274.
doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0143 |
| [14] |
BRADLEY R K, ANCZUKÓW O. RNA splicing dysregulation and the hallmarks of cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23(3): 135-155.
doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00541-7 pmid: 36627445 |
| [15] |
AGRAWAL A A, YU L, SMITH P G, et al. Targeting splicing abnormalities in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2018, 48: 67-74.
doi: S0959-437X(17)30088-6 pmid: 29136527 |
| [16] |
CLIMENTE-GONZÁLEZ H, PORTA-PARDO E, GODZIK A, et al. The functional impact of alternative splicing in cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 20(9): 2215-2226.
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.08.012 |
| [17] |
YAN M X, SUN L, LI J, et al. RNA-binding protein KHSRP promotes tumor growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 478.
doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1479-2 |
| [18] |
MIN H, TURCK C W, NIKOLIC J M, et al. A new regulatory protein, KSRP, mediates exon inclusion through an intronic splicing enhancer[J]. Genes Dev, 1997, 11(8): 1023-1036.
doi: 10.1101/gad.11.8.1023 |
| [19] |
BECHARA E G, SEBESTYÉN E, BERNARDIS I, et al. RBM5, 6, and 10 differentially regulate NUMB alternative splicing to control cancer cell proliferation[J]. Mol Cell, 2013, 52(5): 720-733.
doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.11.010 pmid: 24332178 |
| [20] |
WANG J Z, FU X, FANG Z Y, et al. QKI-5 regulates the alternative splicing of cytoskeletal gene ADD3 in lung cancer[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 13(5): 347-360.
doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjaa063 |
| [21] |
LECHUGA S, AMIN P H, WOLEN A R, et al. Adducins inhibit lung cancer cell migration through mechanisms involving regulation of cell-matrix adhesion and cadherin-11 expression[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2019, 1866(3): 395-408.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.10.001 |
| [22] |
WANG Y B, BAO Y F, ZHANG S R, et al. Splicing dysregulation in cancer: from mechanistic understanding to a new class of therapeutic targets[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2020, 63(4): 469-484.
doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-1605-0 pmid: 32086672 |
| [23] |
REN P P, LU L Y, CAI S S, et al. Alternative splicing: a new cause and potential therapeutic target in autoimmune disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 713540.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713540 |
| [24] |
PAUCEK R D, BALTIMORE D, LI G D. The cellular immunotherapy revolution: arming the immune system for precision therapy[J]. Trends Immunol, 2019, 40(4): 292-309.
doi: S1471-4906(19)30025-0 pmid: 30871979 |
| [25] |
LIU Y T, YAN X, ZHANG F, et al. TCR-T immunotherapy: the challenges and solutions[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 794183.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.794183 |
| [26] |
SELLARS M C, WU C J, FRITSCH E F. Cancer vaccines: building a bridge over troubled waters[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(15): 2770-2788.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.035 pmid: 35835100 |
| [27] |
JAYASINGHE R G, CAO S, GAO Q S, et al. Systematic analysis of splice-site-creating mutations in cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2018, 23(1): 270-281.e3.
doi: S2211-1247(18)30397-8 pmid: 29617666 |
| [28] |
KAHLES A, LEHMANN K V, TOUSSAINT N C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of alternative splicing across tumors from 8, 705 patients[J]. Cancer Cell, 2018, 34(2): 211-224.e6.
doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.07.001 |
| [29] |
BURBAGE M, ROCAÑÍN-ARJÓ A, BAUDON B, et al. Epigenetically controlled tumor antigens derived from splice junctions between exons and transposable elements[J]. Sci Immunol, 2023, 8(80): eabm6360.
doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abm6360 |
| [30] |
FRANKIW L, BALTIMORE D, LI G D. Alternative mRNA splicing in cancer immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(11): 675-687.
doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0195-7 pmid: 31363190 |
| [1] | JIA Liqing, GE Xiaolu, JIANG Lin, ZHOU Xiaoyan. Effects of lncRNA PKD2-2-3 on cell proliferation, clone formation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 717-725. |
| [2] | DONG Hao, QIU Yonggang, WANG Xinbin, YANG Junjie, LOU Cuncheng, YIN Lekang, YE Xiaodan. Predictive value of logistic regression model based on high-resolution CT signs for high-grade pattern in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(8): 768-775. |
| [3] | MU Jiaqian, TENG Xiaoyan, WEI Lirong, QIU Rong, GUI Pengcheng, DU Yuzhen. The role and application value of integrin β3 in bone metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(4): 351-356. |
| [4] | ZHU Haipeng, HU Jun, JIANG Min, CAI Ruonan, WANG Junqiao, LI Li. A study on mechanism of GOLM1 regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to promote proliferation, invasion and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(3): 207-217. |
| [5] | HOU Qinghua, ZHONG Yanfeng, LIU Linzhuang, WU Liusheng, LIU Jixian. Expression, prognostic value of CBX3 in lung adenocarcinoma and its effect on biological behavior of cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(2): 152-160. |
| [6] | ZHANG Longfu, LIU Jie, NI Zheng, LU Xinyuan, HU Bin, WANG Hao, FENG Mingxiang, ZHANG Yong. Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting spread through air spaces in stage ⅠA lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(12): 1210-1217. |
| [7] | HU Guannan , CHEN Lei , ZHOU Liangping , ZHOU Zhengrong . A case report of pulmonary malignant melanoma complicated with lung adenocarcinoma and literature review [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(7): 647-650. |
| [8] | HU Yaqiong , BAI Jun , CHEN Lin , CHEN Xinlu , ZHANG Liping , ZHOU Dandan , WANG Yu , YIN Chonggao , LI Hongli , LIU Yuqing . miR-625-5p promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting PRKACA [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(6): 447-454. |
| [9] | PENG Zishan, KONG Hui, BAO Zhen, ZHAO Hongxing, LIU Xin, LU Shaohua. Clinicopathological analysis of 83 cases of multifocal lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(5): 408-418. |
| [10] | SHI Maolin , BAI Yudi , WANG Chao , LI Siqi , ZHOU Daijun , PENG Jingjing , SUN Feifan , LI Dong , ZHANG Tao . Effect of PD-L1 expression on the efficacy of pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma and its mechanism [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(4): 308-316. |
| [11] | WANG Xiaodong , ZHOU Dandan , ZHANG Liping , ZHENG Quan , MU Qingjie , YIN Chonggao , LI Hongli . FAM83A is highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and promotes invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(8): 586-592. |
| [12] | GAO Zhiqiang,WANG Weimin,CAI Yuqing,QIN Ruoyan,GU Aiqin,XIONG Liwen,HAN Baohui,JIANG Liyan,SHI Chunlei . Clinical efficacy of osimertinib in the treatment of 62 patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(10): 809-814. |
| [13] | WANG Shengping, FU Yi, LIU Quan, et al. Computed tomography features of solitary pulmonary nodules in breast cancer patients: differential diagnosis between primary lung adenocarcinoma and metastatic pulmonary breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2018, 28(6): 411-418. |
| [14] | DAI Xi, LI Guoping, YANG Xiaoqiong, et al. Effects of Lyn kinase on EGFR signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2018, 28(1): 43-49. |
| [15] | TIAN Xigui, LIU Desen, WANG Yuanyu, et al. Postoperative differences in clinical characteristics between adenocarcinoma and other types of nonsmall cell lung cancer and analysis of prognostic factors of adenocarcinoma treated with surgery [J]. China Oncology, 2017, 27(3): 227-232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
