Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (9): 834-843.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.09.004
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIN Yizi1,2( ), LIN Mingxi1,2, ZHANG Jian1,2(
), LIN Mingxi1,2, ZHANG Jian1,2( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Revised:2023-08-30
Online:2023-09-30
Published:2023-10-01
Contact:
ZHANG Jian.
Share article
CLC Number:
JIN Yizi, LIN Mingxi, ZHANG Jian. Receptor discordance between primary breast cancer and liver metastases[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(9): 834-843.
Tab. 1
Baseline characteristics of the included patients [n (%)]"
| Characteristic | Patients (N = 353) | Characteristic | Patients (N = 353) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis of primary breast cancer/year | Time between diagnosis of primary and metastatic disease/month | |||
| Median (Q1-Q3) | 46 (39-54) | <3 | 25 (7.1) | |
| Range | 22-82 | ≥3 | 328 (92.9) | |
| TNM stage | DFI | |||
| Ⅰ | 42 (11.9) | De novo stage Ⅳ | 46 (13.0) | |
| Ⅱ | 130 (36.8) | ≤24 months | 134 (38.0) | |
| Ⅲ | 135 (38.2) | >24 months | 173 (49.0) | |
| Ⅳ | 46 (13.0) | Number of metastatic sites at initial diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer | ||
| Histological type | One site | 173 (49.0) | ||
| Invasive ductal | 323 (91.5) | Two or more sites | 180 (51.0) | |
| Invasive lobular | 8 (2.3) | Visceral metastasis at initial diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer | ||
| Other or not reported | 22 (6.2) | Yes | 318 (90.1) | |
| Primary breast cancer subtype | No | 35 (9.9) | ||
| HR-/HER2- | 43 (12.2) | Previous endocrine therapy before re-biopsy | ||
| HR-/HER2+ | 52 (14.7) | Yes | 229 (64.9) | |
| HR+/HER2- | 217 (61.5) | No | 124 (35.1) | |
| HR+/HER2+ | 41 (11.6) | Previous anti-HER2 therapy before re-biopsy | ||
| Liver metastasis subtype | Yes | 56 (15.9) | ||
| HR-/HER2- | 69 (19.5) | No | 297 (84.1) | |
| HR-/HER2+ | 58 (16.4) | Previous chemotherapy before re-biopsy | ||
| HR+/HER2- | 190 (53.8) | Yes | 310 (87.8) | |
| HR+/HER2+ | 36 (10.2) | No | 43 (12.2) |
Tab. 2
The receptor status of primary breast cancer and liver metastases in patients who underwent second liver re-biopsies"
| Patient | Receptor status of primary breast cancer | Receptor status of first liver re-biopsy | Time point of first liver re-biopsy* | Receptor status of second liver re-biopsy | Timepoint of second liver re-biopsy* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 100 | ER-/PR-/HER2- | 127 |
| 2 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 34 | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 43 |
| 3 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 22 | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 51 |
| 4 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER-/PR+/HER2- | 9 | ER-/PR-/HER2- | 19 |
| 5 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 25 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 42 |
| 6 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 56 | ER+/PR-/HER2- | 84 |
| 7 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 97 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 138 |
| 8 | ER+/PR+/HER2- | ER+/PR+/HER2- | 31 | ER-/PR-/HER2- | 47 |
| 9 | ER-/PR-/HER2+ | ER-/PR-/HER2- | 38 | ER-/PR-/HER2- | 55 |
Tab. 3
Univariate analyses of factors associated with receptor discordance"
| Characteristic | ER status | PR status | HER2 status | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concordant | Discordant | Pvalue | Concordant | Discordant | P value | Concordant | Discordant | Pvalue | |||
| Age at initial diagnosis | 0.202 | 0.683 | 0.370 | ||||||||
| ≤50 | 184 | 39 | 137 | 86 | 214 | 9 | |||||
| >50 | 100 | 30 | 77 | 53 | 122 | 8 | |||||
| DFI | 0.730 | <0.001 | 0.379 | ||||||||
| ≤24 months | 107 | 27 | 96 | 38 | 129 | 5 | |||||
| >24 months | 138 | 35 | 85 | 88 | 162 | 11 | |||||
| De novo stage Ⅳ | 39 | 7 | 33 | 13 | 45 | 1 | |||||
| Histological type | 0.678 | 0.023 | 0.198 | ||||||||
| Invasive ductal | 259 | 64 | 190 | 133 | 306 | 17 | |||||
| Other | 25 | 5 | 24 | 6 | 30 | 0 | |||||
| Time between diagnosis of primary tumor and liver metastasis/month | 0.324 | 0.103 | 0.243 | ||||||||
| <3 | 22 | 3 | 19 | 6 | 25 | 0 | |||||
| ≥3 | 262 | 66 | 195 | 133 | 311 | 17 | |||||
| Previous endocrine therapy before re-biopsy | 0.728 | <0.001 | 0.305 | ||||||||
| No | 101 | 23 | 102 | 22 | 120 | 4 | |||||
| Yes | 183 | 46 | 112 | 117 | 216 | 13 | |||||
| Previous anti-HER2 therapy before re-biopsy | 0.728 | 0.227 | 0.117 | ||||||||
| No | 238 | 59 | 176 | 121 | 285 | 12 | |||||
| Yes | 46 | 10 | 38 | 18 | 51 | 5 | |||||
| Previous chemotherapy before re-biopsy | 0.807 | 0.100 | 0.115 | ||||||||
| No | 34 | 9 | 31 | 12 | 43 | 0 | |||||
| Yes | 250 | 60 | 183 | 127 | 293 | 17 | |||||
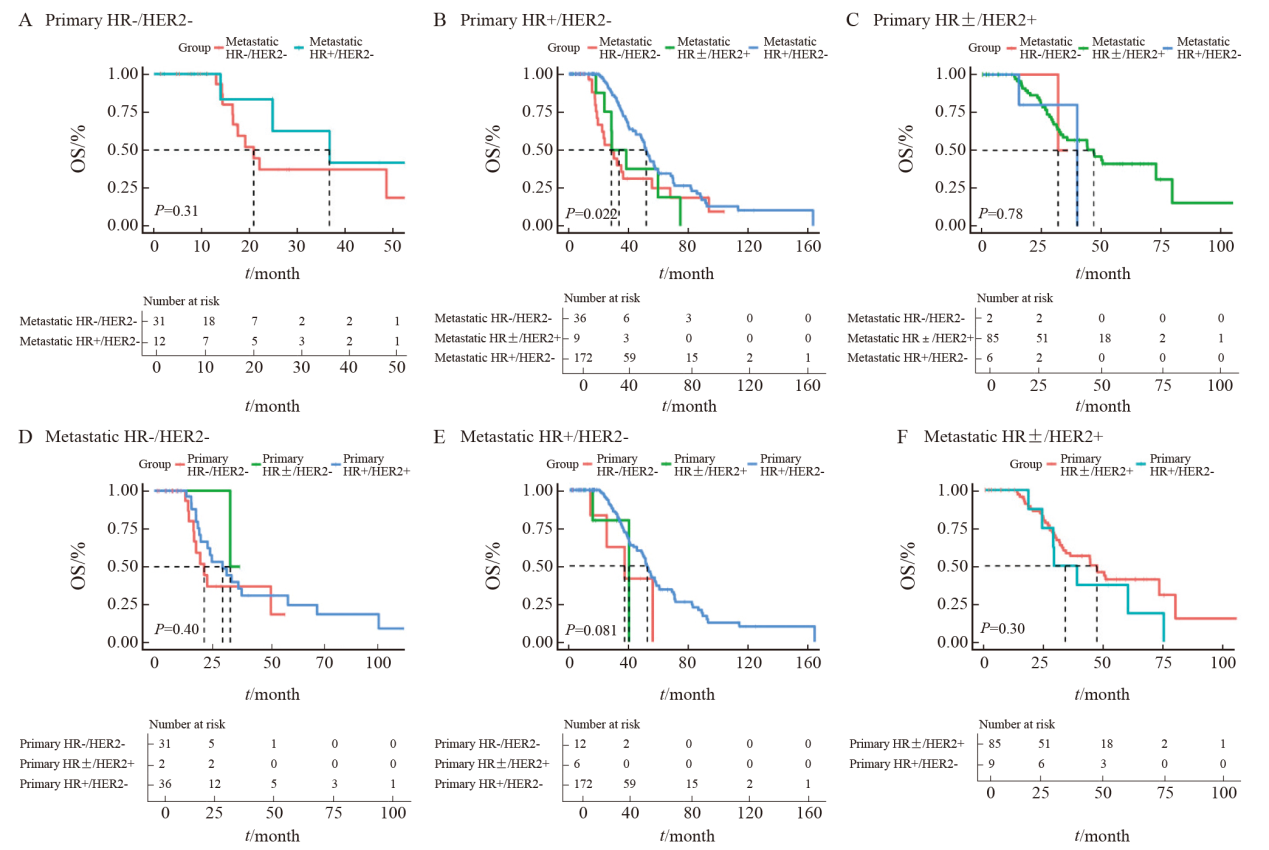
Fig.4
The influence of receptor conversion on OS A: The Kaplan-Meier plot of triple-negative primary breast cancer; B: The Kaplan-Meier plot of HR+/HER2- primary breast cancer; C: The Kaplan-Meier plot of HR±/HER2+ primary breast cancer; D: The Kaplan-Meier plot of triple-negative metastatic breast cancer; E: The Kaplan-Meier plot of HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer; F: The Kaplan-Meier plot of HR±/HER2+ metastatic breast cancer. The dashed line indicates the median OS of each group."
| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-249.
doi: 10.3322/caac.v71.3 |
| [2] |
RUGO H S, RUMBLE R B, MACRAE E, et al. Endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(25): 3069-3103.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.67.1487 pmid: 27217461 |
| [3] |
CARDOSO F, PALUCH-SHIMON S, SENKUS E, et al. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5)[J]. Ann Oncol, 2020, 31(12): 1623-1649.
doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.09.010 |
| [4] |
JI L, CHENG L, ZHU X, et al. Risk and prognostic factors of breast cancer with liver metastases[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 238.
doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07968-5 pmid: 33676449 |
| [5] |
MA R, FENG Y L, LIN S, et al. Mechanisms involved in breast cancer liver metastasis[J]. J Transl Med, 2015, 13: 64.
doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0425-0 pmid: 25885919 |
| [6] |
SCHRIJVER W A M E, SUIJKERBUIJK K P M, VAN GILS C H, et al. Receptor conversion in distant breast cancer metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2018, 110(6): 568-580.
doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx273 pmid: 29315431 |
| [7] |
AURILIO G, DISALVATORE D, PRUNERI G, et al. A meta-analysis of oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 discordance between primary breast cancer and metastases[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2014, 50(2): 277-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.10.004 pmid: 24269135 |
| [8] |
MODI S N, JACOT W, YAMASHITA T, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 387(1): 9-20.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2203690 |
| [9] |
DENKERT C, SEITHER F, SCHNEEWEISS A, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(8): 1151-1161.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00301-6 pmid: 34252375 |
| [10] |
TARANTINO P, CURIGLIANO G, TOLANEY S M. Navigating the HER2-low paradigm in breast oncology: new standards, future horizons[J]. Cancer Discov, 2022, 12(9): 2026-2030.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0703 |
| [11] |
WOLFF A C, SOMERFIELD M R, DOWSETT M, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: ASCO-College of American Pathologists guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(22): 3867-3872.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02864 |
| [12] |
ALLISON K H, HAMMOND M E H, DOWSETT M, et al. Estrogen and progesterone receptor testing in breast cancer: ASCO/CAP guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(12): 1346-1366.
doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02309 pmid: 31928404 |
| [13] |
LIU J Q, DENG H R, JIA W J, et al. Comparison of ER/PR and HER2 statuses in primary and paired liver metastatic sites of breast carcinoma in patients with or without treatment[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(5): 837-842.
doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1150-1 pmid: 22290394 |
| [14] |
CURIGLIANO G, BAGNARDI V, VIALE G, et al. Should liver metastases of breast cancer be biopsied to improve treatment choice?[J]. Ann Oncol, 2011, 22(10): 2227-2233.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdq751 pmid: 21343379 |
| [15] |
HOEFNAGEL L D, MOELANS C B, MEIJER S L, et al. Prognostic value of estrogen receptor α and progesterone receptor conversion in distant breast cancer metastases[J]. Cancer, 2012, 118(20): 4929-4935.
doi: 10.1002/cncr.27518 pmid: 22415862 |
| [16] |
LIEDTKE C, BROGLIO K, MOULDER S, et al. Prognostic impact of discordance between triple-receptor measurements in primary and recurrent breast cancer[J]. Ann Oncol, 2009, 20(12): 1953-1958.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp263 pmid: 19596702 |
| [17] |
DIECI M V, BARBIERI E, PIACENTINI F, et al. Discordance in receptor status between primary and recurrent breast cancer has a prognostic impact: a single-institution analysis[J]. Ann Oncol, 2013, 24(1): 101-108.
doi: 10.1093/annonc/mds248 pmid: 23002281 |
| [18] |
LIN M X, JIN Y Z, LV H, et al. Incidence and prognostic significance of receptor discordance between primary breast cancer and paired bone metastases[J]. Int J Cancer, 2023, 152(7): 1476-1489.
doi: 10.1002/ijc.v152.7 |
| [19] |
LU Y J, TONG Y W, CHEN X S, et al. Association of biomarker discrepancy and treatment decision, disease outcome in recurrent/metastatic breast cancer patients[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 638619.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.638619 |
| [20] |
CURTIT E, NERICH V, MANSI L, et al. Discordances in estrogen receptor status, progesterone receptor status, and HER2 status between primary breast cancer and metastasis[J]. Oncologist, 2013, 18(6): 667-674.
doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0350 pmid: 23723333 |
| [21] |
DUCHNOWSKA R, DZIADZIUSZKO R, TROJANOWSKI T, et al. Conversion of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and hormone receptor expression in breast cancer metastases to the brain[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2012, 14(4): R119.
doi: 10.1186/bcr3244 |
| [22] |
MCGRANAHAN N, SWANTON C. Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: past, present, and the future[J]. Cell, 2017, 168(4): 613-628.
doi: S0092-8674(17)30066-1 pmid: 28187284 |
| [23] |
HU Z, SUN R, CURTIS C. A population genetics perspective on the determinants of intra-tumor heterogeneity[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2017, 1867(2): 109-126.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.03.001 |
| [24] |
NAVIN N, KENDALL J, TROGE J, et al. Tumour evolution inferred by single-cell sequencing[J]. Nature, 2011, 472(7341): 90-94.
doi: 10.1038/nature09807 |
| [25] |
MITTENDORF E A, WU Y, SCALTRITI M, et al. Loss of HER2 amplification following trastuzumab-based neoadjuvant systemic therapy and survival outcomes[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 15(23): 7381-7388.
doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1735 pmid: 19920100 |
| [26] |
HU Z, LI Z, MA Z C, et al. Multi-cancer analysis of clonality and the timing of systemic spread in paired primary tumors and metastases[J]. Nat Genet, 2020, 52(7): 701-708.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-020-0628-z pmid: 32424352 |
| [27] |
MAYNADIER M, NIRDÉ P, RAMIREZ J M, et al. Role of estrogens and their receptors in adhesion and invasiveness of breast cancer cells[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2008, 617: 485-491.
doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-69080-3_48 pmid: 18497073 |
| [1] | WU Wen, ZHANG Ruoxin, WENG Junyong, MA Yanlei, CAI Guoxiang, LI Xinxiang, YANG Yongzhi. Exploring the prognostic value of positive lymph node ratio in stage Ⅲ colorectal cancer patients and establishing a predictive model [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 873-880. |
| [2] | XU Rui, WANG Zehao, WU Jiong. Advances in the role of tumor-associated neutrophils in the development of breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 881-889. |
| [3] | XIAO Feng, XU Tonglin, ZHU Lin, XIAO Jingwen, WU Tianqi, GU Chunyan. Significance of infiltration of M1 tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 726-733. |
| [4] | CAO Xiaoshan, YANG Beibei, CONG Binbin, LIU Hong. The progress of treatment for brain metastases of triple-negative breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 777-784. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jian. Clinical consideration of two key questions in assessing menopausal status of female breast cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 619-627. |
| [6] | JIANG Dan, SONG Guoqing, WANG Xiaodan. Study on the mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction and CPT1A/ERK signal transduction pathway regulating malignant behavior in breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 650-658. |
| [7] | DONG Jianqiao, LI Kunyan, LI Jing, WANG Bin, WANG Yanhong, JIA Hongyan. A study on mechanism of SIRT3 inducing endocrine drug resistance in breast cancer via deacetylating YME1L1 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 537-547. |
| [8] | HAO Xian, HUANG Jianjun, YANG Wenxiu, LIU Jinting, ZHANG Junhong, LUO Yubei, LI Qing, WANG Dahong, GAO Yuwei, TAN Fuyun, BO Li, ZHENG Yu, WANG Rong, FENG Jianglong, LI Jing, ZHAO Chunhua, DOU Xiaowei. Establishment of primary breast cancer cell line as new model for drug screening and basic research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 561-570. |
| [9] | ZHANG Ruoxin, YE Zilan, WENG Junyong, LI Xinxiang. Correlation study between advanced age and inferior prognosis in stage Ⅱ colorectal cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 485-492. |
| [10] | WANG Xiaocong, LI Ming. The value of single-cell sequencing in oral squamous cell carcinoma research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 501-508. |
| [11] | Committee of Breast Cancer Society, China Anti-Cancer Association. Expert consensus on clinical applications of ovarian function suppression for Chinese women with early breast cancer (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 316-333. |
| [12] | ZHANG Qi, XIU Bingqiu, WU Jiong. Progress of important clinical research of breast cancer in China in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 135-142. |
| [13] | ZHANG Siyuan, JIANG Zefei. Important research progress in clinical practice for advanced breast cancer in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 143-150. |
| [14] | WANG Zhaobu, LI Xing, YU Xinmiao, JIN Feng. Important research progress in clinical practice for early breast cancer in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 151-160. |
| [15] | LUO Yang, SUN Tao, SHAO Zhimin, CUI Jiuwei, PAN Yueyin, ZHANG Qingyuan, CHENG Ying, LI huiping, YANG Yan, YE Changsheng, YU Guohua, WANG Jingfen, LIU Yunjiang, LIU Xinlan, ZHOU Yuhong, BAI Yuju, GU Yuanting, WANG Xiaojia, XU Binghe, SONG Lihua. Efficacy, metabolic characteristics, safety and immunogenicity of AK-HER2 compared with reference trastuzumab in patients with metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase Ⅲ equivalence trial [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 161-175. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
