Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2024, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 1123-1133.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2024.12.007
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
PAN Yijin1( ), SHI Cong1, SUN Yuqing1, SUN Di1, ZHAO Yihan1,2, ZHANG Jin3, LIN Yansong1(
), SHI Cong1, SUN Yuqing1, SUN Di1, ZHAO Yihan1,2, ZHANG Jin3, LIN Yansong1( )
)
Received:2024-08-02
Online:2024-12-30
Published:2025-01-21
Share article
PAN Yijin, SHI Cong, SUN Yuqing, SUN Di, ZHAO Yihan, ZHANG Jin, LIN Yansong. Global trends of 131I-therapy for differentiated thyroid cancer in children and adolescents: a bibliometric analysis (1993-2003)[J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(12): 1123-1133.
Tab. 1
The top 10 productive countries/regions in caDTC 131I-therapy field"
| Rank | Country/region | Publications | Percentage | Total citations | Average citations | Collaboration strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States (US) | 64 | 42.67% | 2 643 | 41.30 | 24 |
| 2 | Italy | 16 | 10.67% | 1 028 | 64.25 | 14 |
| 3 | China | 15 | 10.00% | 190 | 12.67 | 1 |
| 4 | Germany | 13 | 8.67% | 1 101 | 84.69 | 28 |
| 5 | Japan | 11 | 7.33% | 869 | 79.00 | 18 |
| 5 | Netherlands | 11 | 7.33% | 313 | 28.45 | 11 |
| 7 | Canada | 7 | 4.67% | 886 | 126.57 | 10 |
| 8 | India | 6 | 4.00% | 83 | 13.83 | 0 |
| 8 | Turkey | 6 | 4.00% | 18 | 3.00 | 0 |
| 10 | Belarus | 5 | 3.33% | 313 | 62.60 | 12 |
Tab. 2
The top 10 productive institutions in caDTC 131I-therapy field"
| Rank | Institution | Publications | Total citations | Country/region | Average citations | Collaboration strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Pennsylvania | 11 | 813 | US | 73.91 | 24 |
| 2 | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | 7 | 297 | US | 42.43 | 7 |
| 3 | Sichuan University | 6 | 41 | China | 6.83 | 0 |
| 3 | University of Pisa | 6 | 167 | Italy | 27.83 | 2 |
| 3 | Yale University | 6 | 1 036 | US | 172.67 | 18 |
| 6 | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia | 5 | 720 | US | 144.00 | 13 |
| 6 | University of Groningen | 5 | 136 | Netherlands | 27.20 | 12 |
| 6 | University of Pittsburgh | 5 | 44 | US | 8.80 | 12 |
| 6 | MD Anderson Cancer Center | 5 | 814 | US | 162.80 | 10 |
| 6 | University of Toronto | 5 | 792 | Canada | 158.40 | 15 |
| 6 | University of Würzburg | 5 | 240 | Germany | 48.00 | 6 |
Tab. 3
The information of top 8 productive authors in the field of caDTC 131I treatment"
| Rank | Author | Publications | Totalcitations | Average citations | H-index (WoS) | Institution | Country | Collaboration strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bauer A J | 7 | 753 | 107.57 | 22 | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia | USA | 25 |
| 2 | Kazahaya K | 6 | 47 | 7.83 | 17 | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia | USA | 4 |
| 3 | Huang R | 6 | 41 | 6.83 | 13 | Sichuan University | China | 23 |
| 4 | Links T P | 5 | 136 | 27.20 | 53 | University Medical Center Groningen | Netherlands | 50 |
| 5 | Mostoufi-Moab S | 5 | 45 | 9.00 | 22 | Children's Hospital of Philadelphia | USA | 19 |
| 6 | Tuttle R M | 5 | 152 | 30.40 | 77 | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | USA | 4 |
| 7 | van Santen H M | 5 | 135 | 27.00 | 26 | Wilhelmina Children's Hospital | Netherlands | 50 |
| 8 | Waguespack S G | 5 | 814 | 162.80 | 46 | MD Anderson Cancer Center | USA | 8 |
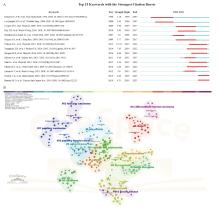
Fig. 3
Visualization analysis of references A: Burst analysis of the top 15 references. The blue line represented the period from 1993 to 2023, while the red line plots represented the periods of each burst keyword. B: Reference clustering map analysis through CiteSpace. A total of 15 categories of references were obtained. The different color blocks represented different reference clusters. This figure was generated by CiteSpace."
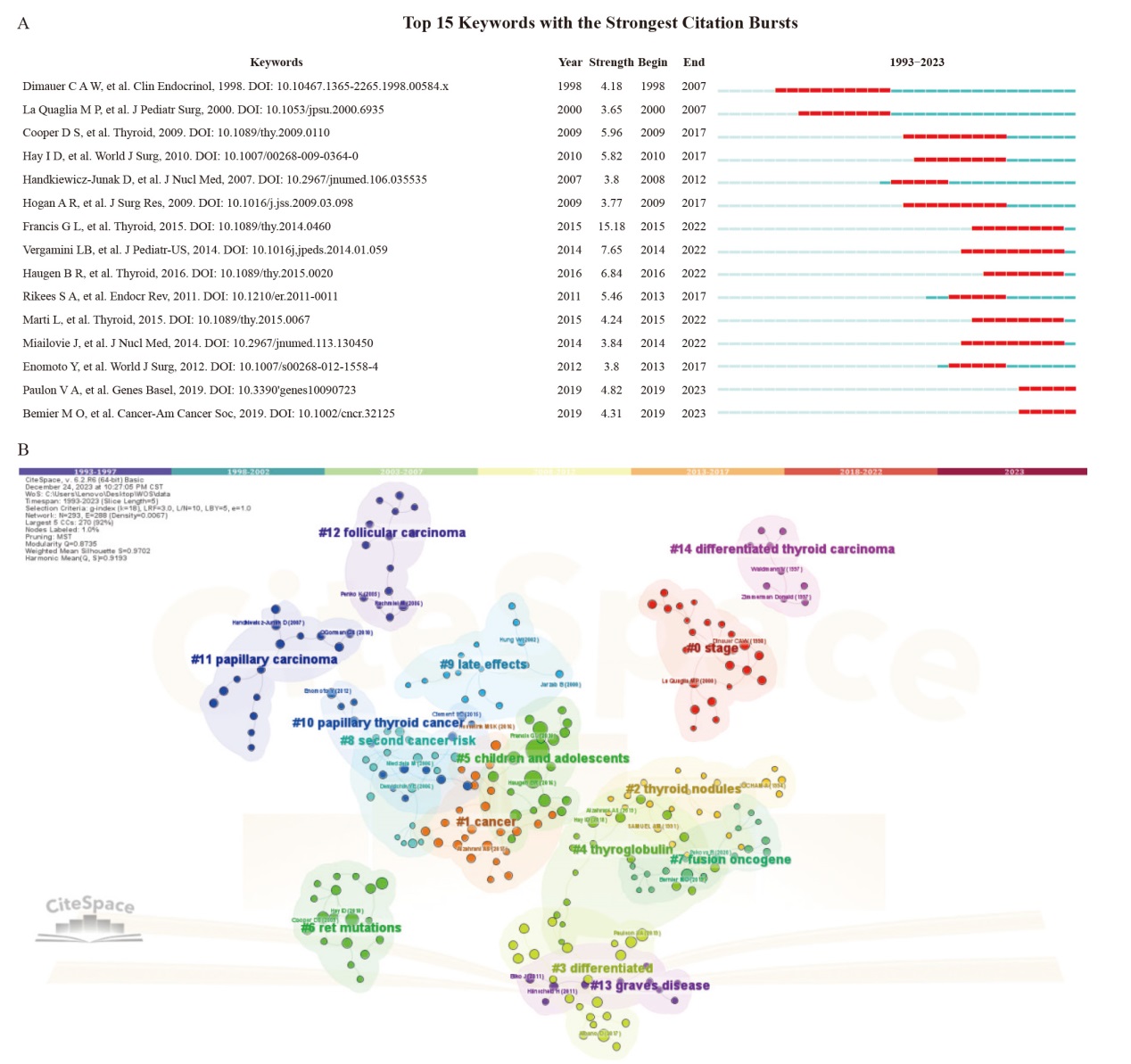

Fig. 4
Visualization analysis of keywords A: Burst analysis of the top 15 keywords. The blue line represents the period from 1993 to 2023, while the red line plots the periods of each burst keyword. B: Keyword clustering map analysis through CiteSpace. The different color blocks represent different reference clusters. This figure was generated by CiteSpace."
| [1] | 中国临床肿瘤学会核医学专家委员会, 中国临床肿瘤学会甲状腺癌专家委员会, 中国医疗保健国际交流促进会甲状腺疾病专业委员会, 等. 儿童及青少年分化型甲状腺癌核医学诊治中国专家共识(2022年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2022, 32(5): 451-468. |
| Expert Committee of Nuclear Medicine, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, Expert Committee of Thyroid Cancer, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology, et al. Expert consensus on management of differentiated thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents (2022 edition)[J]. Chin Oncol, 2022, 32(5): 451-468. | |
| [2] | KUHLEN M, WELLBROCK M, KUNSTREICH M, et al. Incidence and temporal patterns of differentiated thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents in Germany: a pooled analysis based on data from the German malignant endocrine tumor registry and the German childhood cancer registry[J]. Thyroid, 2024, 34(12): 1540-1550. |
| [3] | ZHENG R S, CHEN R, HAN B F, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2024, 4(1): 47-53. |
| [4] | DE SOUSA M S A, NUNES I N, CHRISTIANO Y P, et al. Genetic alterations landscape in paediatric thyroid tumours and/or differentiated thyroid cancer: systematic review[J]. Rev Endocr Metab Disord, 2024, 25(1): 35-51. |
| [5] | FRANCIS G L, WAGUESPACK S G, BAUER A J, et al. Management guidelines for children with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2015, 25(7): 716-759. |
| [6] | GUAN Q, WANG Y. Pathology features and clinical significances of thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2022, 42(6): 638-43. |
| [7] | BOUCAI L, ZAFEREO M, CABANILLAS M E. Thyroid cancer: a review[J]. JAMA, 2024, 331(5): 425-435. |
| [8] | LIU Y J, WANG J F, HU X P, et al. Radioiodine therapy in advanced differentiated thyroid cancer: resistance and overcoming strategy[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2023, 68: 100939. |
| [9] | PETERMANN-ROCHA F, DIAZ-TORO F, VALERA-GRAN D, et al. Bibliometric analysis of research on sarcopenic obesity: a review of scientific literature[J]. Obes Rev, 2024, 25(9): e13784. |
| [10] | SUN Z C, WANG X Y, XIAO J H, et al. Knowledge mapping and emerging trends in neural stem cell transplantation research for spinal cord injury: a bibliometric analysis (2004-2023)[J]. Int J Surg, 2024, 110(12): 8215-8219. |
| [11] | CHEN C M, SONG M. Visualizing a field of research: a methodology of systematic scientometric reviews[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(10): e0223994. |
| [12] | LIU X J, YUAN J Y, FENG Y F, et al. Knowledge graph and development hotspots of biochar as an emerging aquatic antibiotic remediator: a scientometric exploration based on VOSviewer and CiteSpace[J]. J Environ Manage, 2024, 360: 121165. |
| [13] | BOYACK K W, SMITH C, KLAVANS R. A detailed open access model of the PubMed literature[J]. Sci Data, 2020, 7(1): 408. |
| [14] | JOCHAM A, JOPPICH I, HECKER W, et al. Thyroid carcinoma in childhood: management and follow up of 11 cases[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 1994, 153(1): 17-22. |
| [15] | MU Z Z, ZHANG X, SUN D, et al. Characterizing genetic alterations related to radioiodine avidity in metastatic thyroid cancer[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2024, 109(5): 1231-1240. |
| [16] | MU Z Z, ZHANG Y Q, SUN D, et al. Effect of BRAFV600E and TERT promoter mutations on thyroglobulin response in patients with distant-metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Endocr Pract, 2022, 28(3): 265-270. |
| [17] | LEBBINK C A, LINKS T P, CZARNIECKA A, et al. 2022 European Thyroid Association guidelines for the management of pediatric thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid carcinoma[J]. Eur Thyroid J, 2022, 11(6): e220146. |
| [18] | 孙迪, 孙郁青, 张鑫, 等. 局部晚期或转移性儿童及青少年分化型甲状腺癌的基因特征与临床特征及131I疗效的关系[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2022, 32(5): 380-387. |
| SUN D, SUN Y Q, ZHANG X, et al. The relationship between genetic characteristics and clinical characteristics and the efficacy of 131I therapy in children and adolescents with locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Chin Oncol, 2022, 32(5): 380-387. | |
| [19] | NIES M, VASSILOPOULOU-SELLIN R, BASSETT R L, et al. Distant metastases from childhood differentiated thyroid carcinoma: clinical course and mutational landscape[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 106(4): e1683-e1697. |
| [20] | 潘逸缙, 鞠高达, 慕转转, 等. 转移性儿童及青少年分化型甲状腺癌基因与临床特征的关系[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2024, 104(20): 1837-1843. |
| PAN Y J, JU G D, MU Z Z, et al. The relationship between differentially expressed thyroid cancer genes and clinical characteristics in metastatic children and adolescents[J]. Natl Med J Chin, 2024, 104(20): 1837-1843. | |
| [21] | PAWELCZAK M, DAVID R, FRANKLIN B, et al. Outcomes of children and adolescents with well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma and pulmonary metastases following ¹³¹I treatment: a systematic review[J]. Thyroid, 2010, 20(10): 1095-1101. |
| [22] | KIM K J, KIM K J, CHOI J, et al. Linear association between radioactive iodine dose and second primary malignancy risk in thyroid cancer[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2023, 115(6): 695-702. |
| [23] | VASSILOPOULOU-SELLIN R, GOEPFERT H, RANEY B, et al. Differentiated thyroid cancer in children and adolescents: clinical outcome and mortality after long-term follow-up[J]. Head Neck, 1998, 20(6): 549-555. |
| [24] | PASQUAL E, SCHONFELD S, MORTON L M, et al. Association between radioactive iodine treatment for pediatric and young adulthood differentiated thyroid cancer and risk of second primary malignancies[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2022, 40(13): 1439-1449. |
| [25] | ZHAO X L, CHEN M J, QI X J, et al. Association of radioiodine for differentiated thyroid cancer and second breast cancer in female adolescent and young adult[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 12: 805194. |
| [1] | GENG Qianqian, YANG Aimin. Progress and prospect on treatment for radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 30-39. |
| [2] | LI Ruping, YANG Hui. Current status and future prospects of clinical trials for radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 40-48. |
| [3] | WANG Renfei, LU Gaixia. The unique value and controversy of nuclear medicine molecular imaging in the evaluation of radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 49-57. |
| [4] | LIN Qiuyu, WANG Yuxin, LIN Chenghe. Application and prospect of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 58-67. |
| [5] | JIANG Xiaotong, LIU Jinchuan, ZHANG Yingqiang, WANG Tong, GUO Ning, SUN Yuqing, SHI Cong, YAN Bing, LIN Yansong. The role of diagnostic whole body scan in decision-making of 131I treatment for differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2025, 35(1): 77-84. |
| [6] | DENG Shuting, FENG Yuan, QIAN Kai, GUO Kai, WANG Zhuoying. Meta-analysis of the association between gene alterations and distant metastasis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(5): 388-396. |
| [7] | GUO Wenting, MU Zhuanzhuan, LI Zheng, ZHANG Yingqiang, JIN Xiaona, LIN Yansong. Clinical outcome of 131I therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer patients with suspicious high thyroglobulin concentration [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(5): 410-416. |
| [8] | Expert Committee of Nuclear Medicine, Chinese society of Clinical Oncology, Expert Committee of Thyroid Cancer, Chinese society of Clinical Oncology, Committee of Thyroid Disease Society, China International Exchange and Promotive Association for Medical and Health Care, Committee of Thyroid Disease Prevention and Treatment Society, China Population Culture Promotion Association. Expert consensus on management of differentiated thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents (2022 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(5): 451-468. |
| [9] | MEI Xiaoran, FENG Fang, WANG Hui, WEI Zhixiao. Analysis of therapeutic response of iodine positive metastasis lymph nodes in differentiated thyroid cancer after 131I treatment [J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(11): 1091-1097. |
| [10] | LIU Wei , WANG Xiaojiang , ZHANG Jing , ZHU Weifeng , PENG Fengying , WANG Jianchao , XIAO Weijin , HU Dan . Clinicopathological characteristics and prognostic analysis of medullary thyroid carcinoma in children and adolescents [J]. China Oncology, 2021, 31(11): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | LI Min, WEN Peng, QIAN Qiuqin, QIN Ang, ZENG Li, SHI Feng. Clinical study of iodine-125 seeds implantation in the treatment of lymph node metastasis of radioactive iodine- refractory differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2020, 30(2): 122-127. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liyang, LIU Chunhao, CAO Yue, LIU Hongfeng, GAO Weisheng, LI Xiaoyi. Experiences of 125 cases of re-operated persistent/recurrent differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(6): 412-417. |
| [13] | YANG Ke, ZHENG Rong, LIN Yansong. The interpretation of management guidelines for children with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: radioactive iodine therapy and new progress [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(6): 401-411. |
| [14] | GAO Luying, LIN Yansong, JIANG Yuxin, LI Jianchu, LI Hui, ZHANG Bo, LIU Ruyu, XI Xuehua, GAO Qiong, WANG Ying, ZHAO Ruina. Evaluation of short-term efficacy of apatinib using cervical ultrasound and thyroglobulin in the treatment of progressive radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(6): 418-422. |
| [15] | ZHANG Na, LIN Yansong, LIANG Jun. The clinical significance of thyroglobulin antibody measurement in 131I therapy of differentiated thyroid carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2019, 29(6): 452-456. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
