Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2023, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (7): 664-672.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2023.07.004
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Cong1( ), HE Lina1, CHENG Xiaojiao1, HUANG Tinglei2, TU Shuiping1(
), HE Lina1, CHENG Xiaojiao1, HUANG Tinglei2, TU Shuiping1( )
)
Received:2022-10-30
Revised:2023-04-25
Online:2023-07-30
Published:2023-08-10
Contact:
TU Shuiping.
Share article
CLC Number:
ZHOU Cong, HE Lina, CHENG Xiaojiao, HUANG Tinglei, TU Shuiping. Effect of RSPO3 on inhibiting the growth of colorectal cancer transplanted tumors and increasing NK cell infiltration in vivo[J]. China Oncology, 2023, 33(7): 664-672.
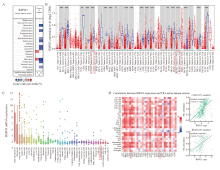
Fig. 1
Expression of RSPO3 in pancarcinoma A, B: The Oncomine database suggests that RSPO3 is relatively low expressed in a variety of human solid tumors, including colorectal cancer; C: Expression of RSPO3 in various tumor cell lines in CCLE database; D: TISIDB database showed the correlation between RSPO3 expression and various immunoinfiltrated lymphocytes, and RSPO3 expression in colorectal cancer was significantly positively correlated with NK cells. TIL: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001."
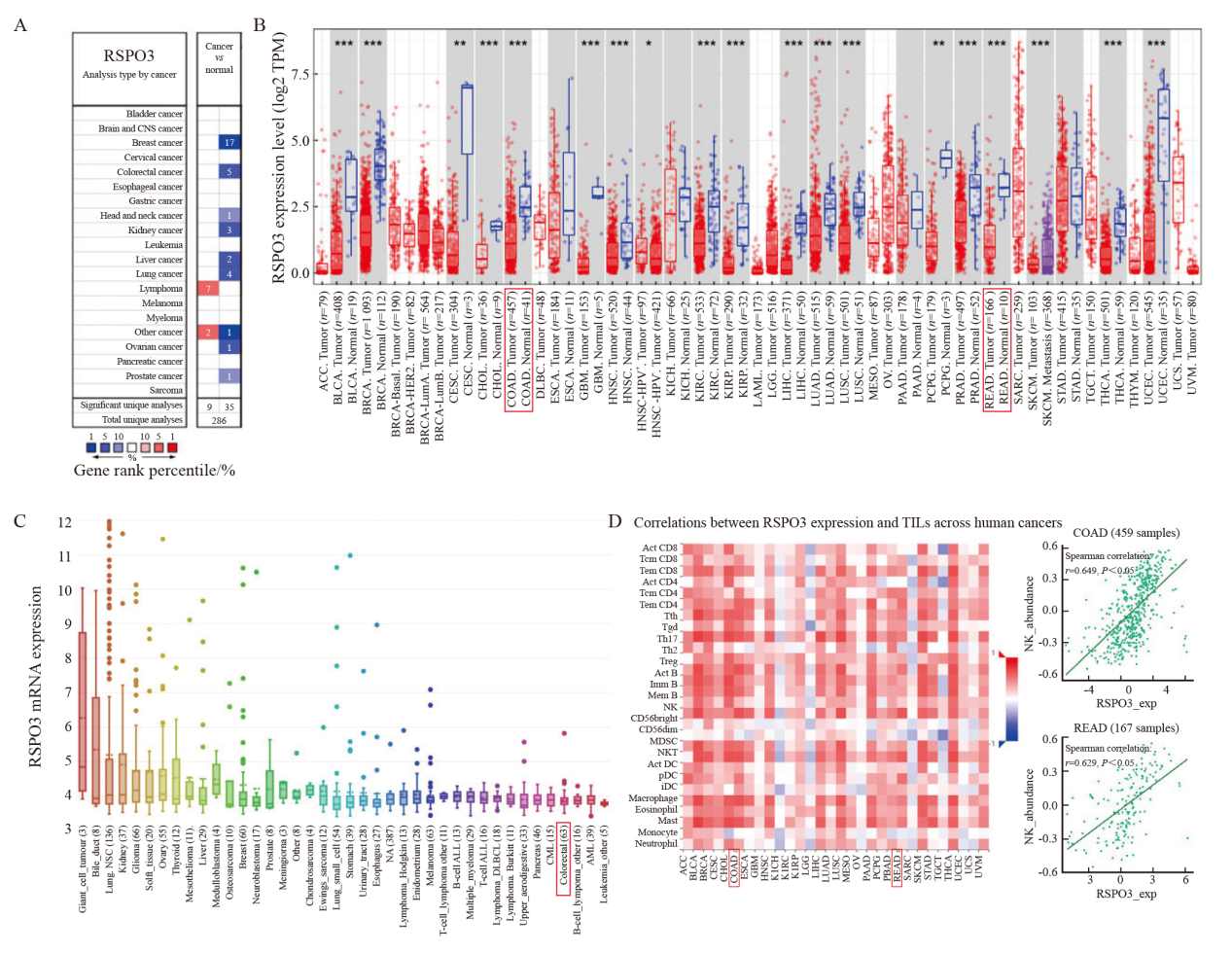
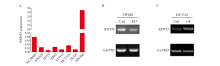
Fig. 2
Construction of RSPO3 knockdown or overexpressed colon cancer cell lines A: RSPO3 expression in human colon epithelial cells NCM460 and a variety of colon cancer cell lines; B: shRNA knockdown RSPO3 expression in SW480 cell line; C: Lentivirus infection induced RSPO3 overexpression in HCT116 cell line. KD: Knock down; OE: Overexpression."
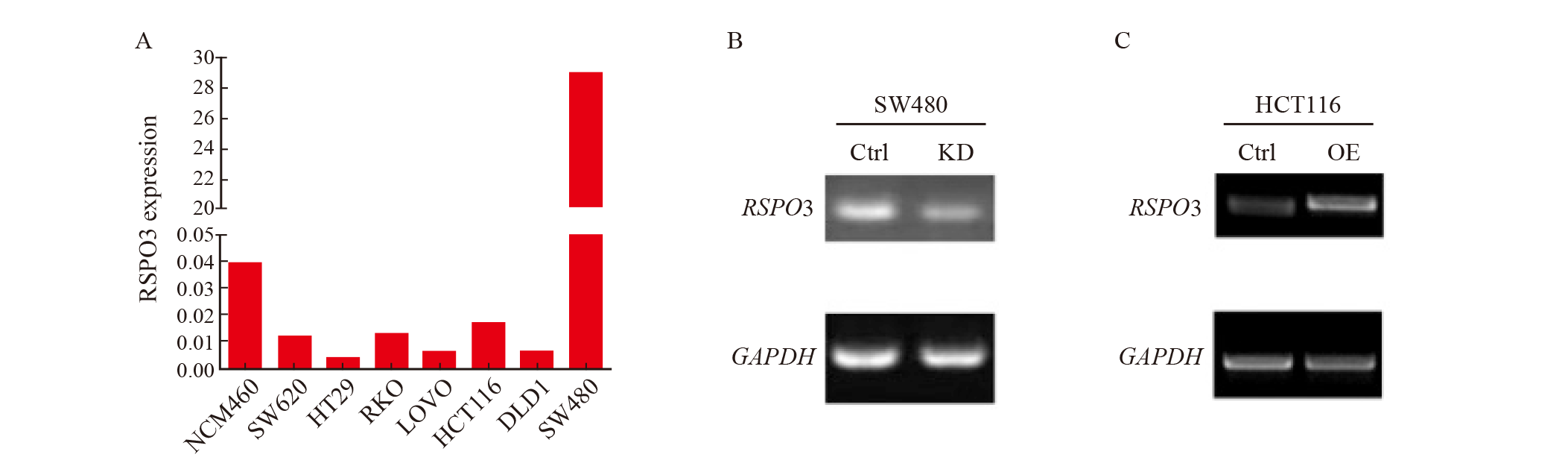
Fig. 3
Effects of RSPO3 on the growth of SW480 or HCT116 cell line in vitro and in vivo A, B: The effects of RSPO3 knockdown or overexpression on cell proliferation of SW480 or HCT116 cell line were analyzed by CCK-8; C, D: Flow cytometry was used to detect the effects of RSPO3 knockdown or overexpression on SW480 or HCT116 cell cycles; E, F, G: Effects of RSPO3 knockdown on the growth of SW480 subcutaneous xenograft tumors; H, I, J: Effects of RSPO3 overexpression on the growth of HCT116 subcutaneous xenograft tumors.*: P>0.05."
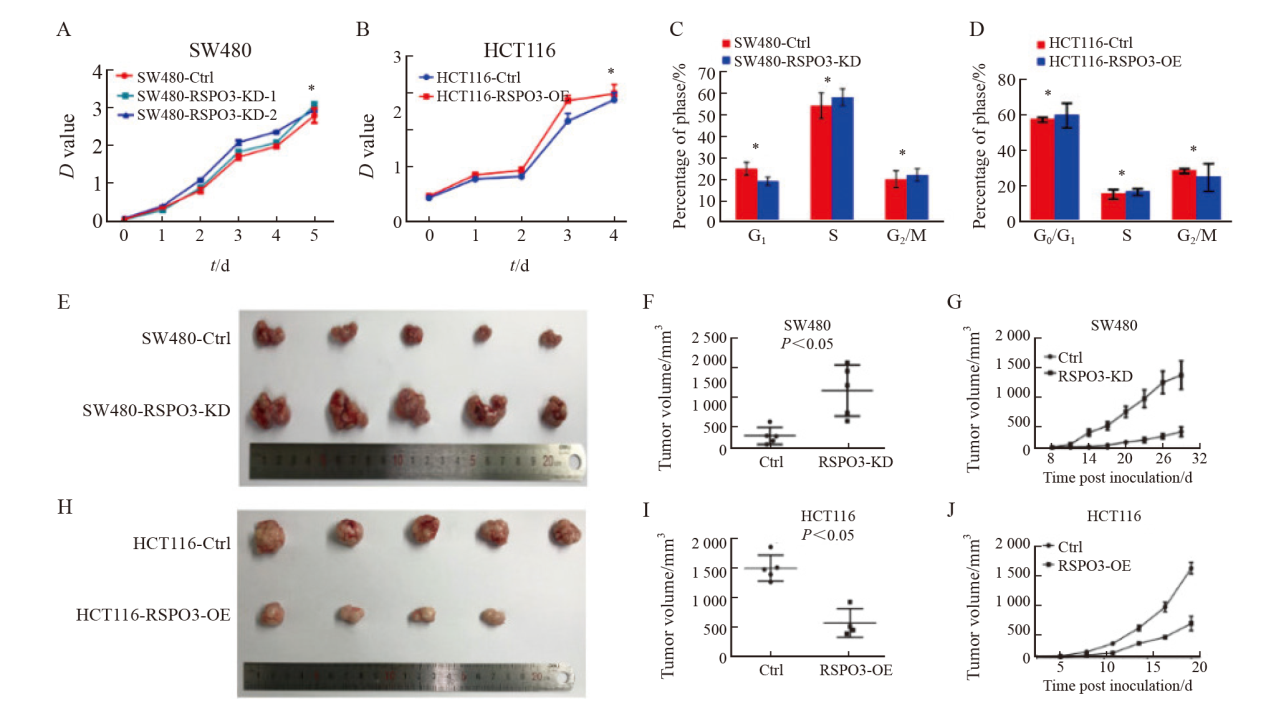
Fig. 4
RSPO3 affects the proportion of NK cells in vivo A, B: Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of NK cells in single cell suspension of spleen after transplantation of SW480-RSPO3-KD or SW480-Ctrl subcutaneous xenograft tumor; C, D: Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of NK cells in the subcutaneous tumor of SW480-RSPO3-KD or SW480-Ctrl; E, F: Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of NK cells in spleen single-cell suspension after transplantation of HCT116-RSPO3-OE or HCT116-Ctrl subcutaneous xenograft tumor; G, H: Flow cytometry was used to analyze the proportion of NK cells in the subcutaneous xenograft tumor of HCT116-RSPO3-OE or HCT116-Ctrl."
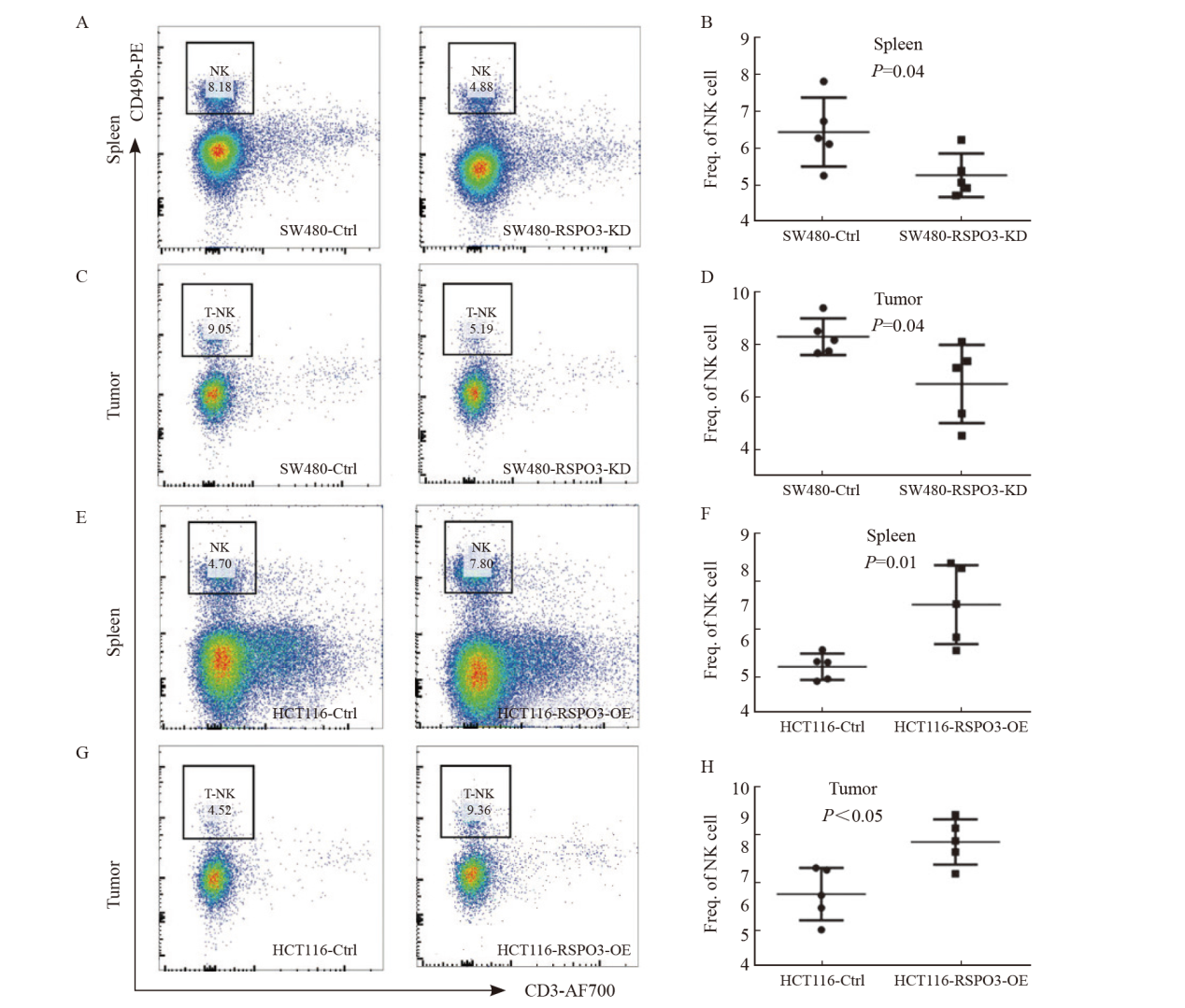
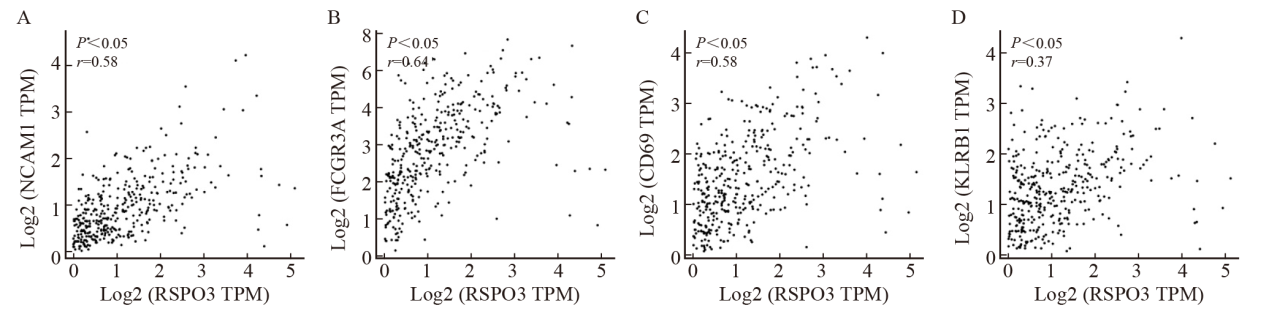
Fig. 5
Correlation analysis of RSPO3 expression level with NK cell markers and NK activated markers A: Spearman correlation analysis based on TCGA colorectal cancer database showed that RSPO3 was highly positively correlated with CD56 (NCAM1), r= 0.58, P<0.05; B: RSPO3 was highly positively correlated with CD16 (FCGR3A), r= 0.64, P<0.05; C: RSPO3 was highly positively correlated with CD69, r= 0.51, P<0.05; D: RSPO3 was moderately positively correlated with KLRB1 (r= 0.37, P<0.05)."
| [1] |
AOKI M, MIEDA M, IKEDA T, et al. R-spondin3 is required for mouse placental development[J]. Dev Biol, 2007, 301(1): 218-226.
doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.018 pmid: 16963017 |
| [2] |
KNIGHT M N, HANKENSON K D. R-spondins: novel matricellular regulators of the skeleton[J]. Matrix Biol, 2014, 37: 157-161.
doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2014.06.003 pmid: 24980904 |
| [3] |
NILSSON K H, HENNING P, EL SHAHAWY M, et al. RSPO3 is important for trabecular bone and fracture risk in mice and humans[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 4923.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25124-2 pmid: 34389713 |
| [4] |
KAZANSKAYA O, OHKAWARA B, HEROULT M, et al. The Wnt signaling regulator R-spondin 3 promotes angioblast and vascular development[J]. Development, 2008, 135(22): 3655-3664.
doi: 10.1242/dev.027284 pmid: 18842812 |
| [5] |
KURTOVA A V, HEINLEIN M, HAAS S, et al. Disruption of stem cell niche-confined R-spondin 3 expression leads to impaired hematopoiesis[J]. Blood Adv, 2023, 7(4): 491-507.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022007714 |
| [6] |
LOH N Y, MINCHIN J E N, PINNICK K E, et al. RSPO3 impacts body fat distribution and regulates adipose cell biology in vitro[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 2797.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16592-z pmid: 32493999 |
| [7] |
KUROKAWA K, WANG T C, HAYAKAWA Y. R-spondin 3 governs secretory differentiation in the gastric oxyntic glands[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132(21): e163380.
doi: 10.1172/JCI163380 |
| [8] |
OGASAWARA R, HASHIMOTO D, KIMURA S, et al. Intestinal lymphatic endothelial cells produce R-spondin 3[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 10719.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29100-7 |
| [9] | GREICIUS G, KABIRI Z, SIGMUNDSSON K, et al. PDGFRα+ pericryptal stromal cells are the critical source of Wnts and RSPO3 for murine intestinal stem cells in vivo[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018, 115(14): E3173-E3181. |
| [10] |
YAN K S, JANDA C Y, CHANG J L, et al. Non-equivalence of Wnt and R-spondin ligands during Lgr5+ intestinal stem-cell self-renewal[J]. Nature, 2017, 545(7653): 238-242.
doi: 10.1038/nature22313 |
| [11] |
ANNUNZIATO S, SUN T, TCHORZ J S. The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module in liver homeostasis, regeneration, and disease[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 76(3): 888-899.
doi: 10.1002/hep.32328 |
| [12] |
KUANG S Q, TONG W G, YANG H, et al. Genome-wide identification of aberrantly methylated promoter associated CpG islands in acute lymphocytic leukemia[J]. Leukemia, 2008, 22(8): 1529-1538.
doi: 10.1038/leu.2008.130 pmid: 18528427 |
| [13] |
KANEDA H, ARAO T, TANAKA K, et al. FOXQ1 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and enhances tumorigenicity and tumor growth[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(5): 2053-2063.
doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2161 pmid: 20145154 |
| [14] |
THEODOROU V, KIMM M A, BOER M, et al. MMTV insertional mutagenesis identifies genes, gene families and pathways involved in mammary cancer[J]. Nat Genet, 2007, 39(6): 759-769.
doi: 10.1038/ng2034 pmid: 17468756 |
| [15] |
TER STEEGE E J, BOER M, TIMMER N C, et al. R-spondin 3 is an oncogenic driver of poorly differentiated invasive breast cancer[J]. J Pathol, 2022, 258(3): 289-299.
doi: 10.1002/path.v258.3 |
| [16] |
GU H F, TU H, LIU L L, et al. RSPO3 is a marker candidate for predicting tumor aggressiveness in ovarian cancer[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(21): 1351.
doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3731 pmid: 33313096 |
| [17] |
CHEN Z H, ZHOU L J, CHEN L, et al. RSPO3 promotes the aggressiveness of bladder cancer via Wnt/β-catenin and Hedgehog signaling pathways[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2019, 40(2): 360-369.
doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy140 pmid: 30329043 |
| [18] |
CHEN Z L, ZHANG J Z, YUAN A W, et al. R-spondin 3 promotes the tumor growth of choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cells[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2020, 318(3): C664-C674.
doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00295.2019 |
| [19] |
TANG Y T, XU Q, HU L, et al. Tumor microenvironment-derived R-spondins enhance antitumor immunity to suppress tumor growth and sensitize for immune checkpoint blockade therapy[J]. Cancer Discov, 2021, 11(12): 3142-3157.
doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0833 |
| [20] |
SESHAGIRI S, STAWISKI E W, DURINCK S, et al. Recurrent R-spondin fusions in colon cancer[J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7413): 660-664.
doi: 10.1038/nature11282 |
| [21] |
TANG Y, ZHOU C, LI Q L, et al. Targeting depletion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells potentiates PD-L1 blockade efficacy in gastric and colon cancers[J]. Oncoimmunology, 2022, 11(1): 2131084.
doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2022.2131084 |
| [22] | 焦红丽, 王珺娆, 胡敏萱, 等. SAFB通过调节Wnt信号通路活性促进结直肠癌增殖[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2022, 38(4): 385-391 |
| JIAO H L, WANG J R, HU M X, et al. SAFB promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by regulating Wnt signaling pathway activity[J]. Chin J Clin Exp Pathol, 2022, 38(4): 385-391 | |
| [23] |
RHODES D R, KALYANA-SUNDARAM S, MAHAVISNO V, et al. Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18 000 cancer gene expression profiles[J]. Neoplasia, 2007, 9(2): 166-180.
doi: 10.1593/neo.07112 |
| [24] |
GHANDI M, HUANG F W, JANÉ-VALBUENA J, et al. Next-generation characterization of the cancer cell line encyclopedia[J]. Nature, 2019, 569(7757): 503-508.
doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1186-3 |
| [25] |
RU B B, WONG C N, TONG Y, et al. TISIDB: an integrated repository portal for tumor-immune system interactions[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(20): 4200-4202.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz210 pmid: 30903160 |
| [26] |
TANG Z F, LI C W, KANG B X, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(W1): W98-W102.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx247 |
| [27] |
RUSSICK J, TORSET C, HEMERY E, et al. NK cells in the tumor microenvironment: prognostic and theranostic impact. Recent advances and trends[J]. Semin Immunol, 2020, 48: 101407.
doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101407 |
| [28] |
OHKAWARA B, GLINKA A, NIEHRS C. RSPO3 binds syndecan 4 and induces Wnt/PCP signaling via clathrin-mediated endocytosis to promote morphogenesis[J]. Dev Cell, 2011, 20(3): 303-314.
doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.01.006 pmid: 21397842 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
