Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2022, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 624-634.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.07.006
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
HONG Yaping( )(
)( ), HUANG Yunjian, HUANG Zhangzhou, CHEN Shengjia, ZHONG Qiaofeng, ZENG Hongfu, ZHUANG Wu(
), HUANG Yunjian, HUANG Zhangzhou, CHEN Shengjia, ZHONG Qiaofeng, ZENG Hongfu, ZHUANG Wu( )(
)( )
)
Received:2022-02-14
Online:2022-07-30
Published:2022-08-09
Contact:
ZHUANG Wu
E-mail:yipinghong2018@163.com;zhuangwu2008@126.com
Share article
CLC Number:
HONG Yaping, HUANG Yunjian, HUANG Zhangzhou, CHEN Shengjia, ZHONG Qiaofeng, ZENG Hongfu, ZHUANG Wu. Efficacy and prognostic predictors of first-generation EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(7): 624-634.
Tab. 1
Clinicopathological characteristics of patients [n (%)]"
| Characteristic | Number of patients | Characteristic | Number of patients | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | M1a | 32 (27.1) | ||
| Male | 45 (38.1) | M1b | 8 (6.8) | |
| Female | 73 (61.9) | M1c | 72 (61.0) | |
| Age/year | Pleural effusion | |||
| ≥60 | 61 (51.7) | Yes | 44 (37.3) | |
| <60 | 57 (48.3) | No | 74 (62.7) | |
| Smoking history | Intrapulmonary metastasis | |||
| Yes | 17 (14.4) | Yes | 61 (51.7) | |
| No | 101 (85.6) | No | 57 (48.3) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | Bone metastasis | |||
| Yes | 99 (83.9) | Yes | 50 (42.4) | |
| No | 19 (16.1) | No | 68 (57.6) | |
| Overall stage | Brain metastasis | |||
| ⅢB-ⅢC | 6 (5.1) | Yes | 48 (40.7) | |
| ⅣA | 42 (35.6) | No | 70 (59.3) | |
| ⅣB | 70 (59.3) | Liver metastasis | ||
| Postoperative recurrence | Yes | 8 (6.8) | ||
| Yes | 14 (11.9) | No | 110 (93.2) | |
| No | 104 (88.1) | Adrenal metastasis | ||
| T stage | Yes | 4 (3.4) | ||
| T1 | 24 (20.3) | No | 114 (96.6) | |
| T2 | 24 (20.4) | Carcinomatous lymphangitis | ||
| T3 | 6 (5.1) | Yes | 2 (5.1) | |
| T4 | 64 (54.2) | No | 112 (94.9) | |
| N stage | EGFR detected by tissue | |||
| N0 | 32 (27.1) | 19DEL | 55 (46.6) | |
| N1 | 8 (6.8) | L858R | 49 (41.5) | |
| N2 | 27 (22.9) | Rare mutation | 14 (11.9) | |
| N3 | 51 (43.2) | EGFR detected by blood | ||
| M stage | positive | 86 (72.9) | ||
| M0 | 6 (5.1) | Negative | 32 (27.1) |
Tab. 2
Clinicopathological characteristics and efficacy of different types of EGFR mutations"
| Item | 19DEL | L858R | Rare mutation | P value | Item | 19DEL | L858R | Rare mutation | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.408 | Intrapulmonary metastasis | 0.044 | ||||||
| Male | 19 | 22 | 4 | Yes | 29 | 29 | 3 | ||
| Female | 36 | 27 | 10 | No | 26 | 20 | 11 | ||
| Age/year | 0.976 | Bone metastasis | 0.671 | ||||||
| ≥60 | 29 | 25 | 7 | Yes | 22 | 23 | 5 | ||
| <60 | 26 | 24 | 7 | No | 33 | 26 | 9 | ||
| Smoking history | 0.254 | Brain metastasis | 0.724 | ||||||
| Yes | 10 | 4 | 3 | Yes | 21 | 20 | 7 | ||
| No | 45 | 45 | 11 | No | 34 | 29 | 7 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 0.589 | Liver metastasis | 0.859 | ||||||
| Yes | 45 | 41 | 13 | Yes | 3 | 4 | 1 | ||
| No | 10 | 8 | 1 | No | 52 | 45 | 13 | ||
| Overall stage | 0.039 | Adrenal metastasis | 0.054 | ||||||
| ⅢB-ⅢC | 1 | 5 | 0 | Yes | 0 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Ⅳa | 25 | 15 | 2 | No | 55 | 45 | 14 | ||
| Ⅳb | 29 | 29 | 12 | Carcinomatous lymphangitis | 0.316 | ||||
| Postoperative recurrence | 0.577 | Yes | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 8 | 4 | 2 | No | 54 | 45 | 13 | ||
| No | 47 | 45 | 12 | Best curative effect | 0.040 | ||||
| Pleural effusion | 0.235 | PR | 34 | 34 | 6 | ||||
| Yes | 19 | 22 | 3 | SD | 20 | 10 | 5 | ||
| No | 36 | 27 | 11 | PD | 1 | 5 | 3 |
Tab. 3
Univariate analysis of the correlation between clinical characteristics and PFS/OS in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation"
| Item | mPFS/month | 95% CI | P value | mOS/month | 95% CI | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.660 | 0.360 | ||||
| Male | 11.5 | 8.0-15.0 | 30.5 | 23.7-37.4 | ||
| Female | 11.3 | 9.0-13.6 | 33.8 | 24.1-43.6 | ||
| Age/year | 0.204 | 0.266 | ||||
| ≥60 | 12.2 | 10.1-14.4 | 30.5 | 17.7-43.4 | ||
| <60 | 10.1 | 7.5-12.7 | 35.2 | 26.6-43.8 | ||
| Smoking history | 0.258 | 0.206 | ||||
| Yes | 14.1 | 11.3-16.8 | 43.4 | 26.9-59.8 | ||
| No | 10.7 | 8.4-13.0 | 30.7 | 25.0-36.4 | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 0.956 | 0.262 | ||||
| Yes | 11.4 | 9.5-13.4 | 34.0 | 29.7-38.3 | ||
| No | 8.4 | 5.6-11.1 | 20.4 | 4.6-36.2 | ||
| Overall stage | 0.115 | 0.656 | ||||
| ⅢB-ⅢC | 13.3 | 6.9-19.6 | - | - | ||
| Ⅳa | 12.6 | 10.4-14.8 | 34.0 | 27.4-40.6 | ||
| Ⅳb | 9.0 | 8.0-10.0 | 30.5 | 21.4-39.6 | ||
| Postoperative recurrence | 0.008 | 0.070 | ||||
| Yes | 20.9 | 15.4-26.5 | 36.5 | - | ||
| No | 9.1 | 7.5-10.7 | 29.9 | 19.5-40.2 | ||
| T stage | 0.035 | 0.002 | ||||
| T1 | 13.2 | 0.543-25.8 | 41.9 | - | ||
| T2 | 8.3 | 4.7-11.8 | 30.7 | 22.3-39.1 | ||
| T3 | 4.6 | 2.9-6.3 | 7.8 | 3.2-12.3 | ||
| T4 | 11.4 | 9.7-13.1 | 34.0 | 28.3-39.7 | ||
| N stage | 0.100 | 0.013 | ||||
| N0 | 14.0 | 9.1-18.9 | 41.9 | 19.9-64.1 | ||
| N1 | 16.9 | 4.1-29.6 | 33.7 | 18.5-48.9 | ||
| N2 | 9.1 | 4.1-14.0 | 29.9 | 8.6-51.1 | ||
| N3 | 8.6 | 5.0-12.1 | 18.1 | 7.7-28.4 | ||
| M stage | 0.365 | 0.181 | ||||
| M0 | 13.3 | 8.0-18.6 | - | - | ||
| M1a | 12.2 | 10.4-14.0 | 37.0 | 32.5-41.4 | ||
| M1b | 12.3 | 1.8-22.8 | 13.5 | 0.7-30.5 | ||
| M1c | 9.0 | 7.7-10.3 | 30.5 | 21.4-39.7 | ||
| Pleural effusion | 0.018 | 0.487 | ||||
| Yes | 9.3 | 5.0-13.7 | 29.9 | 25.8-34.0 | ||
| No | 12.1 | 8.8-15.3 | 35.1 | 25.8-37.0 | ||
| Intrapulmonary metastasis | 0.806 | 0.851 | ||||
| Yes | 10.2 | 6.8-13.6 | 33.8 | 28.0-40.0 | ||
| No | 11.4 | 8.8-13.9 | 30.8 | 22.5-39.1 | ||
| Bone metastasis | 0.050 | 0.020 | ||||
| Yes | 8.8 | 7.2-10.5 | 13.7 | 2.8-22.5 | ||
| No | 11.4 | 9.4-13.5 | 35.1 | 29.6-40.6 | ||
| Brain metastasis | 0.679 | 0.841 | ||||
| Yes | 9.1 | 5.8-12.4 | 30.8 | 23.3-38.3 | ||
| No | 11.5 | 9.3-13.7 | 32.0 | 25.8-38.3 | ||
| Liver metastasis | 0.074 | 0.064 | ||||
| Yes | 4.1 | 0.3-8.0 | 8.0 | 0.0-17.2 | ||
| No | 11.4 | 8.5-14.2 | 34.0 | 29.1-38.9 | ||
| Adrenal metastasis | 0.455 | 0.247 | ||||
| Yes | 16.9 | 4.8-28.9 | - | - | ||
| No | 10.2 | 7.3-13.1 | 33.7 | 28.6-38.8 | ||
| Carcinomatous lymphangitis | 0.008 | 0.097 | ||||
| Yes | 4.1 | 1.8-8.6 | 8.0 | 1.0-22.1 | ||
| No | 11.5 | 9.1-13.9 | 33.8 | 29.4-38.3 | ||
| EGFR detected by tissue | 0.201 | 0.032 | ||||
| 19DEL | 11.5 | 9.7-13.3 | 35.1 | 30.1-40.1 | ||
| L858R | 8.6 | 6.4-10.7 | 23.3 | 13.5-33.1 | ||
| Rare mutation | 11.4 | 5.4-17.5 | 38.6 | 19.8-57.4 | ||
| EGFR detected by tissue | 0.027 | 0.015 | ||||
| 19DEL | 11.5 | 9.7-13.3 | 36.5 | 31.4-41.6 | ||
| L858R | 8.6 | 6.4-10.7 | 23.3 | 12.8-33.8 | ||
| EGFR detected by blood | 0.407 | 0.574 | ||||
| Positive | 11.4 | 9.3-13.5 | 35.1 | 27.7-42.5 | ||
| Negative | 10.2 | 7.2-13.2 | 29.4 | 24.8-33.9 | ||
| Best curative effect | 0.000 | 0.001 | ||||
| PR | 12.1 | 10.5-13.7 | 36.5 | 32.2-40.8 | ||
| SD | 10.8 | 6.8-14.7 | 28.5 | 17.0-40.1 | ||
| PD | 1.0 | 0.5-1.5 | 7.8 | 3.6-12.0 | ||
| Baseline LDH | 0.000 | 0.011 | ||||
| Normal | 11.4 | 8.4-14.3 | 34.0 | 28.4-39.6 | ||
| Elevated | 4.9 | 3.7-6.2 | 12.0 | 4.9-19.1 | ||
| T790M | 0.002 | |||||
| Yes | 36.5 | 31.7-41.3 | ||||
| No | 8.3 | 4.6-12.1 |
Tab. 4
Univariate COX analysis of continuous variables"
| Item | PFS | OS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | HR (95% CI) | P value | B | HR (95% CI) | P value | ||
| Age/age | -0.018 | 0.982 (0.964-1.001) | 0.060 | -0.005 | 0.995 (0.975-1.015) | 0.627 | |
| LDH | 0.001 | 1.001 (1.000-1.002) | 0.004 | 0.000 | 1.001 (1.000-1.002) | 0.001 | |
| Long diameter of primary lesion | 0.166 | 1.181 (1.037-1.345) | 0.012 | 0.144 | 1.155 (1.013-1.317) | 0.031 | |
| Sum of long diameters of target lesions | 0.013 | 1.047 (1.021-1.073) | 0.000 | 0.044 | 1.045 (0.985-1.107) | 0.143 | |
| Sum of area of target lesions | 0.016 | 1.016 (1.002-1.030) | 0.026 | 0.008 | 1.008 (0.995-1.020) | 0.231 | |
| PFS | -0.101 | 0.904 (0.864-0.945) | 0.000 | ||||
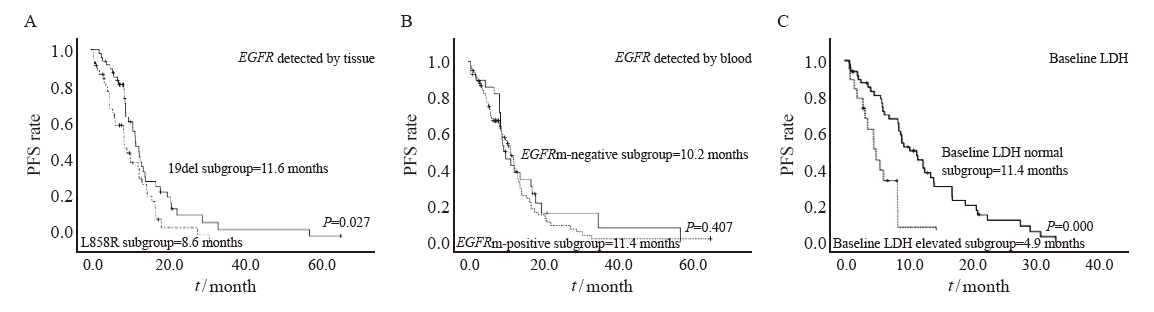
Fig. 1
PFS survival curves of patients in different variable groups A: Median PFS in EGFR 19del subgroup vs L858R subgroup. B: Median PFS in the plasma ctDNA EGFR mutant-positive subgroup vs ctDNA EGFR mutant -negative subgroup. C: Median PFS in baseline LDH normal subgroup vs Baseline LDH elevated subgroup."
Tab. 5
Multifactorial analysis of the correlation between clinicopathological characteristics and PFS in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation"
| Item | HR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline LDH | 2.788 (1.239-6.270) | 0.013 |
| Bone metastasis | 0.324 (0.316-1.464) | 0.324 |
| EGFR type | 2.318 (1.037-5.181) | 0.040 |
| Pleural effusion | 2.604 (1.072-6.329) | 0.035 |
| Carcinomatous lymphangitis | 1.219 (0.348-4.262) | 0.757 |
| long diameter of primary lesion | 1.021 (0.792-1.316) | 0.874 |
| Best curative effect | 2.513 (1.365-4.625) | 0.003 |
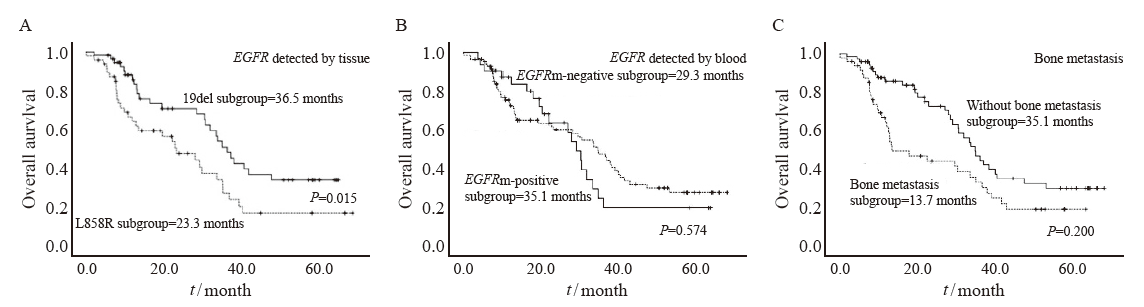
Fig. 2
OS survival curves of patients in different variable groups A: Median OS in EGFR 19del subgroup vs L858R subgroup. B: Median OS in the plasma ctDNA EGFR mutant-positive subgroup vs ctDNA EGFR mutant-negative subgroup. C: Median OS in with bone metastasis subgroup vs without bone metastasis subgroup."
Tab. 6
Multifactorial analysis of the correlation between clinicopathological characteristics and OS in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation"
| Item | HR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| T stage | 0.571 (0.296-1.103) | 0.095 |
| N stage | 3.595 (1.287-10.041) | 0.015 |
| Bone metastasis | 13.106 (2.095-81.995) | 0.006 |
| Baseline LDH | 0.381 (0.074-1.957) | 0.248 |
| PFS | 0.866 (0.754-0.995) | 0.042 |
| EGFR type | 1.207 (0.273-5.338) | 0.804 |
| T790M | 0.150 (0.023-0.995) | 0.049 |
| [1] |
ROCCO D, BATTILORO C, GRAVARA L D, et al. Advanced non-small cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutation: first line treatment and beyond[J]. Rev Recent Clin Trials, 2019, 14(2): 120-128.
doi: 10.2174/1574887114666181205155211 |
| [2] |
LEE D H. Treatments for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): the road to a success, paved with failures[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 174: 1-21.
doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.001 |
| [3] |
JEMAL A, BRAY F, CENTER M M, et al. Global cancer statistics[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61(2): 69-90.
doi: 10.3322/caac.20107 |
| [4] | CHEN W Q, ZHENG R S, ZHANG S W, et al. Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer registries, 2008[J]. Chung Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu, 2012, 24(3): 171-180. |
| [5] |
GELATTI A C Z, DRILON A, SANTINI F C. Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. Lung Cancer, 2019, 137: 113-122.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017 |
| [6] |
NORONHA V, RAJENDRA A, JOSHI A, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: a primer on contemporary management[J]. Cancer Res Stat Treat, 2019, 2(1): 36.
doi: 10.4103/CRST.CRST_51_19 |
| [7] |
FUKUOKA M, WU Y L, THONGPRASERT S, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase Ⅲ, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(21): 2866-2874.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235 |
| [8] |
SHI Y K, WANG L, HAN B H, et al. First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): a phase 3, open-label, randomized study[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(10): 2443-2450.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx359 |
| [9] |
O’KANE G M, LIU G, STOCKLEY T L, et al. The presence and variant allele fraction of EGFR mutations in ctDNA and development of resistance[J]. Lung Cancer, 2019, 131: 86-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.03.019 |
| [10] |
GRAY J E, OKAMOTO I, SRIURANPONG V, et al. Tissue and plasma EGFR mutation analysis in the FLAURA trial: osimertinib versus comparator EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(22): 6644-6652.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1126 |
| [11] | TRAN H T, LAM V K, ELAMIN Y Y, et al. Clinical outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and other targeted therapies based on tumor versus plasma genomic profiling[J]. JCO Precis Oncol, 2021, 5: PO.20.00532. |
| [12] |
LEDUC C, MERLIO J P, BESSE B, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR mutation: results of the nationwide French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT) program[J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(11): 2715-2724.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx404 |
| [13] |
YANG J C H, WU Y L, SCHULER M, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(2): 141-151.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71173-8 |
| [14] | BAE H M, LEE S H, KIM T M, et al. Prognostic factors for non-small cell lung cancer with bone metastasis at the time of diagnosis[J]. Lung Cancer Amsterdam Neth, 2012, 77(3): 572-577. |
| [15] |
CETIN K, CHRISTIANSEN C F, JACOBSEN J B, et al. Bone metastasis, skeletal-related events, and mortality in lung cancer patients: a Danish population-based cohort study[J]. Lung Cancer, 2014, 86(2): 247-254.
doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.08.022 |
| [16] | CHEN Y Y, WANG P P, FU Y, et al. Inferior outcome of bone metastasis in non-small-cell-lung-cancer patients treated with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors[J]. J Bone Oncol, 2021, 29: 100369. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
