Welcome to China Oncology,
China Oncology ›› 2022, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (9): 818-826.doi: 10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2022.09.009
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jingchen( ), LI Xin, LI Jiangtao, LI Haiping, CHEN Yanli, NIU Bing, QI Chuanchuan, YE Beibei
), LI Xin, LI Jiangtao, LI Haiping, CHEN Yanli, NIU Bing, QI Chuanchuan, YE Beibei
Received:2022-01-06
Revised:2022-03-25
Online:2022-09-30
Published:2022-10-24
Contact:
ZHANG Jingchen
Share article
CLC Number:
ZHANG Jingchen, LI Xin, LI Jiangtao, LI Haiping, CHEN Yanli, NIU Bing, QI Chuanchuan, YE Beibei. LINC02163 targeting miR-338-3p affects proliferation, invasion and migration of breast cancer cells[J]. China Oncology, 2022, 32(9): 818-826.
Tab. 2
Compare of c-Myc, MMP2, MMP9, E-cadherin, and N-cadherin protein expression in each group of MDA-MB-231 cells"
| Group | MMP9/β-actin | MMP2/β-actin | c-Myc/β-actinc | N-cadherin/β-actin | E-cadherin/β-actin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.62±0.22 | 1.23±0.17 | 1.50±0.25 | 1.04±0.10 | 0.43±0.06 |
| sh-NC | 1.61±0.25 | 1.22±0.18 | 1.49±0.23 | 1.03±0.09 | 0.42±0.08 |
| sh-LINC02163 | 0.68±0.03* | 0.33±0.06* | 0.52±0.08* | 0.21±0.05* | 1.40±0.21* |
| sh-LINC02163+inhibitor-NC | 0.67±0.05 | 0.34±0.05 | 0.53±0.07 | 0.20±0.03 | 1.41±0.25 |
| sh-LINC02163+miR-338-3p inhibitor | 1.28±0.12# | 1.15±0.10# | 1.40±0.22# | 0.89±0.08# | 0.70±0.11# |
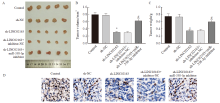
Fig. 8
Comparison of tumor-forming ability and Ki-67 proliferation index of MDA-MB-231 cells in each group A: Nude mouse tumor pictures; B: tumor volume; C: Tumor weight; D: Ki-67 proliferation index (×200). *: P<0.05, compared with control group; #: P<0.05, compared with sh-LINC02163 group."
| [1] |
LIANG Y R, SONG X J, LI Y M, et al. LncRNA BCRT1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting miR-1303/PTBP3 axis[J]. Mol Cancer, 2020, 19(1): 85.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01206-5 pmid: 32384893 |
| [2] |
ZHAO W Y, GENG D H, LI S Q, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(3): 842-855.
doi: 10.1002/cam4.1353 |
| [3] |
SHEN Y, PENG X W, SHEN C L. Identification and validation of immune-related lncRNA prognostic signature for breast cancer[J]. Genomics, 2020, 112(3): 2640-2646.
doi: S0888-7543(20)30065-3 pmid: 32087243 |
| [4] |
QIN C L, JIN L F, LI J, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC 02163 accelerates malignant tumor behaviors in breast cancer by regulating the microRNA-511-3p/HMGA2 axis[J]. Oncol Res, 2020, 28(5): 483-495.
doi: 10.3727/096504020X15928179818438 |
| [5] |
TIAN Y, ZHOU J, ZOU Y F, et al. Upregulated long noncoding RNAs LINC02163 and FEZF1-AS1 exert oncogenic roles in colorectal cancer[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2021, 32(1): 66-73.
doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000975 |
| [6] |
HE J J, WANG J, LI S C, et al. Hypoxia-inhibited miR-338-3p suppresses breast cancer progression by directly targeting ZEB2[J]. Cancer Sci, 2020, 111(10): 3550-3563.
doi: 10.1111/cas.14589 |
| [7] | 周大为, 朱征涛, 靳明明, 等. hsa_circ_0070260靶向miR-27a-3p/Fbxw7对乳腺癌增殖,侵袭调控研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49(S1): 24-28. |
| ZHOU D W, ZHU Z T, JI M M, et al. hsa_circ_0070260/miR-27a-3p/Fbxw7 regulates the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells[J]. Chongqing Med, 2020, 49(S1): 24-28. | |
| [8] |
MILLER K D, NOGUEIRA L, MARIOTTO A B, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2019, 69(5): 363-385.
doi: 10.3322/caac.21565 |
| [9] |
XIU B Q, CHI Y Y, LIU L, et al. LINC02273 drives breast cancer metastasis by epigenetically increasing AGR2 transcription[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 187.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1115-y pmid: 31856843 |
| [10] |
SHI Q F, LI Y D, LI S Y, et al. LncRNA DILA1 inhibits cyclin D1 inhibits cyclin D1 degradation and contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 5513.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19349-w |
| [11] |
DONG L M, HONG H S, CHEN X W, et al. LINC02163 regulates growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype via miR-593-3p/FOXK1 axis in gastric cancer cells[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2018, 46(sup2): 607-615.
doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1464462 pmid: 29893595 |
| [12] |
MA J W, ZHANG L H, SHANG A Q, et al. LINC02163 promotes colorectal cancer progression via miR-511-3p/AKT3 axis[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2020, 48(1): 961-968.
doi: 10.1080/21691401.2020.1773486 pmid: 32524841 |
| [13] | 罗毅, 房晓瑜, 谢薇佳, 等. 长链非编码RNA LINC02163在肝细胞肝癌中表达上调并促进肝癌细胞迁移和侵袭[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2020, 42(1): 81-87. |
| LUO Y, FANG X Y, XIE W J, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC02163 is up-regulated and promotes cell migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Third Mil Med Univ, 2020, 42(1): 81-87. | |
| [14] | 来旭, 范亚楠, 王瑞丰. LINC01106靶向miR-744-5p影响乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭[J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2021, 28(4): 577-582. |
| LAI X, FAN Y N, WANG R F. LINC01106 affects the proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by targeting miR-744-5p[J]. Labeled Immunoass Clin Med, 2021, 28(4): 577-582. | |
| [15] |
YU Y, LUO W, YANG Z J, et al. miR-190 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by regulation of TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 70.
doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0818-9 pmid: 29510731 |
| [16] | ZHENG J J, QUE Q Y, XU H T, et al. Hypoxia activates SOX5/Wnt/β-catenin signaling by suppressing miR-338-3p in gastric cancer[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 19: 1533033820905825. |
| [17] |
ZHANG L, DING F P. Hsa_circ_0008945 promoted breast cancer progression by targeting miR-338-3p[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 6577-6589.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S213994 |
| [18] |
DUAN X, GUO G C, PEI X H, et al. Baicalin inhibits cell viability, migration and invasion in breast cancer by regulating miR-338-3p and MORC4[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 11183-11193.
doi: 10.2147/OTT.S217101 |
| [1] | WEN Ziqiang, LAN Junliang, ZHOU Bo, XU Qiwei. PARP1 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating expression of POU2F2 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 848-856. |
| [2] | XU Rui, WANG Zehao, WU Jiong. Advances in the role of tumor-associated neutrophils in the development of breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(9): 881-889. |
| [3] | CAO Fei, YU Wenhao, TANG Xiaonan, MA Zidong, CHANG Tingmin, GONG Yabin, LIAO Mingjuan, KANG Xiaohong. Mechanism of LINC01410 promoting proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 753-762. |
| [4] | CAO Xiaoshan, YANG Beibei, CONG Binbin, LIU Hong. The progress of treatment for brain metastases of triple-negative breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(8): 777-784. |
| [5] | ZHANG Jian. Clinical consideration of two key questions in assessing menopausal status of female breast cancer patients [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 619-627. |
| [6] | JIANG Dan, SONG Guoqing, WANG Xiaodan. Study on the mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction and CPT1A/ERK signal transduction pathway regulating malignant behavior in breast cancer [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(7): 650-658. |
| [7] | DONG Jianqiao, LI Kunyan, LI Jing, WANG Bin, WANG Yanhong, JIA Hongyan. A study on mechanism of SIRT3 inducing endocrine drug resistance in breast cancer via deacetylating YME1L1 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 537-547. |
| [8] | HAO Xian, HUANG Jianjun, YANG Wenxiu, LIU Jinting, ZHANG Junhong, LUO Yubei, LI Qing, WANG Dahong, GAO Yuwei, TAN Fuyun, BO Li, ZHENG Yu, WANG Rong, FENG Jianglong, LI Jing, ZHAO Chunhua, DOU Xiaowei. Establishment of primary breast cancer cell line as new model for drug screening and basic research [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 561-570. |
| [9] | CHEN Xun, ZHENG Zhenxia, RUAN Xueru. Effects of TMCO1 on proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(6): 571-580. |
| [10] | SUN Rongqi, SONG Ning, ZHENG Wentian, ZHANG Xinyue, LI Minmin, GONG Hui, JIANG Yingying. Effect of long noncoding RNA FLJ30679 on proliferation and migration of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 439-450. |
| [11] | XIONG Jiayan, LEI Wei, YOU Bo, ZHANG Zhenxin, XIE Haijing, SHAN Ying, XIA Tian, ZHOU Yong. Study on the mechanism of DDX6 promoting proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by regulating stability of CKMT1A mRNA [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 451-459. |
| [12] | ZHOU Xueqin, LUAN Yanchao, ZHAO Li, RONG Chaochao, YANG Na. Expression of CDC20 in lung adenocarcinoma tissues and its effect on the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 460-472. |
| [13] | GUAN Ruirui, HAO Qian, ZHANG Yaqi, SUN Qinggang, CHEN Yitian, LI Xiumin, ZHOU Xiang, HAN Tao. CDC20 facilitates the proliferation of esophageal carcinoma cell by stabilizing NLRP3 expression [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(5): 473-484. |
| [14] | Committee of Breast Cancer Society, China Anti-Cancer Association. Expert consensus on clinical applications of ovarian function suppression for Chinese women with early breast cancer (2024 edition) [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(3): 316-333. |
| [15] | ZHANG Qi, XIU Bingqiu, WU Jiong. Progress of important clinical research of breast cancer in China in 2023 [J]. China Oncology, 2024, 34(2): 135-142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
沪ICP备12009617
Powered by Beijing Magtech Co. Ltd
